* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 8: Human Inheritance
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
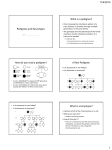
UNIT VIII - HUMAN INHERITANCE I. HUMAN GENETICS (pp. 270 – 271, 299 - 301) A. Human Somatic Cells body cells) are _______ diploid or 2n. Human somatic cells (_____ 46 chromosomes, or 23 pairs Each human somatic cell has ___ of chromosomes. Of these 23 pairs, 22 pairs are called homologous pairs, meaning they contain the same _____________ genes in the same order. The 44 chromosomes that make up the 22 homologous pairs in each cell are called ____________. autosomes sex chromosomes. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are the ____ XX o In female somatic cells, the sex chromosomes are ___. XY o In a male’s somatic cells, the sex chromosomes are ___. All human somatic cells contain: o ____ 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes. o ___ 1. Karyotypes homologous A karyotype is a micrograph of _______________ chromosome pairs. Arranged in decreasing size. B. Human Gametes Gametes are haploid _______ or n, and contain 23 ___ chromosomes. egg cells, and male gametes are sperm Female gametes are ____ ______ cells. meiosis in the ovaries or testes, respectively. Gametes are produced through the process of ________ In meiosis, when the tetrad, or homologous pairs of chromosomes separate in anaphase I of meiosis, the sex chromosomes separate also. X chromosome, while the sperm cell produced has a The resulting egg cell can ONLY contain an __ MALE 50% chance of containing an __, X and a 50% chance of containing a __. Y Therefore, the ______ determines the sex of the offspring. C. Analyzing Human Inheritance Pedigree chart is a diagram that follows the inheritance of A _________ a single _____ generations of a family. trait through several ___________ Pedigree Rules: squares and • In a pedigree, males are represented by ________, females are represented by ______. circles Horizontal • _______ Vertical lines connect parents to children. __________ lines connect siblings or spouses. Children are placed in birth order, from left to right. • Roman numerals show ___________. generations • Individuals who are affected by the trait are represented with shaded _______ symbols. Individuals that are not affected non-shaded figures. by the trait are shown by ___________ • Half shaded = _____________ carrier of heterozygous or a “_________” the trait. • Circle with a ____ female dot = X-linked carrier (always _______) (Video: What are Pedigree Charts? (Mark Drollinger 4:23)) An attached ear lobe is a recessive trait. Determine the genotypes of each individual below. Hint: label all homozygous recessives first!!! Analysis Questions: 1. How many are males have attached earlobes? 3 2. How many are females have free earlobes? 5 3. How many aunts are in this family? 2 4. How many heterozygous traits exist? 5 How many are possible? 7 A widow’s peak hairline is a dominant trait. Determine the genotypes of each individual below. Hint: label all homozygous recessives first!!! Key: W = widow’s peak w = no widow’s peak The following pedigree shows the inheritance of a recessive trait. rr R? Rr R? rr R? R? R? Rr R? R? rr R? Rr Rr R? R? rr rr rr rr Rr rr R? • How many generations are shown in this pedigree? 5 (V) • How many children did Parents I-I and I-2 have? 3 • How many were boys? 1 Girls? 2 • How many children did Parents II-1 and II2 have? 3 • How many were boys? 2 Girls? 1 • Key: R = non-affected; r = affected • Determine the genotypes of each person in this pedigree. II. AUTOSOMAL DISORDERS (pp. 296 – 304) autosomes the 44 chromosomes other than the 2 sex • Most genes are carried on the __________, chromosomes. So it follows that most genetic disorders are autosomal disorders. equally • These disorders affect males and females _______. • Autosomal disorders can be divided into: A. Recessive ________ 1. Albinism 2. Cystic Fibrosis 3. Tay-Sachs Disease 4. Phenylketonuria B. Dominant _________ 1. Huntington Disease 2. Marfan’s C. _______ Number Disorders A. AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE DISORDERS (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_oVvTkjDm6g) melanin 1. Albinism – Characterized by failure to produce the pigment, _______. hair and _____. eyes • Affected individuals lack coloration in skin, ____, cancer and are very sensitive to light. • Very susceptible to skin _______ • Symptoms appear at _____; birth they have a normal life expectancy. • Mode of Inheritance: o From recessive alleles on chromosome # ___ 11 mucus production in lungs & respiratory system. 