* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angiosperms
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
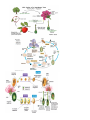
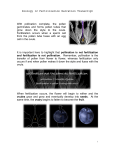
Angiosperms Name __________________________ Date _________________________ Block _________________ • • • ________________________ that reproduce sexually through their _________________ _________________________________ within fruit Most widespread of all land plants Angiosperm Adaptations to Life on Land • Alternation of generations • _______________ tissue o Xylem tissue has ________________________ and ________________ cells instead of __________________________ Vessel element cells evolved from tracheid cells Arranged __________________ and forming continuous tubes that are better at carrying water than tracheids but not as good for giving supporting Fiber cells also evolved from the tracheid cell. Have ________________________and are specialized for supporting • o Resist drying out due to thick _______________________ (cuticle) o Stomata • • Gymnosperm Adaptations to Life on Land o o ________________________ and nourish _____________ until environmental conditions are favourable • o Pollen grains are dust-like particles carried by _______________, ____________, _____________, animals Angiosperm Subclasses • Two subclasses of angiosperms: • _____________________ (_____________________) • _____________________ (_____________________) Monocots: angiosperms whose ________________________________ Dicots: angiosperms whose _____________________________________ Cotyledons: ____________________ of the embryo Filled with _______________ First leaves to carry out ___________________________ Monocot & Dicot Characteristics Angiosperm Reproduction • Reproduce _________________ through their _________________ in a process that involves _______________________ • Pollination is the ________________________ from one flowering plant to another • Plants _____________________________ have ________________________ with little or no smell o Ex. corn, wheat, grass • Vector pollination – pollination by ______________________ o _______________________ relationship Animals get food (nectar or pollen) Plants get pollinated Female Reproductive Structures • Pistil: contains the _____________, the __________________, and the _____________________ within the ovary • Stigma: captures and ________________ the _______________ with a sticky or hairy substance • Style: allows the _______________________ to ____________________ to the ovule • Ovary: encloses and _____________________________. o Contains one or more ovules for double fertilization to take place o The ovule contains the female gametophyte (the egg (N) and the polar nuclei (N+N) Male Reproductive Structures • Stamen: contains the _________________ and the __________________ • Anther: undergoes meiosis to produce the __________________________ (male gametophyte) • Filament: _____________________________________Other Flower Parts • Receptacle: the ________________ where the petals, ovary, and sepals are _____________ • Sepals: they are ________________ and they enclose and ________________ the developing ____________________ • Petals: they are ____________________________ and _________________ to attract _________________________________ Pollination • Pollen is _______________________________ by insects, bats, birds, or wind _____________________________ to the sticky ___________________ and germinates producing a pollen tube • The two sperm nuclei _________________________________ to the opening of the ovule Fertilization • ____________________________ nuclei enter the ovule opening • __________________ fertilization takes place o ____________________________ (N) _________________ with the polar nuclei (N+N) producing an __________________ (provides nutrients for the developing embryo) o The ____________________________ (N) ______________________________ (N) producing a zygote (2N) which develops into an embryo in a seed • ____________________ thickens to become a fruit • The ________________ toughens to produce the seed coat Coevolution of Animals and Flowers • Initially, this relationship must have evolved accidentally o However, the coevolutionary relationship strengthened because it was beneficial to the survival of both plants and animals o Ex. bees remember the color, shape and odor of a flower it finds food on very clearly • the bee will continue to look for those flowers • on its way to the food (pollen) the bee might pollinate the flower with pollen from the last flower it visited this ensures the survival of the plant o Ex. flowers that are pollinated by moths are very fragrant (we use them for perfumes) • moths can't see color but have an excellent sense of smell o Ex. flowers pollinated by flies smell like rotting meat! (flies are looking for places to lay egg) Seed Dispersal • _______________________________ the process of distributing ____________________ from __________________ plants • Why do seeds need dispersal? o If seeds fall to the ground beneath the parent plant instead of being dispersed they will ____________________ with one another and with the parent plant for sunlight, water, and nutrients competition will ____________________________________ for the growing seeds seed dispersal also __________________________________________________ Seeds can be dispersed by o o o ______________________________get eaten, the fleshy part is digested by the animal but the seeds are not _________________________________ from the animal in a new environment with fertilizer Have you ever wondered why unripe fruits are green and have bitter taste? • Inside unripe fruit the seeds are _______________________ o Unripe fruits are _______________________________ to try to keep animals from eating them • if they are eaten too soon, the immature seeds will not be able to grow o Unripe fruit is _____________________ so that they are ________ _______________________________ and are not easily found by animals