* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 8 Evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
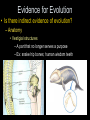
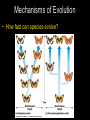
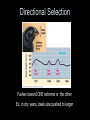
Unit VI - Evolution ~ a unifying theme of biology ~ Introduction to Evolution • What does biological “evolution” mean? – Change in organisms over time • How does this relate to the “origin of life”? – It doesn’t…two different topics! – Much more evidence to support evolution – Remember: science deals with natural world, not belief Introduction to Evolution • How could “life” have started? – Old Idea: • “spontaneous generation” (abiogenesis)…nonliving matter makes living • Disproved by Redi and Pasteur – New Idea: • “biogenesis”…life comes from life Introduction to Evolution • So, then where did the first cells come from? – Early earth • Very hot; volcanoes; violent storms/lightning – Miller & Urey experiment • Under early earth conditions, organic compounds form & group together into “protocells” Introduction to Evolution • But, when did we actually get cells? And how? – Evidence of first cells • 3.4 bln yrs ago • Most likely anaerobic bacteria (no O2 in air) – First photosynthetic cells • 2.8 bln yrs ago • Increased O2 in atmosphere • Led to ozone layer that protects from UV rays = more cells • Aerobic cells could now develop Darwin’s Idea • How did Darwin form ideas about evolution? – Fossils showed organisms changed over time Darwin’s Idea • How did Darwin form ideas about evolution? – Geologists showed that earth was very old Darwin’s Idea • How did Darwin form ideas about evolution? – He saw diverse species (ex: finches on Galapagos Islands, all with variations) Darwin’s Idea • How did Darwin form ideas about evolution? – Malthus noticed populations grow faster than their food supplies (they produce too many offspring) Darwin’s Ideas • What did Darwin conclude about species? – He identified that populations change due to “natural selection” (nature selects who goes on) Darwin’s Ideas • What did Darwin conclude about species? – Four assumptions: • Populations produce large #’s of offspring (more than can survive with given food) • Individuals in population have variations • Certain variations are more useful (these will survive better) • Over time, “good” genes prevail in the population, while “bad” ones fade out Evidence for Evolution • What direct evidence supports this theory? – Changes in populations over time • Ex: peppered moth Evidence for Evolution • What direct evidence supports this theory? – Structural adaptations • Ex: mimicry; camouflage Evidence for Evolution • What direct evidence supports this theory? – Physiological changes • Ex: drug-resistant bacteria; • Ex: pesticide-resistant insects Evidence for Evolution • Is there indirect evidence of evolution? – Fossils • show changes through time Evidence for Evolution • Is there indirect evidence of evolution? – Embryology • Early similarities may show relation Evidence for Evolution • Is there indirect evidence of evolution? – Embryology • Early similarities may show relation Evidence for Evolution • Is there indirect evidence of evolution? – Embryology Evidence for Evolution • Is there indirect evidence of evolution? – Biochemistry • Similar chemicals in most life forms (DNA, ATP) • More similarities in code means closer relationship Evidence for Evolution • Is there indirect evidence of evolution? – Anatomy • Homologous structures – Similar origin, but may now have different function – Shows common ancestry – Ex: bird wing, whale flipper, human arm Evidence for Evolution • Is there indirect evidence of evolution? – Anatomy • Analogous structures – Similar function, but very different structure – Shows separate development…not related – Ex: bird wing & butterfly wing Evidence for Evolution • Is there indirect evidence of evolution? – Anatomy Evidence for Evolution • Is there indirect evidence of evolution? – Anatomy • Vestigial structures – A part that no longer serves a purpose – Ex: snake hip bones; human wisdom teeth Mechanisms of Evolution • Can individuals evolve? – No! – Genes are genes…cannot alter them* – Only populations can evolve – Gene pool = sum of all genes in population Mechanisms of Evolution • How do populations evolve? – Any factor that affects genes in gene pool may disrupt equilibrium…leads to change (evolution) – Mutations may cause a shift – Smaller populations more affected…higher chance to concentrate recessives – Organisms moving in/out cause changes – Large populations not as affected by these factors Mechanisms of Evolution • How do species evolve? – Called “speciation” (same species can breed) – Geographic isolation • keeps individuals apart so cannot interbreed…over time they develop different traits (Ex: finches on islands) Mechanisms of Evolution • How do species evolve? – Called “speciation” (same species can breed) – Geographic isolation Mechanisms of Evolution • How do species evolve? – Called “speciation” (same species can breed) – Reproductive isolation • no longer capable of interbreeding (timing, parts, gametes differ,…) Mechanisms of Evolution • How fast can species evolve? – Gradualism • Species start up over long time with gradual changes (millions of years) – Punctuated equilibrium • Speciation occurs in quick bursts with equilibrium in between (~10,000 yrs or less) Mechanisms of Evolution • How fast can species evolve? Mechanisms of Evolution • Does evolution show patterns? – Divergent evolution • Ancestral species evolves into many species that fit different habitats • Ex: finches; common on islands Mechanisms of Evolution • Does evolution show patterns? – Convergent evolution • Distantly related organisms end up with similar traits • Occurs when have similar habitats • Ex: cactus in S. American & African deserts Mechanisms of Evolution • Does evolution show patterns? – Convergent evolution Modes of Selection Directional Selection Pushes toward ONE extreme or the other Ex: in dry years, beak size pushed to larger Diversifying Selection Pushes toward both extremes Ex: small beak for soft seeds; large beak for hard seeds; medium beak is bad at both types of seeds so selected against Stabilizing Selection • Pushes to average • Ex: cactus with few spines eaten by animals more; cactus with too many spines invaded by more parasites The End Quiz – Evolution for use with Questions 1 & 2 Quiz – Evolution for use with Questions 3-5 Quiz – Evolution for use with Question 6 Quiz – Evolution for use with Question 7