* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10.2 Notes
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
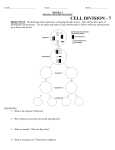
Chapter 10.2 Notes NAME_____________________________________ Honors Biology Organisms have tens of thousands of genes that determine individual traits Genes don’t exist free in the nucleus but lined up on a __________________________ Diploid and Haploid Cells In the body cells of animals and most plants, chromosomes occur in _____________ One comes from ______________ parent, one from _____________ parent A cell with ______ of each kind of ________________________ is called a ___________________ cell Contains a diploid, or ________, number of chromosomes This supports ___________________ idea that we have 2 _____________ for every _____________ A cell containing ________ of each kind of chromosome is called ______________________ cell Contains a haploid, or ______, number of chromosomes Homologous chromosomes ______________________ chromosomes are ___ chromosomes of each ________ in a diploid cell On homologous chromosomes, ___________ are arranged in the ________ order but because there are different possible alleles for the same gene, the 2 chromosomes in a homologous pair are not always __________________ to each other. Every pea plant has ______ copies of chromosome 4 (just an example) One came from each ______________ Since the _________________ chromosomes in the picture are the ________ for each allele, the plant is _______________________ for each trait Why meiosis? Remember ______________ – cell division results in _____ cells with exactly the same ___________ and kind of ______________________ But if mitosis were the _________ form of cell division, each pea plant parent (_____ chromosomes) would produce ______________ with a _________________ set of 14 chromosomes That means that each ______________ formed by fertilization would have ______ the number of _____________________________ as its parents F1 would have _____ chromosomes; F2 would have _____ chromosomes….. That’s a __________________! To solve it------___________________! Meiosis ________________ – cell division that produces ___________________ containing ________ the number of ___________________________ as a parent’s body cell Meiosis is broken down into _____________________ and ___________________________ Meiosis I = _________ cell creates _________ 2n cells Meiosis II = ________ cell creates two ____ cells Sexual reproduction is the uniting of sperm and egg to form a _______________ The _________________ sex cells are ___________________ (male is sperm, female is egg) Phases of Meiosis Interphase The cell ____________________ its chromosomes Now each chromosome consist of 2 ______________ sister chromatids held together by a ________________________ Prophase I __________ coils up, ________________ forms _________________________ chromosomes line up with each other and form a _____ part structure called a ________________ _______________ = 2 homologous _______________________, each made up of 2 _____________ chromatids They pair so _____________ that _________-sister chromatids from ___________________ chromosomes can actually break and ______________ genetic material = _____________ _______ Estimated that during ________________ in humans an average of ________ crossovers occurs for each pair of homologous chromosomes Metaphase I Centromere becomes attached to _______________ fiber Spindle fibers pull _____________ into __________________ Anaphase I Homologous chromosomes _______________________ Each new cell will receive only _______ chromosome from each homologous ___________ Telophase I Spindle breaks down, chromosomes ____________, and cytoplasm __________ into 2 new cells Each cell has _________ of the ___________________ information of original cell Meiosis II The __________ division is simply a _________________ division of products of meiosis I Has prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II Prophase II Spindle forms, spindle fibers attach to chromosome Metaphase II Chromosomes (sister chromatids) pulled to the center of cell Anaphase II Each chromosome splits to opposite poles Telophase II Nuclei re-form, spindles break down, and cytoplasm divides All of ____________________ is identical to _______________, except the chromosomes don’t _________________ before dividing At the end of meiosis II, ___ ______________ cells are formed They become ______________, ready to give genetic information to ________________ Genetic Variation Mitosis results in genetically ______________________ cells _________ ____________ during meiosis provides a way to __________________ allele combinations This means there is an ____________ genetic _____________________ in every generation Genetic Recombination How many sperm can a pea plant produce? Each cell has _____ pairs of chromosomes The 7 pairs can line up in 2 different ways, 128 different kinds of sperm are possible (2n = 27 = 128) Factor in the same number for eggs Now multiply number of possible _______ x number of possible __________ to get the number of different possible offspring 128x128 = 16,384 possible offspring!! The genetic combinations very depending on the way __________________ chromosomes line up during __________________ (randomly) For humans, n = ________ So possible sperm = 223 = over 8 million Possible eggs = 223 = over 8 million Multiplied together gives you over ______ trillion different zygotes that are possible! _________________ ______________________ – major source of genetic variation among organisms caused by re-assortment or _______________ _____________ during meiosis Nondisjunction Sometimes chromosomes fail to ________________ correctly This is called ____________________________ Both chromosomes of a homologous pair move to the ___________ pole Results in one with an ___________ chromosome, and one with a ___________ chromosome If fertilization of the one with the ____________ chromosome takes place, it results in ___________ In humans, trisomy occurs if chromosome __________ is the one with an extra, and results in a baby with __________ Syndrome. If ______________ a chromosome it is called _________________ Offspring usually don’t _________________ _______________ Syndrome is monosomy. Only found in _________________; it is when they lack one of their ______ chromosomes Polyploidy ___________________ – organisms with ________ than the usual number of chromosome sets Rare in _______________, usually results in death of zygote Frequently occurs in _______________ The flowers and fruits are ______________ and plants are ___________________ An example: ________________ plant