* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Periodic Table Trends
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Surface properties of transition metal oxides wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Reflection high-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
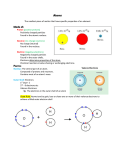
The Periodic Table Trends They Might Be Giants - Meet the Elements Element Funkiness Daniel Radcliffe - Element Song Here are some chemistry jokes with elements as punch-lines I apologize for them ahead of time What did the silver atom say to get the gold atom’s attention? Au There is more to the periodic table than just what can be found in the element boxes. The periodic table is organized by increasing atomic number and elements with similar properties & same valence electrons are placed together in a column The periodic table of elements • Is organized to maximize trends • Can be used to predict the properties of undiscovered or unfamiliar elements • Can predict reactions between elements without actually doing the experiment. Trends we will study Atomic Mass Atomic Number State of Matter Metallic Character Valence Electrons & Bonding Electronegativity Atomic Radius Ionization Energy Reactivity Some Trends in Depth Valence Electron Trend What are Valence Electrons? Valence electrons are electrons in the last & highest electron energy level. 1? Valence shell electron pattern Why are Valence Electrons Important?? When atoms get close to each other, the nucleus of one atom will interact with the other atom’s valence electrons. A chemical reaction and bond can result from that interaction. 9+ 9+ Valence Electrons are Importance because…. chemical reactions are just a rearranging of valence electrons & valence electrons are the cause of bonding (ionic, covalent, metallic) Valence electrons are rearranged in chemical reactions so atoms complete their valence level of electrons. Bonding also results from atoms completing their valence shell. When Atoms react and bond valence electrons are transferred or shared. How the Periodic Table can be used to Predict Bonding • Metallic – Two Metal Atoms (both atoms would like to lose valence electrons) • Covalent – Two Nonmetals (both atoms would like to gain electrons) • Ionic – Metal and Nonmetal (metal atom would like to lose electrons and nonmetal would like to gain electrons) Ionic Bonds • A metal atom Loses electron(s) & a nonmetal Gains electron(s) Sodium and Chlorine Video Ionic bonds are created by attraction between oppositely charged atoms / particles. Covalent Bonds • Sharing of electrons between two nonmetals • If two atoms need electrons to complete their valence shell they make covalent bonds. Nonmetals need electrons. Metallic Bonds • Sharing electrons b/w two metals both of which want to lose electrons Quiz – Valence Electrons & Bonds 1. What are valence electrons? 2. What is the pattern for increasing valence electrons? 3. Why are valence electrons important? Quiz – Valence Electrons & Bonds Type of Bond What combo of elements make the bond? Describe the role of electrons in the bond Bond type can more accurately be predicted with ELECTRONEGATIVITY Electronegativity • Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons from another atom. Value of Electronegativity •0 no attraction for more e • 4 great attraction for e The absolute difference of two elements electronegativities will tell whether the bond will be covalent or ionic Calculating Bond Character • Absolute difference b/w the electronegativities determines type of bond Metallic: Two Metals Nonpolar Covalent: 0 ≤ X ≤ 0.4 Polar Covalent: 0.4 < X ≤1.7 Ionic: X > 1.7 There is no firm cut-off between Ionic and Covalent it is gradual and continuous transition. Increasing electronegativity difference + - + - Fluorine Video – University of Nottingham Atomic Radius Atomic radius (volume) is how far the outside electrons are from the nucleus. Depends on: •The strength of attraction between the electrons & nucleus (atomic number) •The number energy levels Adding Electron Energy Levels Increases Atomic Radius • Each new energy level occupies a larger more distant region around the nucleus. 2s 1s 1s Contraction Along a Period Adding more protons without adding an energy level contracts atomic radius. The greater positive charge in the nucleus the stronger the pull the nucleus has on the electrons within the existing energy level. Atomic Radius Atomic Radius increases to the left (fewer p+) and down (new energy levels). The largest radius is bottom left corner (Fr). NI3 Demo Which is more stable NH3 and NI3? IONIZATION ENERGY Ionization energy is the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion (ionization always requires energy) Energy + X (g) + X + (g) e Ionization Energy • The stronger the nuclear charge (more protons) and smaller atoms (electrons are closer to nucleus) the I.E. is higher • IE is highest for He and lowest for Fr st 1 Ionization Energies Ionization Energy increases to the right and up Reactivity Metal element reactivity increases Nonmetal element reactivity increases Give an Explanation of Metal and Nonmetal Reactivity using Atomic Radius and Atomic Number (or Ionization Energy) END Good videos from University of Nottingham, Mg Video Ag Video When atoms complete their valence energy level they lower their potential energy Two atoms go to an ice cream shop……… Electron Affinity e + X (g) X (g) Electron Affinity • Electron affinity measures energy lost or gained when adding an electron. Sign of Electron Affinity Values • While IEs are all positive, some electron affinities are negative. • Negative values indicate that energy is lost by the atom when it gains an electron. C4.9 Introduced: X I can state the Periodic Law and give it as the organizing principle for the periodic table. Outermost (valence) energy level is the skin of the atom Gain or Loss of Electrons? Positive ions are formed by metal elements. They lose electrons because that is a less energetic pathway. Nonmetals make negative ions….