* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download neotectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
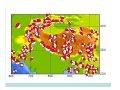
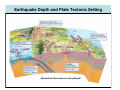
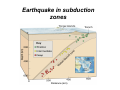
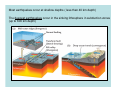
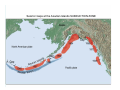
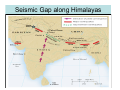
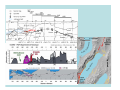
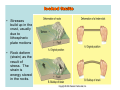
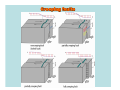
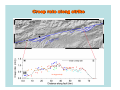
NEOTECTONICS Yrd.Doç.Dr. Ziyadin Çakır 14.03.2007 İTÜ Earthquake Belts 95% of energy released by earthquakes originates in narrow zones that wind around the Earth • These zones mark of edges of tectonic plates Locations of earthquakes from 1980 to 1990 Broad bands are subduction zone earthquakes, narrow are MOR Depths of Earthquakes Earthquakes originate at depths ranging from 5 to , rarely, nearly 700 kilometers Definite patterns exist in depth – Shallow focus 20 km faults between MOR – Large Transform (San Andreas) fault 80 km – Deep earthquakes occur in Pacific landward of oceanic trenches 80 km down to about 600 km associated with subduction zones Earthquake Depth and Plate Tectonic Setting Subduction Zones discovered by Benioff Earthquake in subduction zones Most earthquakes occur at plate boundaries A small percentage of earthquakes occur along old faults on the continents Divergent boundaries – normal faults Convergent boundaries – reverse and thrust faults Transform fault boundaries – strike slip faults Most earthquakes occur at shallow depths ( less than 40 km depth) The deepest earthquakes occur in the sinking lithosphere in subduction zones (up to 600 km depth) Seismic Hazard Map The most destructive earthquakes occur at convergent boundaries Earthquake prediction • Long-range forecasts • Calculates probability of a certain magnitude earthquake occurring over a given time period • Short-range predictions • Ongoing research, presently not much success Long Term Predictions Seismic Gaps Long Term Predictions • Strain Energy - accumulates uniformly - release irregularly • Some locked by friction “Seismic gaps” –Prime candidates for major earthquake • Some release energy continuouslycreep –No major earthquakes there Seismic Gaps at the Aleutian Islands SUBDUCTION ZONE Seismic Gap along Himalayas 2005 Can earthquakes be predicted? Short Term, Not very well • Short-range predictions • Goal is to provide a warning of the location and magnitude of a large earthquake within a narrow time frame • Research has concentrated on monitoring possible precursors – phenomena that precede a forthcoming earthquake such as measuring uplift, subsidence, and strain in the rocks locked faults • Stresses build up in the crust, usually due to lithospheric plate motions • Rock deform (strain) as the result of stress. The strain is energy stored in the rocks. locked faults • When the rocks reach their elastic limit, they break, and energy is released in the form of seismic waves, radiating out from the earthquake focus • The rocks return to their original shape, with a displacement (slip) along the fault Creeping faults Surface creep in İsmetpaşa Creep rate along strike No triggered slip