* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section: Sexual Reproduction
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
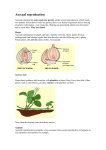
Section: Sexual Reproduction Key Words: gene, DNA, reproduction, sexual reproduction, sperm, egg, gamete, pollen, pollination, stigma, anther, ovum, chromosome Essential Questions: • • • How are gametes involved in sexual reproduction? How do plants reproduce sexually? How does sexual reproduction lead to species diversity? Sexual reproduction - formation of a diploid cell § joining of 2 haploid cells § created by the process of meiosis § cells that have half the number of chromosomes as the diploid § normal human cell – 46 chromosomes § human gamete cell – 23 chromosomes § § male human gamete (23) + female human gamete (23) = normal human cell (46) DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid § Forms the strands called chromosomes § Makes up “genes” – parts of the DNA strands that code for a specific protein § § Phenotypes – physical traits § Eye color § Tongue-rolling § Right hand/left hand § Skin tone § Hair color Genotypes – genetic make up coding traits § Dominate and recessive traits § Homozygous (same) and heterozygous (different) “gametes” § § Sperm or egg (or ovum) - combination of both parent’s traits - offspring resembles both parents, rarely one - combination varies with each offspring - creates species diversity - once fertilization occurs – mitosis allows for growth Fertilization - mechanisms differ among plant and animal kingdom - animals § males deposit gametes on or near the female gamete § land – internally via copulation § - water – externally because of fluid environment plants § pollination – sexual reproduction among plants § gymnosperms - “naked seed” § angiosperms – “flowering plants” § male gametes on anthers – pollen grains § transported by wind, water, or animals § female gamete is attached to stigma