* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants: An Introduction
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
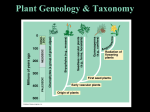
Plants: An Introduction The Plant Kingdom can be viewed as having the true terrestrial plants and those that are “almost” true terrestrial plants. Outline Key concepts Important roles of Plants provide food, air (oxygen), clothing, etc. Comparison Classification: Evolutions Conclusions Key Concepts: The plant kingdom consists of multicelled photoautotrophs Nearly all plants live on land Plants have structural adaptations that allow them to photosynthesize, absorb water and ions, and conserve water Land plants are reproductively adapted to withstand dry periods Key Concepts: Early divergences gave rise to the bryophytes, then the seedless vascular plants, and then the seed-bearing vascular plants Gymnosperms are the seed-bearing vascular plants and the angiosperms are also vascular plants that bear flowers and seeds Angiosperms include two classes of flowering plants Eudicots (Dicots) and Monocots Comparison Animals 1. heterotrophic 2. stop growing 3. reproductive tissue present all times times Plants autotrophic continuing growing reproductive tissue not present at all Classification & Evolution 1. Bryophytes: Non-vascular Plants 2. Seedless Vascular Plants 3. Gymnosperms: Seed-bearing Plants 4. Angiosperms: The Flowering SeedBearing Plants Bryophytes Mosses Nonvascular Moist habitats mostly Small < 20 cm tall Simplest plants Moss-covered rocks Seedless Vascular Plants Whisk ferns, Lycophytes, Horsetails, Ferns Has vascular tissues Psilotum Habitat Moist places Sperm needs Equisetum water to reach egg Ferns Lycopodium GymnospermsPlants with “Naked” Seeds Conifers, Cycads, Ginkgos, Gnetophytes Conifers Pines, - cones cypress, firs, spruces, redwoods Gymnosperm Diversity Bristlecone pine A cycad’s seed-bearing cone Gymnosperm Diversity Ginkgo Ginkgo seeds Ginkgo leaf and fossil Gymnosperm Diversity Welwitschia mirabilis– Gnetophyte It grows in hot deserts of Africa with a deep taproot. It has one or two strap-shaped leaves that split lengthwise repeatedly as the plant ages. Pine trees Angiosperms: flowering seed plants The dominant plant form on earth (>250,000 species) Flowers Fruit to increase insect pollination to protect the seed and developing embryo until favorable germination conditions occur Broad leaves to increase photosynthesis during the growing season are shed during periods of cold and drought Angiosperms The Flowering Seed-Bearing Plants Flowers Coevolution with pollinators Insects Bats Birds Seed Ovary Dicots and Monocots Almost 180,000 (Eudicots) Dicots Cabbage and Daisies Flowering Water shrubs and trees lilies Cacti About 80,000 Monocots Orchids, palms, grasses, crop plants, rice Angiosperms Evolution of Plants In Conclusion Green algae probably gave rise to plants Trends in evolution can be identified by comparing different lineages Mosses are bryophytes, nonvascular plants Vascular The plants are adapted to land seedless vascular plants include the whisk ferns, lycophytes, horsetails, and ferns In Conclusion Gymnosperms and angiosperms are vascular plants Only angiosperms produce flowers