* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is RF diathermy?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
GROUP MEMBERS:
UMAIR MAJEED NAGRA (EE-01083244)
ABID BILAL (EE-305-011)
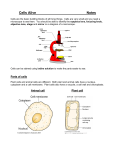
Physiotherapy involves evaluating,
diagnosing, and treating a range of diseases,
disorders, and disabilities using physical
means.
Physiotherapy
therapy
is also referred to as physical
Infrared
Heat Therapy
RF-Diathermy
Ultrasound Therapy
Muscle And Nerve Stimulators
Infrared
heat therapy uses infrared lamps,
heaters, and infrared saunas to boost
immune function, reduce inflammation,
stimulate detoxification and weight loss,
promote cardiovascular health and
circulation, relieve pain, increase healing of
wounds, relieve stress and depression,
among other clinical benefits.
An understanding of Infrared ("IR") firstly
requires an understanding of radiant heat.
Radiant heat is also called infrared energy.
Radiant heat is simply a form of energy that
heats objects directly through a process called
conversion, without having to heat the air space
in between.
IR is the emission of energy as electromagnetic
waves in the portion of the spectrum just beyond
the limit of the red portion of the visible
spectrum.
The
infrared segment of the electromagnetic
spectrum is divided into 3 segments by wave
length, measured in microns or micrometers
(one micron = 1/1,000,000 of a meter):
0.076 - 1.5 microns = Near Infrared (NIR);
1.5 - 5.6 microns = Middle Infrared (MIR); and
5.6 - 1000 microns = Far or long wave
infrared (FIR).
It
increases the extensibility of collagen
tissues
It decreases joint stiffness directly
It produces pain relief
It increases blood flow
More recently, it has been used in cancer
therapy
THE INTRODUCTION for
RF DIATHERMY DEVICE
JAN. 12, 2009
What is RF diathermy?
Over 100KHz (High Frequency Current, HFC)
Same as Radio Frequency Range → Radio Frequency → RF
Lavatron 420KHZ
RF diathermy History
1886 Development of Radio Frequency Device
1897 Approve the effect of Radio Frequency for Diabetes, Obesity
1899 Report the generating of heat in body tissues by passing RF
1906 Study for the break of tumor tissue by RF
1930 RF diathermy device development
RF Tumor Coagulation
Short wave(10MHz) Diathermy device
RF Lesion Generator
Physiotherapy Diathermy Treatment
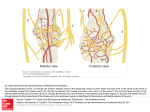
Monopolar
electrode
→
Patient plate
Transformation of Over 100KHz inside body
→
Activation of Ion
movement inside of body
→
Collision
between Ion
Generate Core body
temperature 40~50°C and
3~5CM depth
Monopolar Type - Lavatron
420 KHZ = Ion inside of body moves 420,000 times movement / sec
+ Pole
- Pole
•Current flows between two poles (Electrode and Patient plate).
Electrode is “+ Pole” and Patient plate is “– Pole”. Current flow from
Electrode(+ Pole) to Patient Plate(- Pole).
In the mono polar, heat is generated in the deepest side of body comparing
bipolar and tripolar type.
Bipolar Type
•+ pole and – pole are in one electrode.
•RF current flows between two poles like above picture. So the patient plate
is not required.
• The depth of penetration is fixed and limited to approximately half of the
distance between the two poles.
• This means, less energy of sufficient density reaches the deeper skin
layers, rendering a more superficial effect regardless of the emitted energy
level.
•It is effective on face to remove wrinkle and tightening but it can not touch
the fat cell so it is not effective on body.
Tripolar Type
•One + pole and two – poles are in one electrode.
•RF current flows between 3 poles. So current flows between three poles
and the penetration depth is a little bit deeper than bi-polar but its depth of
penetration is shallower than mono polar RF.
•It touch on superficial area on the skin like bi polar RF. Its basic electricity
principle is same with bipolar. With this reason, its result is also similar with
bi polar. It is effective on face treatment but it is hard to expect good effect
on the body.
