* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Marketing Concept - Nutley Public Schools
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional branding wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
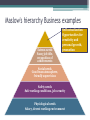
The Marketing Concept Marketing Concept • About half of every consumer dollar spent pays for marketing costs. • Satisfying customer needs is the most important aspect of marketing. • Marketing Concept ▫ keeping the focus on satisfying the customer’s needs for a product or service Marketing Concept • Give an example of a store that successfully implements the marketing concept and a store that needs improvement. Customer Focus • Productivity ▫ Rate at which companies produce goods or services in relation to the amount of materials and number of employees utilized Breakeven Point • The minimum attendance and sales required to cover all of the expenses of organizing, promoting, and running an event. • Revenues earned beyond the breakeven point are the profits. Successful Marketing Strategy • Identify customer • Needs • Location • Provide products perceived as superior • Maintain successful customer relationships • Offer the appropriate marketing mix • • • • Product Price Place Promotion Opportunity Cost • The value of the next best alternative that you forgo when making a choice. • The value is measured in terms of the benefits that you are giving up. • Choosing to go to a concert vs. a football game because you can only afford to go to one, the opportunity cost would be the football game. Understand Buyer Behavior • Economic Market • All of the consumers who will purchase a product or service • Two major goals of marketing: • 1. Determine what consumers want. • 2. How much are they willing to pay? Consumer Spending Habits • Benefits derived • The value people believe they receive from a product or service • Comparative advantage • The capability to produce products or services more efficiently and economically than the competition Consumer Wants and Needs • Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs • Identifies five human areas of needs • Most basic needs must be satisfied first to progress to higher-level needs Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs • Physiological Needs These include the most basic needs that are vital to survival, such as the need for water, air, food, and sleep. • Maslow believed that these needs are the most basic and instinctive needs in the hierarchy because all needs become secondary until these physiological needs are met. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs • Security Needs These include needs for safety and security. Security needs are important for survival, but they are not as demanding as the physiological needs. • Examples of security needs include a desire for steady employment, health care, safe neighborhoods, and shelter from the environment. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs • Social Needs These include needs for belonging, love, and affection. Maslow described these needs as less basic than physiological and security needs. • Relationships such as friendships, romantic attachments, and families help fulfill this need for companionship and acceptance, as does involvement in social, community, or religious groups. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs • Esteem Needs After the first three needs have been satisfied, esteem needs becomes increasingly important. • These include the need for things that reflect on self-esteem, personal worth, social recognition, and accomplishment. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs • Self-actualizing Needs This is the highest level of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. • Self-actualizing people are self-aware, concerned with personal growth, less concerned with the opinions of others, and interested fulfilling their potential. Maslow's hierarchy Business examples Esteem needs Fancy job title, recognition of achievements Self-actualization Opportunities for creativity and personal growth, promotion Social needs Good team atmosphere, friendly supervision Safety needs Safe working conditions, job security Physiological needs Salary, decent working environment Buying Motives • Emotional purchases • Spending with little thought during emotional times • Rational purchases • Define wants and needs • Assess priorities and budget • Conduct research • Compare alternatives • Make a well thought out purchase Buying Motives • Patronage purchases • Based on loyalty to a particular brand or product Consumer Decision Making Process • • • • • Recognize a need or a want Conduct product research Evaluate choices Decide what to purchase Evaluate the product after the purchase Information Needed for Marketing Decisions • Information about consumers that is important to consider include: • Demographics • Shopping behaviors • How consumers spend money • Product and brand preferences • Frequency of purchases Business Environment Impacts Consumer Spending • Economic uncertainty reduces consumer spending • Marketplace competition provides consumers with choices • Technological advances have impacted how consumers research and buy products Determine The Target Market • Target Market is a specific group of consumers you want to reach • Market Segment is a group of consumers within a larger market who share one or more characteristics ▫ Millions of people enjoy college basketball, but a smaller group specifically enjoys University of Kentucky basketball Market Segmentation • Geographic Segmentation divides markets into physical locations – Eastern, Northern, Southern and Western regions of the U.S. • Demographic Segmentation focuses on information that can be measured – age, income, profession, gender, marital status, etc. • Psychographics Segmentation focuses on characteristics that cannot be measured – values, interest, attitudes, lifestyle choices, etc. Market Segmentation • Behavioral-based segmentation focuses on a customer’s attitude toward products and services. • Two categories: ▫ Product usage – what products you use and how often ▫ Product benefits – the positive experiences or associations people derive from using a product or service Market Share • Market share is the percentage of total sales of a product or service that a company expects to capture in relation to its competitors. Outstanding Services Equal Success • Business success depends on excellent customer service. • Customer relationships should continue after the sale of goods and services. Track Record for Great Customer Service • Customer service gap • The difference between customer expectations and the services actually received • Customers are likely to tell at least 10 people about their poor customer service experiences. Effective Customer Service Principles • Demonstrate a values-based culture that is rooted in high performance and excellent customer service. • Follow the “FAST” (Focus, Action, Search, Tenacity) strategy. • Passion results in energy. • Demonstrate pride in every sale. • Remember the value of long-term positive relationships.