* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magnetism
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
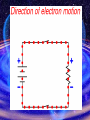
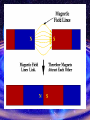
Magnetism Physical Science Mr. Holmes • • • • Loadstones are: natural magnets found in ground contain iron ore (magnetite) earliest use as simple compass because it will align north-south • Man-made magnets: most are made from iron, steel, nickel, cobalt • Magnetic substances are materials that are attracted to a magnet Theory of magnetism most elements electrons spin opposed to one another and magnetic forces cancel each other out but in magnetic substances this spinning motion reinforces each other (domain theory) • Law of magnetic poles – a magnet has the greatest strength at the poles (little or no strength in middle) – ends are called poles (free ends) – hang bar magnet from ring stand – the bar end pointing north = north pole • Law of magnetic pole – like poles repel, unlike poles attract Force of attraction or repulsion depends on strength of magnets and distance between poles • Magnetic field – region around a magnet in which magnetic effects are observed, which is produced by the motion of the electric charge. • Lines of force – closed arc from north to south pole, never cross, most concentrated at poles Making a magnet stroke bar of magnetic material in one direction with a magnet (re-aligns domains) use electricity bring magnet nearby (if soft iron) How to demagnetize a magnet heat contact (pass magnet alternating direction) hammering Electromagnets • When electric current passes through a wire – a magnetic field is produced in the space surrounding the wire • (electromagnet = placing soft iron bar in center of coil of wire with electricity passing through it) 3 things needed to make electromagnet: soft iron bar (core) coil of insulated wire source of electric current • How to change strength of electromagnet varying the number of turns of wire around core increasing the current varying the thickness of core change core material (if use wood = no electromagnet, use cobalt = strength increased 170 times, but if you use iron = strength increased 1000 times) ۩ Electromagnet summary magnetic field around straight wire that carries current bending wire into loops causes each loop to act as a separate magnet adding more coils increased strength of electromagnet increasing number of electrons through wire increases strength of electromagnet larger and thicker iron core provides more magnetic domains = increases strength of electromagnet Useful Vocabulary • • • • • • • • • • • • • Static electricity Volts Amps Ohmns V=I x R Electricity Circuits Parallel Series Alternating Current Direct Current Insulators Conductors