* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6 th Grade Science Ms. Koennecke Growing and
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
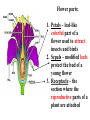
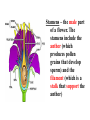
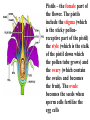
6th Grade Science Ms. Koennecke Growing and Flowing 6.L.1.1 – Structures of Flowering Plants LEAVES STEM ROOTS Basic Parts of Plants 1. Leaves: take in carbon dioxide & sunlight to be used in photosynthesis 2. Stems: support branches, leaves, & flowers 3. Roots: secures plant in place, absorbs minerals & water, stores energy Stomata: tiny openings under leaves through which gases and water vapor pass Guard Cell: paired cells that control the opening & closing of a leaf’s stoma The process of sexual reproduction in flowering plants takes place in the flower, which is made up of several parts. Some parts of the flower are directly involved in fertilization and seed production. Other flower parts have functions in pollination. Flower parts: 1. Petals – leaf-like colorful part of a flower used to attract insects and birds 2. Sepals – modified leafs protect the bud of a young flower 3. Receptacle – the section where the reproductive parts of a plant are attached Stamens – the male part of a flower. The stamens include the anther (which produces pollen grains that develop sperm) and the filament (which is a stalk that support the anther) Pistils – the female part of the flower. The pistils include the stigma (which is the sticky pollenreceptive part of the pistil) the style (which is the stalk of the pistil down which the pollen tube grows) and the ovary (which contain the ovules and becomes the fruit). The ovule becomes the seeds when sperm cells fertilize the egg cells Pollination: When pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma (if same plant=self pollination; if different plant of same species = cross-pollination). Plants that are cross pollinated produce stronger plants. Kidsgrowingstrong.org Kidsgrowingstrong.org There are three different ways pollination can occur: through insect/animal transfer, through wind transfer, and through human transfer. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/media/16679/Dandelions-arecapable-of-both-self-pollination-and-cross-pollination http://www.britannica.com/EBchec ked/topic/467948/pollination/7589 7/Agents-of-pollen-dispersal How do plants defend themselves? 1. Secrete bad smells 2. Secrete poisons 3. Built in defenses like “thorns” http://www.mbgnet.net/bioplants/pollination.html