* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download major food source of the world
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
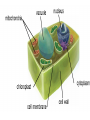
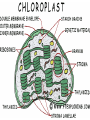
Introduction to Plants major food source of the world Background Q: When the first organic molecules began forming on Earth, what wasn’t present in the atmosphere? Q: What is now present in the atmosphere? Oxygen Revolution 1. Oxygen first produced, dissolved into the ocean 2. Dissolved oxygen @ saturated levels 3. Combined with iron in ocean and solidified into iron oxide 4. Oxygen then began to enter the atmosphere Where is the evidence of oxygen in ocean? Evidence supporting dissolved oxygen in ocean Iron Oxide (Fe2O3) What do plants provide for the PLANET? Common Knowledge that plants produce oxygen… but how? Consider a large oak tree, where does its mass come from? light, air, soil or water? Look at Brief History Imperfect by nature “Some 3.4 billion years ago, a puddle of green slime kick-started a process that would terraform an inhospitable Earth into a planet with oxygen and ecosystems. Ancient cyanobacteria had stumbled onto something incredible: using photons of light to split water, and channeling the resultant burst of energy to turn carbon from the air into sugar. Today, that process—photosynthesis—is the basis of nearly every food web and ecosystem on our planet. It’s also been responsible for recycling the atmosphere these last few eons, by drawing down CO2 and releasing oxygen as a waste product. If plants stopped spinning sunlight into sugar tomorrow, every animal on Earth would soon starve and asphyxiate.” - courtesy of Maddie Stone (7/4/2015) WHAT MAKES PLANTS SO SPECIAL? ❏ Plants are made of cells ❏ They have a cell membrane, made of phospholipids ❏ Is anything unfamiliar in diagram? Cell terminology Eukaryote- organism whose cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles Organelle- a specific structure that carries out specific activities for the cell. Cytoplasm- fluid space inside cells ● Plants are eukaryotes and their special organelle is a chloroplast Entering a Cell Plant Cell Terminology Cell wall- rigid structure surrounding a cell membrane that provides extra support in maintaining cell shape Vacuole- organelle that stores water for plant cells Chloroplast- organelle that absorbs light (form of energy) to make carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water. thylakoid- location where energy is captured and transferred to electrons in the chlorophyll. granum- stack of thylakoids Up NExt: Photosynthesis Metabolism: involves either using energy to build molecules or breaking down molecules in which energy is stored