2. Cystic Fibrosis – Characterized by excess _______ • Symptoms appear just after birth which include frequent respiratory infections, poor nutrition due to blockage of pancreas & can cause liver failure.. 20’s & 30’s • With treatment, patients can survive to their ____ ____. fatal genetic disorder in the US among Caucasians. • Cystic fibrosis is the most common _____ (1:30) 7 • Recessive allele on chromosome # ___ 3. Tay-Sachs Disease – Characterized by the inability of nerve cells to break down a specific type of lipid ____. 3-6 months. • Symptoms appear between the ages of ____ blindness degeneration of mental & motor skills, and • Lipid build-up causes seizures _______, _________, 5 _____ death at or before age ___. Jewish population, although genetic testing has decreased its • Historically associated with ______ incidence. • Recessive allele on chromosome # 15 ___ PKU – Characterized by an inability to breakdown the amino acid, 4. Phenylketonuria or ____ phenylalanine _____________. brain damage & mental impairment. • Build-up results in severe ______ easily treated with a diet • All babies born in US hospitals are tested for PKU because it is _____ low in phenylalanine. 12 • Recessive allele on chromosome # ___ B. AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT DISORDER https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yANF0bxHpzU brain cell degeneration 1. Huntington _________ Disease – characterized by genetically programmed _____ psychological • Affects ______, motor cognitive & ____________changes. • S/SX: mood swings, depression, loss of memory and ability to learn. As well as loss of muscle control, difficulty swallowing, speech impairment, and eventually death. normal • Genotypes: hh = _______ one parent must have it for the • HH ___ or ___= Hh will have disease (therefore, only ____ child to inherit the disease.) 4 • Affiliated with Chromosome # __ 2. Marfan Syndrome – Dominant disorder that affects the __________ connective tissue ______of the skeletal system, eyes, and circulatory system. Affected individuals have very long limbs ______ aortic vision problems, and are susceptible to ______rupture. _____, C. NUMBER DISORDERS • Number disorders occur because of a failure of a separate correctly in chromosome pair to _________ Anaphase I or II of meiosis. This is referred to as nondisjunction ______________. • Nondisjunction can occur during Meiosis I, in homologous _____ pairs fail to separate or in which ___________ sister__________ chromatids fail to Meiosis II, in which _____ separate. • In both cases, the gametes produced have an abnormal number of chromosomes. _________ • **Number disorders are NOT inherited; therefore, they CANNOT be Predicted with Punnett _______** square ________ • Can involve autosomal chromosomes or sex chromosomes A. Autosomal Number Disorders https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ze_6VWwLtOE lethal The ONLY autosomal number disorder that Most autosomal number disorders are ______. Down syndrome allows survival into adulthood is ______ _________. 3 chromosomes at the 21 because there are __ 1. Down syndrome is also known asTrisomy ___________ 21st position, instead of just ___. 2 ____ • Individuals have characteristic facial features; growth, behavior, and mental development impaired There is also a higher risk of congenital heart defects. The incidence are all _________. older mothers. of babies with Down syndrome is much higher in _____ 2 . Edward’s Syndrome Also called _________ ____, is a chromosomal condition associated with abnormalities in many parts of the body. • Slow growth before birth (intrauterine growth retardation) and a low birth weight. • May have heart defects & abnormalities of other organs that develop before birth. • Other features are a small, abnormally shaped head; a small jaw and mouth; and clenched fists with overlapping fingers. Due to the presence of several life-threatening medical problems • Many die before birth or within their first month. Five to 10 percent of children with this condition live past their first year, and these children often have severe intellectual disability. 