* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Tissues and Organs
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
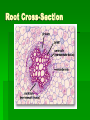
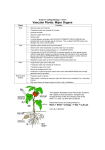
Plant Tissues and Organs What is a plant? A plant is a multicellular eukaryote that has cellulose in the cell walls, stores food in the form of starch, has a cuticle- a waxy, waterproof coating on the stems and leaves. Cuticles help to prevent water loss Plant Tissues Dermal- surrounds plant Vascular- transports food and water - Xylem- moves WATER UP - Phloem- flows FOOD (SUGAR) DOWN Ground- photosynthesis, storage, support Meristematic- area where growth occurs Roots Function: take in water and nutrients from the soil Anchor the plant in the soil Sometimes act as storage (radishes, carrots, etc) Most grow underground Contains vascular tissue (xylem & phloem), ground tissue (cortex), dermal tissue and meristematic tissue (root tips) Root Cross-Section Stems Function: provides support for growth transports water, food and minerals to and from roots and leaves Contains all tissue types Leaves Function: usually the site of photosynthesis Increased surface area to allow maximum absorption of sunlight Contains guard cells & stomata sites of gas exchange Reproduction Mosses and ferns use spores All other plants produce seeds- contain the embryo, food source, and a protective coat Flowers are the reproductive structure in highly evolved plants Most flowers contain both male and female reproductive parts (complete flower)