* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Botany
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
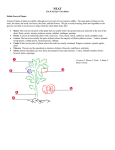
Botany is… Basic Botany Master Gardener General Training … the science of plants, including their structure and function and the environmental factors that affect their growth and development. By Sharon Morrisey Consumer Horticulture Agent Milwaukee Co. UWEX Horticulture is… MG General Training • Botany …the science of producing, using and maintaining ornamental plants, fruits and vegetables. It is garden (hortus) culture. – Anatomy – Physiology – Factors affecting plant growth • Horticulture – – – – – – Fruits (pomology & viticulture) Vegetables (olericulture) Trees, shrubs and vines (woodies) Flowers (floriculture) Lawns Houseplants • Entomology (insects) • Plant Pathology (diseases) • Soil Science Life Cycles Terminology & Classification • Annual • Features – Life cycle – Misc. others • Scientific names – Binomial – Latin seed -----vegetative------flowering------seed 1 Year • Biennial vegetative flowering Seed ---(rosette) (“bolt”)----seed 2nd Year 1st Year • Perennial seed ---vegetative & flowering & seed-----Many Years (some portion survives year to year) 1 Other Terminology Nomenclature • Stem types: – herbaceous – Woody • Leaf-holding ability: – Deciduous – Evergreen – needle; broadleaf • Habit: – – – – – Tree Shrub Vine Groundcover grass Binomial nomenclature • System to classify and name all living things • Developed by Carolus Linneaus in 1750’s • All plants known by two names – Genus – species Classification 2 Scientific names • Genus Picea • Species pungens • Variety var. • Cultivar Pneumonic device to remember: King David Came Over From Greece Sunday! Identification Keys ‘Glauca’ Plant Anatomy & Physiology • Structure • Function • Terminology Principle Parts of a Vascular Plant Plant Parts • • • • • • • Roots Stems Buds Leaves Flowers Fruits Seeds 3 Roots Roots • Functions: – Anchor & support – Absorb nutrients & water – Store “food” Root Meristem Stems • Function – Supports leaves, buds, flowers, fruit and seeds – Carries nutrients, water and food • Vascular system – Xylem – Phloem – Adds to girth and height • Cambium (meristem) Stems Stems – Storage • Modifications – Above ground » Crown » Runner/ stolon » Spur – Below ground » Rhizome » Bulb » Corm » tuber 4 Stems Stems Stems Stems Stems Stems 5 Stems Modifications: above ground • runner/ stolon Stems Modifications: below ground • rhizome Stems Modifications: below ground • bulb Stems Modifications: below ground • corm Stems Buds Modifications: below ground • tuber • Functions – Produce stems, leaves, flowers (no root buds) – Site of growth meristems 6 Leaves Buds • Functions – Absorb sunlight – Produce sugars through photosynthesis – Transport – Water regulation – Temperature control – Types • Venation • Shapes Leaves Leaves • Photosynthesis light Carbon dioxide + water------ sugar + oxygen chlorophyll • Respiration dark sugar/starch + oxygen ------ carbon dioxide + water + energy Leaves Leaves • Cross-section 7 Leaves • Transpiration Leaves • Stomates with guard cells Roots • Transpiration Leaves • Translocation – Water – Sugars – nutrients Leaves 8 Leaves Leaves Leaves Leaves Leaves Flowers • Functions – Produce viable seed(s) through pollination 9 Flowers Flowers Flowers Asteraceae Flowers Fruits • Inflorescence • Functions – Carry seeds – Disperse seeds – Is a mature ovary 10 Fruits Fruits Seeds Seeds • Dicot – Two seed leaves • Functions – Carry genetic information for next generation Seeds Factors Affecting Growth • Monocot – One seed leaf • • • • • Light Water Temperature Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio Plant Growth Regulators 11 Light • Required for photosynthesis and production of sugars Light • 3 components: – Quantity • Involved in transpiration – Quality • Involved in all chemical reactions – Duration Light • Quantity Light • Quantity – Measured in footcandles (fc) – Light meters • measure in footcandles (fc) – Degree of contrast of shadow on white paper Outside full sun = 5,000 fc winter 10,000 fc summer Indoor Houseplants: lowest to survive = 50 fc low light = 50 – 11 fc medium = 100 – 250 fc high = over 250 – 650 fc Light • Quantity Light • Quality – Spectrum of light The light level outside in summer in dense shade is brighter than a south facing window indoors in the winter. • Visible light – ROY G. BIV • Plants need most of red and blue 12 Light • Quality – Blue light responses • • • • • Photosynthesis Petiole length Internode length Leaf expansion Phototropic reactions 13 Light • Quality – Red & Far Red responses • • • • • • Photosynthesis Seed germination, seedling growth Fruit ripening Tuber and bulb formation Photoperiodism flowering Light – Indoor Lighting • Incandescent bulbs – Mostly yellow to red and far red – Produce heat • Fluorescent bulbs – Cool white – blues – Warm white - reds Light • Duration – Photoperiod • Length of day/ night • Varies with the season • May be artificially manipulated • “Grow Lights” – Try to mimic spectrum of natural sunlight » May have extra far red to promote flowering Photoperiod Photoperiod 14 Light • Longest