* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Systems Vocab List: Gravitropism, Hydrotropism, Nastic
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
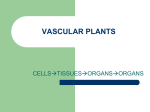
Plant Systems Vocab List: Gravitropism, Hydrotropism, Nastic response, Phloem, Phototropism, Pistil, Stamen, Stigma, Stoma (stomates), Thigmotropism, Xylem. Review of Plant Cells – Plants are multicellular eukaryotes w/ cell walls made of ________________. – Plants are ____________ that carryout __________________ to obtain energy. ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL To carry out cellular functions, plants need: Sunlight, Water, CO2, and Minerals Photosynthesis - the process by which plants convert light energy and carbon dioxide into sugars as a food source for the plant. (Carbon dioxide) (water) (glucose) (oxygen) 1. Photosynthesis is a ___________ reaction because it combines simple molecules into more complex molecules2. Is photosynthesis an endergonic or exergonic reaction? Explain why. 3. What serves as the carbon source for photosynthesis? 4. Sunlight is absorbed as packets of energy called _____________ (particles of light) 5. Besides C02, _________is also used in photosynthesis to produce ______________ molecules such as the sugar ______________ 6. ____________ energy is converted into _________________ energy. 7. Plants can make their own food so they are called ________________ (aka producers). Heterotrophs are consumers. Examples of producers, ________________, and___________ 8. Photosynthesis occurs mainly in the ______________ of plants. 9. Pores in the underside of leaves are called _____________, while the cells in leaves that contain chlorophyll are called _________________ cells. 10. The organelle in mesophyll cells that contains chlorophyll is called the ________________ 11. Name two gases exchanged through the stomata of a leaf? 12. Besides gases, ___________ vapor can be lost from a leaf. 13. The second part of photosynthesis is called the ___________ cycle. 14. Does the Calvin cycle require light energy? 15. The Calvin cycle is also called the __________ fixation or the ______ pathway. 16. Where do the light reactions of photosynthesis take place in a chloroplast? Plants have __________ _______ (different cell types perform specific functions). EX Root cells, stem cells, and flower petal cells all have specific functions (jobs) that they carry out for the plant. 3 TYPES OF PLANT TISSUES __________ – PROTECTION FOR THE PLANT (__________ COATING) _______________ – TRANSPORT FOOD & WATER _______________ – Cells that lie between dermal and vascular tissue CONTAINS CELLS THAT ARE THE SITE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS Veins in a plant are called ________________ There are 2 types of Vascular Tissue: 1. __________ – transports __________ from __________ to the rest of the plant 2. __________ – transports _______ and other __________ throughout a plant (FOOD) MERISTEMATIC TISSUE _________________ – has not yet become specialized. These cells are produced in the ___________l ________________ (tips of roots & stems). Meristematic tissue is the only plant tissue that produces ____________________________! Specialized Tissues - __________________ ____________ is the organ where most ______________________, and ____________________ [evaporation from plants] occurs. Remember, photosynthesis is used by plants to ________________. Through the leaf run __________ transport water, sugars, and minerals to the plant cells. ______________ are __________ or holes in the epidermis of the ________ that allow ____ exchange (stoma – singular) ______________ comes in through the opening and __________ leaves through the ___________ ________________ on each side of the ______________ control its opening and closing. _______ is also lost through the stomata in a process called _____________, so plants only leave stomata open long enough to do _________________ When water pressure within the guard cells is _______ (lots of water inside of plant) the thick outer walls of the cells are forced into a _________ shape, which _________ the stoma. When water pressure within the guard cells is _______ the inner walls pull together and _______ the stoma. Specialized Tissues - Stems _____________ are specialized cells that _________ leaves to hold them up to sun and ____________ water, sugars, and nutrients through the plant. Some stems are also_______________________ [glucose] storage areas. Produce branches &_____________ Hold ___________ up to the ________________ _____________ substances between __________ and _____________ (through _________) In most plants, stems contain distinct _______, where __________ are attached, and _____________ regions ____________________ the nodes. __________________– scattered vascular bundles _____________ – vascular bundles arranged in a ring Secondary Growth of Stems - Takes place in lateral meristematic tissues called _______________________ – produces vascular tissues and increases stems thickness (wood) ______________________ – makes the outer covering (________________) Specialized Tissues - _______________ ___________ are_________________ organs that absorb water and minerals necessary for transport in the plant and anchor [hold] the plant in the soil. They help to prevent _____________________. ___________ – (ex: ___________) single large central root ______________ – (ex: __________) clump of short threadlike divisions Transport Tissues Just like in animals, vascular [_______] tissue is the transport system for the plant. _____________ – transports _____________ in stacked cells to form tube like drinking straws; movement is _______ from ________ to _____________ ______________ – transports ____________; movement can be _________________ The reproductive life cycle of plants is called __________________ of _________________ _______________ Tissues - Flowers _________________ are a reproductive organ (but not all plants have flowers). They have ___________ and _________ parts. ________________ – transporting pollen (_____________) from the male to female parts (_________) _________________ – union of sperm with egg (creates a development of a plant embryo [seed] which grows into a mature plant). Flower Parts Male ___________ – consist of the _________ (produces pollen) and ___________(supports anther) _________ – contains sperm Female ____________ – consist of the ___________ (where pollen lands), __________ (connects stigma to ovary) and the ___________ (develops into the _______________) __________ – develops into an egg, eventually becomes the seeds when fertilized Non-sexual - ____________ – colored parts, attract pollinators (ex bees) _____________ – green parts, protect flower parts Reproductive Tissues - Seeds Seed Plants form _____________ (a ___________________________________) in order to reproduce. Seeds are encased in a protective covering called a _____________________. ex _________________ such as strawberries, apple, tomato, peach, cucumber; ex ______________ such as walnuts and acorns Seedless Reproduction Seedless plants do not form hard seeds (EX mosses and ferns) and therefore these plants ________________________________ in order for the sperm to swim to the egg. Another type of response, specifically to changes in pressure, is called a ________________________. The most common example is the infamous Venus flytrap which closes its leaf when the plant senses an insect through changes in cell pressure.