* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
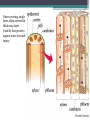
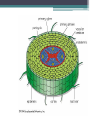
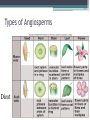
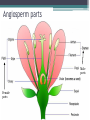
Plants What is a Plant? • • • • • Plants are multicellular Eukaryotes Cell walls made of cellulose Carry out photosynthesis Using the green pigments called chlorophyll a and b • Plants include trees, shrubs, grasses, mosses and ferns Plant life cycle • Sporophyte- is the diploid (2N) phase of the plant life. Or a spore producing plant • Gametophyte- is the haploid (N) phase of the plant life. Or the gamete-producing plant Spore (N) Sporophyte (2N) Sperm (N) Eggs (N) Vascular Plant • Phleom- passes a variety of materials mostly carbohydrate. ▫ Sieve tube elements- these are arranged end to end to form tubes these tubes have holes in them so material can get through • Xylem- conducts water. It has cells called tracheids that are long, narrow cells with walls that are impermeable to water. Outer covering, single layer, often covered in thick waxy layer (cuticle) that protects against water loss and injury. Plant Groups • Bryophytes- depend on water for reproduction, lack vascular tissue ▫ These are mosses, liverwort, hornwart • Vascular Plants- these have specialized parts that deal with transportation of material. ▫ These include, ferns, club mosses, horsetails. And all other kinds of plants that have specialized parts to move material (ex. Flowers, trees) • Seed Plants- are divided into two groups. ▫ Gymnosperms- bear their seeds directly on the surface of cones Examples of gymnosperms: conifers; such as pines and spruces, palm like plants; ginkgoes, cycads ▫ Angiosperms- flowering plants, bear their seeds within a layer of tissue that protects the seed. Angiosperms can be broken down into two groups woody and herbaceous. There are three categories; annual, biennial, and perennial. They then are broken into dicot and monocot Types of Angiosperms Dicot Angiosperm parts Male parts Female parts Root systems • Three of the principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves • Roots- bring up water and dissolved nutrients, they also anchor the plant to the ground, helps to hold soil in place to help stop erosion. • Stem-transports nutrient from roots to leaves, storage of nutients, production of new tissue, elevation of leaves so they can be in the sun. • Leaves- are the place where photosynthesis occures.