* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Reproduction and Development
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
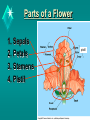
Name Type What ? Organisms + - 1. Binary Fission Asexual Cell splits and • bacteria replicated DNA goes with each part • fast • easy • all offspring have same DNA 2. Regeneration/ Fragmentation asexual Lost or Invertebrates damaged • worms tissues, organs • Starfish or limbs are restored • easy • parent broken • same DNA 3. Budding asexual Offspring grows off of parent • fast •Somewhat easy •All offspring have same DNA 4. Pollination sexual When pollen is Flowering transferred plants from the anther to the stigma • plants don’t have to move • mixes DNA • need a pollination vector 5. Sexual Reproduction sexual Egg and sperm Most animals unite to form a and some zygote plants • results in genetically differences • slow •Yeast •hydras Class Starter Questions 1. Draw a picture of a flower and try to label it’s parts as best you can. 2. Can you Identify which are the female and male parts? Parts of a Flower 1. Sepals 2. Petals 3. Stamens 4. Pistil pistil Sepals Sterile, leaf-like structures. (do not have the capacity to produce gametes) May be brightly colored. Function Protect other flower parts. Attract pollinators. Petals Sterile flower part. Often brightly colored. Function Attract pollinators. Stamens Male reproductive flower structure. Function Produce pollen (like plant sperm). Stamen Structure Anther - pollen producing sac. Filament - stalk. Pistil Female reproductive flower structure. Function Produce ovules. Pistil Structures – receives the pollen. Style – stalk. Ovary – contains the ovules. Stigma Ovule An immature seed before fertilization. The ovules are the female gamete. Pollen Development Pollen is the male gamete. Pollination The transfer of pollen from the filament to the stigma. Pollen Vectors Bees Butterflies Birds Bats Flies Moths Beetles Wind Fertilization The union of the ovum and sperm to produce a zygote. After Fertilization Zygote (fertilized egg cell) plant embryo Ovule Seed Ovary Fruit Fruit Functions Protect the seeds. Aid in seed dispersal. Seeds Contain a miniature plant. Main dispersal mechanism for plants.