3. Patau Syndrome Also called _______ Trisomy ___, 13 is a chromosomal condition associated with severe intellectual disability and physical abnormalities in many parts of the body. Occurs in about 1 in 16,000 newborns • _____ Heart ______, defect brain or spinal cord abnormalities, very small or poorly developed _____ eyes (microphthalmia) • Extra fingers or toes lip (a cleft lip) with or without an • An opening in the ___ opening in the roof ____ of the mouth (a cleft palate) • Weak muscle tone (hypotonia). Due to the presence of several life-threatening medical problems, many infants with trisomy 13 die within their first 5-10 ____ days or weeks of life. Only ______% of children with this condition live past their _____ first year B. Sex Chromosome Number Disorders https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YQG8o5b4lKg nd sex chromosome 45 XO because individuals lack a 2____________________. 1. Turner Syndrome – Also called _______ females typically short in stature, underdeveloped sexually, sterile, with a • Patients are ________, normal life expectancy. 47XXY https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6qTPdSJc9Cs 2. Klinefelter Syndrome – Also called ______. extra sex chromosome. Symptoms do not appear until _______ puberty at which • Individuals inherit an _____ males show poor sexual development and infertility. Treated with hormone time affected ______ therapy. Normal life expectancy. • Most common sex disorder (1 out of 500 males) III. SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE X or ___). Y A gene is referred to as “sex-linked” if it is located on a sex chromosome ( ___ X chromosome. In humans, sex-linked genes are almost always located on the larger ___ Y chromosome is much smaller and carries only a few genes related to sexual The __ two X chromosomes; males have one development. Females have ___ ___ X. • Females will only show recessive traits located on the X chromosome if they are homozygous __________ recessive. higher incidence of sex-linked disorders. • But a male will always having a much ______ • Genotypes for sex-linked traits are written using the X and Y chromosomes to show path of inheritance. • For example: red-green color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait. If C = normal vision and c = colorblindness: XcY colorblind female = ____. carriers XcXc Females can be _______ • KEY: colorblind male = ____; for sex-linked recessive disorders. A carrier someone who has the defective allele, show the trait The genotype of a female carrier is _____. XCXc Males but doesn’t ___________. _______ CANNOT be carriers for a sex-linked trait because they only have one X chromosome. A. Sex-linked Disorders – All of these disorders are sex-linked __________. RECESSIVE Normal life span 1. Color Blindness – Inability to differentiate and distinguish colors. ______ • Example: red-green colorblindness 2. Hemophilia – Missing an enzyme required for normal blood clotting ______. a. Have uncontrolled bleeding episodes. Main Symptom: bruising and/or bleeding • Blood fails to clot properly leading to excessive _______ internally ________. • Treated with blood __________. transfusions b. Hemophilia can be traced through a pedigree of the _____ Royal family 3. Duchenne’s Muscular Dystrophy 3-6 years of age. • Symptoms develop at ____ breakdown of muscle fibers, leading to eventual • Causes muscle weakness ________ and the __________ cure Death usually occurs before _________. adulthood death. There is no available treatment or ____. Sex-Linked Punnett Squares Practice: In sex-linked traits, probabilities for male and female offspring must be calculated separately because traits are inherited differently. 1. A colorblind female marries a man with normal vision. What is the probability of them having colorblind children? • Key: ________________________________________ • Cross: _______________________________________ • Probability of having a colorblind daughter = ___________ • Probability of having a colorblind son = ____________ 2. A genetics counselor interviews a couple with a family history of hemophilia to evaluate the possibility of having offspring with the disorder. The woman does not have hemophilia, but states that her father had the disorder. The man is normal. • Key: ________________________________________ • Cross: _______________________________________ • Probability of having a daughter with hemophilia = _____ • Probability of having a son with hemophilia = ___________