* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PLANT REPRODUCTION AND HOW IT WORKS!
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
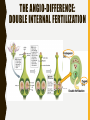
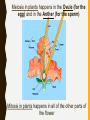
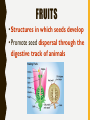
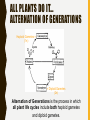
PL ANT SEX! WAIT…WHAT? P L A N T R E P R O D U C T I O N A N D H OW I T WO R K S ! ALL PLANTS DO IT… STRUCTURES FOR PLANT REPRODUCTION: –Cones –Flowers –Pollen –Ovules –Seeds CONES VS. FLOWERS •Cones - the seed bearing structure of non-flowering plants (gymnosperms) •Flowers - the seed bearing structure of flowering plants (angiosperms) GYMNOSPERMS VS. ANGIOSPERMS REPRODUCTION GYMNOSPERMS ANGIOSPERMS THE ANGIO-DIFFERENCE: DOUBLE INTERNAL FERTILIZATION POLLEN, OVULES AND SEEDS • Pollen – The male sex cell (sperm) is carried in a pollen grain • Ovule – The female sex cell (egg) is located in the ovule • Seed – A structure that carries the embryo of a plant (after fertilization) FUNCTIONS OF SEEDS • Protection -from drying out and disease • Nourishment – contain cotyledons (seed leaf) that supply organic nutrients • Dispersal – by wind, water, and animals • Delayed growth – do not germinate until conditions are favorable FLOWERS – THE REPRODUCTIVE STRUCTURE Male Part of the Flower Female Part of the Flower QUICKWRITE: MITOSIS VS MEIOSIS: BUT WHERE? • List at least five things you remember about mitosis and meiosis. • What type of cells does mitosis create? And meiosis? • Where do you think each process would occur in a flower? Meiosis in plants happens in the Ovule (for the egg) and in the Anther (for the sperm) Mitosis in plants happens in all of the other parts of the flower POLLINATION • Size and shape of the flower helps pollination to occur • Cross Pollination: • Self-pollination can also occur: – Pollen is released from the anther and is transferred to the stigma. A pollen tube forms and grows through the style. The pollen tube reaches an ovule within the ovary, where the sperm fertilizes the egg. POLLINATION LEADS TO FERTILIZATION: • https://s-media-cacheak0.pinimg.com/originals/db/fe/c2/dbfec2b304bdc6b267476b9ee9c66f9 0.gif FRUITS • Structures in which seeds develop • Promote seed dispersal through the digestive track of animals ALL PLANTS DO IT… ALTERNATION OF GENERATIONS Haploid Gametes = (1n) = Diploid Gametes (2n) Alternation of Generations is the process in which all plant life cycles include both haploid gametes and diploid gametes. ALTERNATION OF GENERATIONS This allows the plant to grow from a zygote into a mature organism, while also creating both pollen and ovules.