* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Schoolnet
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
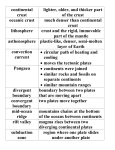
TEST NAME: Geology part 1 TEST ID: 1542715 GRADE: 06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT: Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geology part 1 Page 1 of 6 Student: Class: Date: 1. The picture below shows the layers of Earth. When compared to the other layers of Earth, which layer has the lowest density? A. crust B. inner core C. mantle D. outer core 2. What best describes the mantle of Earth? A. a thin layer that is located on the surface B. a solid layer made of iron and nickel C. the largest layer between the crust and outer core D. the smallest layer that is made up of molten rock 3. Due to extreme pressure, the inner core of Earth is A. solid. B. liquid. C. gas. D. plasma. 4. When an earthquake occurs, the speed of the seismic waves changes as they A. move through different materials. B. are pulled by the force of gravity. C. lose energy to surrounding rocks. D. reflect off of boundaries. 5. A difference between the oceanic crust and the continental crust is that the oceanic crust is A. composed chiefly of sedimentary rocks. B. more dense than the continental crust. C. older than the continental crust. D. continually being created. Geology part 1 Page 2 of 6 6. Which of the following has the greatest direct influence on movement of the lithosphere? A. the Sun B. the Moon C. Earth’s core D. Earth’s mantle 7. Which layers of Earth are mostly made of solid material? A. inner core and outer core B. crust and inner core C. crust and mantle D. mantle and outer core 8. Which of these correctly lists Earth’s layers in order from the center to the surface? A. outer core, inner core, asthenosphere, lithosphere B. asthenosphere, lithosphere, outer core, inner core C. inner core, asthenosphere, lithosphere, outer core D. inner core, outer core, asthenosphere, lithosphere 9. India was once its own continent. According to the theory of continental drift, India has collided with and become part of the continent of Asia. This caused A. glaciers in the area to melt. B. large mountain ranges to form. C. deep mid-ocean trenches to develop. D. deserts in the area to become fertile. 10. Volcanoes are considered constructive because they A. deposit lava. B. cause erosion. C. trigger earthquakes. D. release gases. 11. What type of landform is most likely formed by a divergent tectonic plate boundary? A. island arc B. oceanic trench C. rift zone D. folded mountains 12. The following mountain ranges: the Alps, Appalachians, and Himalayas are formed from A. folded rock. B. earthquakes. C. plate tectonics. D. glacier deposition. Geology part 1 Page 3 of 6 13. Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift around 1912. Which of these components of his theory is now known to be false? A. Similar plants and animals live on continents separated by oceans. B. All existing continents were once joined into a supercontinent. C. The boundaries of many neighboring continents fit together. D. The moon’s gravity and Earth's spin can move the continents. 14. Where does the energy from an earthquake originate? A. from a sudden increase in solar radiation striking Earth B. from the Moon’s gravitational pull during a close orbit C. from rocks under stress shifting deep inside Earth D. from the weight of sediments pushing down on bedrock 15. In the region where two continental plates collide, what geological feature most often forms? A. an ocean B. a volcano C. a river valley D. a mountain chain 16. The Hawaiian Islands are in the middle of a large tectonic plate with many volcanoes. The volcanoes are the direct result of the tectonic plate A. being forced under another tectonic plate at a subduction zones. B. colliding with one another tectonic plate and being forced upward. C. moving over a hot spot where magma breaks through the crust. D. applying great pressure on the crust causing constant earthquakes. 17. Which of the following is the most likely cause of earthquakes? A. shifting rock layers B. crashing meteorites C. rotation of the core D. magnetic force Geology part 1 Page 4 of 6 18. The diagram below shows the stages of development of an ocean. The process above results from A. the ocean forcing the plates apart slowly. B. the ocean forcing the plates apart rapidly. C. convection in the mantle dragging apart the plates slowly. D. convection in the mantle dragging apart the plates rapidly. 19. Which piece of evidence supports plate tectonic theory? A. plant fossils that are similar in size B. the weathering and erosion of coastlines C. new crust formed by seafloor spreading D. rocks with different physical appearances 20. Which of these tectonic plate boundaries is most likely to form a volcano? A. a continental plate colliding with a continental plate B. an oceanic plate sliding past a continental plate C. a continental plate sliding past a continental plate D. an oceanic plate colliding into a continental plate 21. This illustration shows how most of the recycling of rock from Earth’s crust occurs. What is this process called? A. subduction B. convergence C. divergence D. faulting Geology part 1 Page 5 of 6 22. This chart compares three different types of waves. Comparison of P-Waves, Sound Waves, and Light Waves Waves Occurrence Wave Characteristics P-wave earthquake compressions and rarefactions sound vibrating objects compressions and rarefactions light vibrating charges crests and troughs How do the wave characteristics compare for these waves? A. Sound waves and P-waves are longitudinal waves, while light waves are transverse waves. B. Light waves and P-waves are transverse waves, while sound waves are longitudinal waves. C. Sound waves, P-waves, and light waves are all longitudinal waves. D. Light waves, P-waves, and sound waves are all transverse waves. 23. What causes a seismic wave? 24. A. sudden breaking of rock as it releases potential energy B. very loud sound waves from the atmosphere entering the ground C. growing pressure on rocks from the weight of material above them D. energy transferred into Earth from the Sun as electromagnetic waves The point within Earth where faulting begins is known as the ________. A. Epicenter B. Focus C. fault line D. earthquake 25. _________ waves are the fastest, and travel through solids, liquid and gases. A. Primary B. Secondary C. surface D. pressure Geology part 1 Page 6 of 6