* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Flower Dissection FIB
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
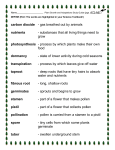
Flower Dissection Activity Review Flowering Plants A flowering plant has both male and female parts. The female part is called the pistil. The male part is called the stamen. Stamen: The male reproductive structure of a flowering plant Anther: the structure located on top of the stamen and carries the pollen Pollen Pollen is the male sex cell that donates half of the DNA to make a seed. It is a powdery substance, usually orange or yellow in color, that gets carried by pollinators. Filament: a thread-like part that holds up the anther Pistil: the female reproductive structure of a flowering plant Stigma: the sticky surface on the top of the pistil; it traps and holds the pollen Style: the tube-like structure that holds up the stigma Ovary: the plant part at the bottom of the flower that has ovules inside (this turns into the fruit and seeds we eat) Ovules: the female sex cells inside the ovary that donate half the DNA to become the seed (They become the seeds when pollinated or fertilized by the pollen.) A baby seed! Petal: the colorful flower parts that surround the reproductive structures Sepal: the green petal-like parts at the base of the flower; they help protect the bud when it develops Perfect: flowers that have both male and female parts (ex. Roses, lilies, and pea plants) Imperfect: flowers with male or female parts (ex- cucumbers, pumpkins, and melons) Pollination: when pollen moves from the male parts to the female parts Pollination is the step before fertilisation in plants. Fertilisation is when the male and female gametes join to form an embryo.