* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
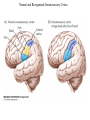
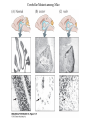
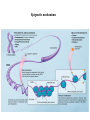
Neuroplasticity (Neural Plasticity) • Brain circuits are changed by experiences • Occurs across the lifespan although more impact during early development • Changes structure – Number of neurons – Density of synapses – Density of dendritic spines which can change shape in seconds. • For Example – In rats, social isolation leads to changes in the brain. – A brain region involved with processing odors, the posterodorsal amygdala, is affected by play. (fig 1.4) The Role of Play in Brain Development Experience Is an Important Influence on Brain Development • Visual deprivation during sensitive period can lead to blindness. • Amblyopia—impairment of vision in one eye with inability to see clear forms • The sensitive period of development is when experience or treatment can make permanent alterations. • Monocular deprivation during this period causes the deprived eye to not respond in adulthood. • Binocular deprivation—no light to both eyes–produces changes in neurons in the visual cortex. Brain Development in the Visual Cortex of Cats Ocular Dominance Histograms Which Line Is More Slanted? The Plasticity of Somatosensory Representations Normal and Reorganized Somatosensory Cortex Inversion goggles • Some preliminary experiments on vision without inversion of the retinal image Stratton 1896 • Erismann and Kohler: Inversion goggle 1950 – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jKUVpBJalNQ • Experiments with goggles, Kohler, Ivo. Scientific American, Vol 206(5), 1962, 62-86. Neurogenesis in Adult Brain • Fred Gage is given credit for discovering adult neurogenesis in mammalian nervous system. Although Michael S. Kaplan found evidence in the 1970’s but had difficulty publishing and convincing other neuroscientists. • neurogenesis in intact adult brain occurs in: – Hippocampus (related to memory and behavior) – cells lining the ventricles and the spinal canal, then migrating to olfactory bulb (OB) • Trauma to nervous system leads to increased neurogenesis – Ischemia – High levels of stress – Toxins • Enriched environment and exercise may also induce increased neurogenesis Neurogenesis in Adult Brain • Important for replacing lost neurons – Olfactory bulb – Hippocampus • Process of forming memory – immature neurons are more excitable • function as pattern integrators of temporally adjacent events • enhancing pattern separation for events separated in time – mature neurons • contribute to pattern separation by being more amenable to learning new information • so there are groups of granule cells that respond to experienced environments. Role of Genes in Guiding Brain Development • Genes can also have an effect on many behaviors. • A mutation is a change in genetic structure. • Animals with mutations may have an altered behavioral phenotype and are useful to study. • One group of mouse mutants includes different single-gene mutations that affect development of the cerebellum. • See fig. 7.19 Animals with mutations are important in researching development: • Site-directed mutagenesis changes the sequence of a nucleotide in a gene. • A knockout organism has a gene disabled. • A transgenic animal has a new or altered gene introduced. Cerebellar Mutants among Mice Role of Genes in Guiding Brain Development Down syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality—the inheritance of an extra chromosome 21. Fragile X syndrome results from inheriting extra trinucleotide repeats, repetitions of nucleotides, in the same gene. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a disorder of protein metabolism. The defect is the absence of an enzyme that metabolizes phenylalanine. If not corrected by diet, high levels of phenylalanine will cause intellectual disability. Genes Influence on Brain Development • Clones are genetically identical animals, yet neurons in clones can show differences in neural connections. • Epigenetics is the study of factors that affect gene expression, without changing the nucleotide sequence of the genes. – An important epigenetic factor that affects brain development is mothering. – Poor maternal care induces methylation of a stress-response gene, causing a lifelong heightened response to stress. – Methylation modifies DNA and makes it less likely to be expressed. Epigenetic Effects on Mouse Behavior Epigenetics Definition • Epigenetics – epi- (Greek: επί- over, above, outer) –genetics – is the study of heritable changes in gene expression – caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence • Wikipedia, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epigenetics • Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance – paternal grandsons of Swedish men who were exposed during preadolescence to famine in the 19th century – less likely to die of cardiovascular disease – if food was plentiful then diabetes mortality in the grandchildren increased Epigenetic mechanisms