day/ shortest night – Summer Solstice, June 21st – Midsummer’s day • Shortest day / Longest night – Winter Solstice December 21 Light • Plant reactions to photoperiod – Long Day Plants (short night) • Inhibits flowering • Vegetative growth in summer; bloom in fall or spring (Long day onions, form bulbs ) • Half way between – Vernal equinox, March 20 – Autumnal equinox, September 20 • Ground Hog’s Day – February 2 – Exactly halfway between Winter Solstice and Vernal Equinox – Short Day Plants (long night) • Promotes flowering (Chrysanthemums, pointsettias) • Vegetative growth in spring; bloom in summer – Day Neutral Plants Light • Other Plant Reactions to Light – Germination • Some plants require light to germinate – Excess light • Burning • Stunting – Inadequate light • Etiolation – Pale – Stretched (“leggy’) – Long internodes Water • Functions: – – – – – – Solvent for minerals & photosynthates Required for chemical reactions Germination Temperature control Turgor pressure Movement of minerals & photosynthates Water • Factors affecting: – Soil moisture • • • • • On soil particles In pore spaces On organic matter Mulch to retain In containers • Diffusion • Osmosis • Transpiration 15 Water • Factors affecting: – – – – Light Air temperature Air humidity Wind Transpiration increases when humidity is low, temperature is high and on windy conditions. Water • Methods of watering: – Overhead • sprinklers – Directed • • • • Watering can Watering wand Soaker hoses Drip & trickle irrigation Water Temperature • Affects the rate of chemical reactions • Timing: – Early in the day • Allows leaves to dry • Droplets DO NOT act like magnifiers and burn leaves – During flowering & fruit production – Q10 Effect • Reaction rate doubles with every increase of 10 degrees C. – Photosynthesis (to 90 degrees) – Respiration • Only to a point – Flowering • Respiration without photosynthesis leads to breakdown of carbohydrates. – Transpiration • Higher temps. Increase evaporation which “boils” water off leaf surfaces which must be replaced by more pulled from soil Temperature • Transpiration – Regulated by stomates • Stomates close due to: – Water stress (too little) – High temperatures – High CO2 – Darkness Temperature Other • Heat cause bitterness in lettuce • Heat causes “bolting” of cool season crops • Cold treatment – Required for dormany which is required for flowering of many plants including bulbs, fruit crops, etc. – causes vernalization of “cole” crops (broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, etc.) • • • • Heat and cold cause abortion of flowers and fruits Heat and cold may cause death of non-hardy plants Germination occurs at specific temperatures Cold soil reduces nutrient uptake 16 Carbon/ Nitrogen Ratio – Sources of Carbon: • Photosynthates – sugars & starches • Wood, dry leaves, dry plant parts – Sources of Nitrogen: • • • • • Absorbed from soil Lightning Green leaves, stems and plant parts Fertilizer Manure Carbon/ Nitrogen Ratio – Low C/N ratio • More N than C (high N fertilizer) • Little C being produced (low photosynthesis) • C being broken down (high respiration) – High C/ N ratio Carbon/ Nitrogen Ratio – Carbon & photosynthesis • Increased photosynthesis creates more carbohydrates – Carbon & respiration • Increased respiration breaks down carbohydrate • Releases energy Plant Growth Regulators – Hormones • • • • • Auxin Gibberellins Cytokinin Abscisic acid ethylene • Increases flowering and fruiting • Mulches – high carbon – Require extra nitrogen Plant Growth Regulators – Auxin • Promote cell elongation • Inhibit lateral bud development (apical dominance) • Promote lateral and adventitious roots (rooting hormones) • Involved in phototropism • Promote flowering and fruit development • High concentrations used as herbicides (broadleaf weed killers) 17 Plant Growth Regulators – Gibberellins • • • • Promote stem elongation Promote germination Causes bolting in biennials May break bud and seed dormancy in plants usually needing light or low temps. to break dormancy • May induce flowering in long-day plants • Gibberellins often work in concert with auxin Plant Growth Regulators – Cytokinins • • • • • • • Regulate cell division Are needed for germination Are found in meristems and immature fruits Migrate from roots to the shoot systems of plants Promote cytokinesis and cell differentiation May promote axilllary bud growth May retard leaf senescence 18 Plant Growth Regulators – Abscisic Acid • Growth-inhibiting hormone • It goes into action during periods of stress • Promotes dormancy activities such as formation of bud scales and seed dormancy. • Promotes stomata closure during leaf water deficit conditions by activating K ions in the guard cells • Plays role in senescence, the breakdown of cell components before cell death. Plant Growth Regulators – Ethylene • • • • • Inhibits cell elongation Promotes ripening in fruits Is the direct cause of leaf and fruit abscission Is produced by bruised tissues Is produced by some seeds when difficulties arise during germination, which stimulates changes that may help push the shoot t the soil surface. • Promotes sprouting of many buds • Can cause flowers to wilt 19