Biological effect of RF Diathermy
Increasing core body temperature up to 40~50℃
Expansion of artery and capillary
Increasing blood flow rate
Increase in
O2 supply
↓
Body Fat
combustion
Increase in
Stimulation of
Nutrition supply Immune system
↓
Collagen
Re composition
Increase in
Metabolism
Removal of
Waste material
↓
Obesity Care
Treatment good for Beauty as well as Health
LIFTING
BODY SHAPING
HAIR RESTORTION
WRINKLE REMOVING
PAIN CONTROL
FAT CONTROL
RF Diathermy Body care part
Body Fat Decomposition
Cellulite Dissolving
Size Decreasing
Abdominal fat care
Size decreasing
Abdominal fat care
Before
Abdominal fat care
After
Lifting
Remove Stretch Marks
Various electrodes
Size(Diam
eter)
Appling part
Effect
20㎜
Wrinkle under eyes, nose, around
mouth
Improve wrinkle
30㎜
Face, around Cheek and Jaw
Improve wrinkle and skin care
40㎜
Face, Neck, back of neck, arm
Skin care and pain relief
50㎜
Arm, Calf, Shoulder
Body care, Skin care, Pain
relief
60㎜
Calf, Thigh, Back
Body care, Pain relief
70㎜
Back, Thigh, abdomen
Obesity, Body care, Pain relief
80㎜
Back, Thigh, abdomen
Obesity, Body care, Pain relief
100㎜
Back, Abdomen
Obesity, Body care, Pain relief
Picture
Medical application of RF Diathermy
Heat’s deep penetration into tissue
Relaxing stressed muscle by overwork and
bad position
Pain Relief
Shoulder pain
Lumbar pain
Application
*Chronic arthritis *Muscle pain *Lumbar pain
*Rheumatic arthritis *Frozen shoulder
Rheumatology
Ultrasound
is high frequency sound waves,
greater than 20,000 Hz. Therapeutic
ultrasound is in the frequency range of 0.9 3 MHz.
The main piece of equipment is a high-frequency
generator, which provides an electrical current
through a cable to a transducer which contains a
piezoelectric crystal. This crystal when exposed to
the current will vibrate at a given
frequency, expanding and contracting, which
produces the necessary compression wave. By using
a different frequency the therapist can target tissues
at different depths for either healing or
destruction, or simply use the device to reduce
pain. Although simple in principle, the use of
ultrasound as a therapeutic modality requires a
comprehensive understanding of its effects on the
body tissues and of the physical mechanisms by which
its effects are produced. The lower the frequency
used, the deeper is the penetration of the waves into
the body.
In
the proliferative phase of healing,
ultrasound effects fibroblasts and stimulates
them to secrete collagen. This accelerates
the process of wound contraction and
increases the tensile strength of the healing
tissue.
What
is Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)?
Technique of inducing a muscle contraction
Uses an electrical impulse from a device
Impulses stimulate action potentials from Central
Nervous System
Uses
Electrotherapy
for EMS?
Prevent atrophy after injury
Muscle Strength Training
Targets a specific muscle to train
Used by athletes
An
electric muscle stimulator is a device that
sends low-level electronic pulses to your
muscles in order to halt atrophy or reduce
spasms.
It is sometimes used by bodybuilders to build
muscle tone.
Also used for back pain.
The
NMES machine works by conducting
electrical currents from the machine to the
muscle at a safe current rate. The process
starts by placing self-adhesive electrodes to
the motor points of the desired muscle or
muscle system. The dial on the machine is
slowly adjusted until the patient can feel the
current passing through the skin and into the
muscle. The higher the setting on the dial,
the faster the muscle will contract and relax.
This process is continued for a varied amount
of time dependent on how large of muscle
the NMES is trying to stimulate.
Electrical nerve stimulation is a non-invasive
nerve stimulation treatment designed to reduce
pain both acute and chronic. It is a small
electrical device that delivers low-intensity
electrical impulses across the skin. The device is
usually pocket size or smaller and is connected
by wires to pads which are placed on the skin. A
typical battery operated unit is able to modulate
pulse width, frequency and intensity. It is
thought to work in two ways: Pads are placed on
or near the area of pain and low-intensity pulses
are sent via the pads through the skin and along
the nerve fibers.
The
pulses (controlled by the user) are
thought to suppress pain signals to the brain
and encourage the body to produce higher
levels of its own natural pain killing
chemicals called endorphins. It is widely
used around the world for a variety of
painful conditions by private individuals,
professionals and some state hospitals.
A nerve stimulator supplies electrons to
depolarize a nerve. The number of electrons
supplied per stimulus equals the current. To
make sure that the nerve is completely
depolarized we keep winding up the stimulating
current until the muscular response does not
increase any more, then we add another 10%.
This is called the supra-maximal stimulus. At this
point we assume that the nerve supplying the
muscle is completely depolarized. As a result the
muscle must be maximally stimulated by the
nerve. The muscle contraction that results must
also be maximal.
The outside of a 'resting' the nerve is charged
positive. It is 'polarised'. If you add negative
electrons to the outside they will neutralise the
charge. This will cause that wave of
depolarisation to wash down the nerve. The
negative electrode should be attached as near as
possible to a nerve, commonly the ulnar nerve at
the wrist or the elbow. (You can use the facial
nerve if you can't get at the hands.) The other
electrode can be placed anywhere else along the
line of the nerve, commonly half way along the
forearm.
Then assessed the amount or strength of
movement in muscles supplied by that nerve,
usually the thumb.
Changing
resistance
Constant Voltage Nerve Stimulators
Constant Current Nerve Stimulators