* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download with oxygen - Don`t Trust Atoms
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
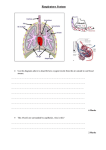
Topic 4: Bioenergetics Respiration Learning Objectives: 1. Recall the equations for aerobic and anaerobic respiration. 2. Analyse the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. 3. Explain the term metabolism. Vocabulary • • • • • • • • • Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration Exothermic Endothermic Oxygen debt (pg. 161) Fermentation Metabolism (pg. 165) Mitochondria (review) Enzymes (review) Respiration The process of transferring energy from glucose, which goes on in every cell. • Involve chemical reactions catalysed by enzymes • Exothermic process (releases energy) Energy is Used To… • Build larger molecules from smaller ones (example: proteins are made from amino acids) this process also makes new cells for growth, repair, and reproduction • Muscle contraction (movement) • Temperature regulation (mammals and birds) Aerobic Respiration • Aerobic means with oxygen • Happens in the mitochondria • Occurs all the time in plants and animals Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O • Releases a large amount of energy Anaerobic Respiration in Muscles • Happens when there is not a large enough supply of oxygen getting to the muscles. • Happens when you need more energy than can be supplied by aerobic respiration. Glucose Lactic Acid • Releases less energy, so only useful in “emergencies”. Oxygen Debt The amount of extra oxygen the body needs after exercise to react with the build up of lactic acid and remove it from the cells. lactic acid + oxygen carbon dioxide + water • Lactic acid is poisonous (it also causes muscle soreness) and needs to be removed. • Breathing rate and heart rate remain high after stopping exercise to “pay back” the oxygen debt. Fermentation The anaerobic respiration in yeast that produces ethanol and carbon dioxide. • Used in industry to produce ethanol (type of alcohol) glucose ethanol + carbon dioxide Comparing Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Is oxygen needed? Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration YES NO CO2 + Water Lactic acid (muscles) Ethanol + CO2 (yeast) LARGE SMALL Products? Amount of energy? Metabolism The sum (total) of all the reactions that happen in a cell or the body. • Enzymes control the reactions in metabolism. Examples of reactions: • Exothermic reactions (such as breaking down large molecules into smaller ones like in respiration) that release energy • Endothermic reactions (such as building large molecules from small ones) use up energy from respiration Summary • http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/scien ce/add_aqa/respiration/aerobic_anaerobicact.sht ml Respiration in humans • http://www.bbc.co.uk/education/clips/zbmd7ty Respiration in plants • http://www.bbc.co.uk/education/clips/z6cygk7 Writing Task • Use all of the vocabulary terms to answer the following essay question. • Compare aerobic and anaerobic respiration and explain the importance of respiration in living things.