* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Relationship
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Value proposition wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service blueprint wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Relationship Marketing
V l
Value creation and strategy implementation
ti
d t t
i l
t ti
A d
Agenda
• Th
The Changing Focus in Marketing
Ch i F
i M k i
• Traditional versus Relationship Marketing Approach
• Transactional versus Relationship Marketing
p
g
• Relationship Marketing: principle and orientation
• The role of RM to competitive marketing strategy
““As a merchant you’d better have a friend in h
’d b
h
f i di
every town”
An ancient Middle Eastern proverb
Th Ch i F
The Changing Focus of Marketing
f M k ti
Customer relationship
focus
Competitive position focus
Service d i
dominant
t
Compleexity
Marketing Mix
focus
Sales Market k
focus
dominant
Production focus
Product
focus
Product Dominant
Time
Pre 1800s
1920s
1950s
1970s
1980s
1990s
2000+
Source: Christopher et al (1991)
T di i
Traditional Marketing Approach
lM k i A
h
• Marketing Mix (4Ps)Approach
Marketing Mix (4Ps)Approach
– Product – Price Price
– Place – Promotion
P
ti
Problems with Traditional Marketing Approach
• It assumes all segments of customers are similar and may be treated in a standardized way
• It assumes consumers are passive absorbers of marketing information
• It assumes short‐term and often one‐off transactions based around the exchange of goods for money Source: Christopher et al (1991)
D fi iti
Definition of Relationship Marketing
f R l ti hi M k ti
Perspective
Definition
Berry (1993) from a service perspective
“Relationship Marketing is attracting, maintaining and multi‐
service organizations enhancing customer relationship”
JJackson (1985)
k
(1985) from an f
industrial marketing perspective
“Marketing concentrated towards
“M
k ti
t t dt
d strong, lasting t
l ti
relationship with individual accounts”
Berry and Parasuramen
Berry
and Parasuramen
(1992) from a service perspective
“Attracting
Attracting, developing and retaining customer developing and retaining customer
relationships”
Gronos ((1995)) from a network perspective
“To identify and establish, maintain and enhance y
,
relationship with customers and other stakeholders, at profit so that the objectives of the partners interest are met, and this achieved by a mutual exchange and fulfillment of promises”
of promises”
Source: Christopher et al (1991
General Model of Relationship General
Model of Relationship
Marketing
• Focuses on a relationship rather than transactional approach to marketing
• Understands the economics of customer retention
d
d h
f
• Highlights the critical role of internal marketing in achieving external marketing success
g
g
• Extends to more diverse market
• Recognizes the quality, customer services and marketing need to be closely integrated
k ti
dt b l l i t
t d
• Ensures that marketing is considered a cross functional context
The Transactional to Relationship The
Transactional to Relationship
Marketing
Emphasis on all market domains and k td
i
d
customer retention
Emphasis on customer acquisition
q
RELATIONSHIP
MARKETING
TRANSACTIONAL MARKETING
Functionality‐based Marketing
Cross‐functionality‐
based Marketing
Source: Christopher, Relationship Marketing, 2002
Transactional Marketing
Transactional Marketing
Relationship Marketing
Relationship Marketing
‐Focus in volume
‐Emphasizes
h
product features
d
f
‐Short timescale
‐Little emphasis on customer p
services
‐Moderate customer contact
‐Primary concern with product
‐Primary concern with product quality
‐Focus on profitable retention
h
l
‐Emphasizes customer value
‐Longer‐term timescalers
‐High customer service g
emphasis
‐High customer contact
‐Concern with relationship
‐Concern with relationship quality
Principles of Relationship Marketing
• Maximizing
Maximizing Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a
fundamental goal of Relationship Marketing
– The
The future flow of net profit discounted back to the future flow of net profit discounted back to the
present
• Focusing marketing action on multiple markets
g
g
p
– Six Markets Model
• It must be cross
It must be cross‐functional
functional
– “Marketing is too important to be left to the marketing department” (David Packard)
The Relationship Marketing Th
R l i hi M k i
Orientation
Quality
RELATIONSHIP
MARKETING
Customer
Service
Marketing
Source: Christopher et al (1991)
Benefits RM to the firms
• To win a new customer is more expensive than to p
it is to to retain an existing customer
• Established customers tend to buy more (share of wallet)
• Satisfied customers are more likely to refer others (reduce cost of acquisition)
(reduce cost of acquisition)
• Loyal customers can be less price sensitive and may be less likely to defect due to price increases
• Retaining customers makes market entry difficult for competitors
The Role of RM to Competitive Marketing Strategy
Marketing Strategy
• Value as the central role to develop and implement relationship marketing strategy
implement relationship marketing strategy
• Stakeholders interaction process
• Key value activities
K
l
ti iti
The Role of Customer Value
h
l f
l
• Customer Perceive Value (CPV)
Customer Perceive Value (CPV)
Is the difference between the prospective customer’s evaluation of all benefits and all the costs of an offering and the ‘perceived’ alternatives.
• Customers tend to be value maximizers
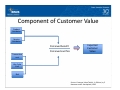
Component of Customer Value
Product P
d
Attributes
Service
Attributes
Perceived benefit
Perceived sacrifice
Perceived sacrifice
Expected Customer
Value
Transaction cost
Life Cycle
Lif
C l
Cost
Risk
Source: Customer Value Toolkit, 1st Edition, by E. Naumann and R. Kordupleski, 1995
The Value Process
•
•
•
•
Value Determination
Value Creation
Value Delivery
Value Assessment
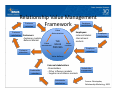
Relationship Value Management Relationship
Value Management
Framework
Employee
recruitment
Customer retention
Customer satisfaction
Value determination
Customers:
‐Customer markets
‐Referral Market
R f
lM k
Value assessment
THE THE
VALUE PROCESS
Value
creation
Employees:
‐Internal Market
‐Recruitment markets
Customer attraction
Employee
satisfaction
Employee
retention
Value delivery
Stakeholder
retention
External stakeholders:
‐Shareholders
‐ Other influence markets ‐ Suppliers and alliance markets
Stakeholder
satisfaction
Stakeholder
engagement
Source: Christopher, Relationship Marketing, 2002
Choice of Relationship Strategy
• Three
Three generic strategies identifies by Treacy
generic strategies identifies by Treacy and and
Wierseman:
– Operational excellence
Operational excellence
Providing customers with reliable products or services at competitive prices and minimal inconvenience
– Product leadership
Providing products that continually redefine the state of art
– Customer intimacy
Customer intimacy
Selling the customer a total solution not just a product or service
R f
References
•
•
•
Chistopher, Martin, Adrian Payne and Davidballantyne (2002). “Relationship Marketing, creating stakeholder value”Butterwor.th‐Heinemann.
Harwood, Tracy,T. Garry and A Broderick (2008). “Relationship Marketing: Perpectives, Dimensions and Context, McGraw Hill.
N
Naumann, E. And R. Kordupleski
E A d R K d l ki (1995). “Customer Value Toolkit, 1
(1995) “C t
V l T lkit 1st edition. South diti
S th
Western College \publishing.
g{tÇ~ lÉâ
l