* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Wonder of Flowering Plants KEY 9 Reading
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive suppression wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
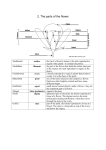
Name ____________________________________ Date _______ Period ___________ Lesson 9 Reading Questions The Wonder of Flowering Plants – pg. 116-119 1. What type of organ is a flower? A reproductive organ 2. What is the male reproductive structure on a plant? Stamen 3. What parts make up this structure and what do they do? Anther-produces pollen Filament-supports anther. 4. What is the female reproductive structure on a plant? Pistil 5. What parts make up this structure and what do they do? Stigma-collects pollen style-supports stigma ovary-holds ovules 6. What is the difference between a “perfect” and an “imperfect” flower? Perfect-female and male parts Imperfect-female or male part 7. What is pollination? When the pollen from an anther contacts the stigma. 8. What are the two types of pollination and how do they differ? Self-pollination-pollen not transferred (self-pollinated) Cross pollination-pollen transferred from different flower. 9. How do plants get pollen? Explain the method for each type of pollination. Self-falls into stigma by gravity, wind, or water. Cross – a pollinator transfers the pollen (insects, birds, rodents, wind.) 10. What is fertilization? When a sperm cell meets an egg cell 11. How is the endosperm produced? Sperm unite with nuclei in egg 12. What part of the original flower eventually becomes a fruit? Ovary 13. What is the function of the fruit? To protect and disperse the seeds. 14. Why do flowers need to adapt in order to enhance pollination? They are rooted and can’t move around 15. How are flowers adapted to encourage pollination? Scent, bright colors, and location 16. Draw and label a perfect flower (p. 108). Label the following: petal, sepal, stigma, style, anther, filament, stamen, ovary, and stem.