* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geosphere!
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
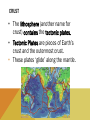
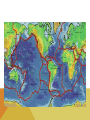
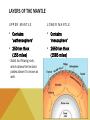
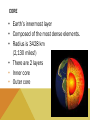
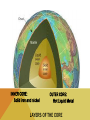
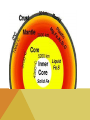
WHEN YOU THINK OF A SYSTEM, WHAT COMES TO MIND? WHAT DO ALL THESE SYSTEMS HAVE IN COMMON? • • • • 1. THEY ALL HAVE INTERCONNECTING PARTS! THE EARTH AS A SYSTEM A system is a collection of interdependent parts within a defined area. The Earth is described as a system since it also has connecting ‘parts’ that make up its ‘whole.’ GEOSPHERE (AKA LITHOSPHERE) The solid part of Earth that consists of all solid rock, as well as soils and loose rocks on the surface. LAYERS OF THE EARTH Most of the geosphere is located underground. CRUST • Earth’s outermost layer (the thinnest layer) • It is between 5 -20 km thick (3-12 miles!) • Less than 1% of the Earth’s mass is crust. CRUST • The lithosphere (another name for crust) contains the tectonic plates. • Tectonic Plates are pieces of Earth’s crust and the outermost crust. • These plates ‘glide’ along the mantle. MANTLE • The middle and thickest layer of the Earth’s layers • Accounts for almost 2/3 of the Earth’s mass! • Two layers: Upper & Lower LAYERS OF THE MANTLE UPPER MANTLE LOWER MANTLE • Contains ‘asthenosphere’ • Contains ‘mesosphere’ • 250 km thick (155 miles) • 2550 km thick (1585 miles) • Solid, but flowing rock, which allows the tectonic plates above it to move as well. CORE • Earth’s innermost layer • Composed of the most dense elements. • Radius is 3428 km (2,130 miles!) • There are 2 layers • Inner core • Outer core INNER CORE: Solid iron and nickel OUTER CORE: Hot Liquid Metal LAYERS OF THE CORE PARTS OF THE GEOSPHERE • Tectonic Plates – Plates of rock gliding on the mantle •Plate tectonics are constantly moving either •Away from one another (Divergent) •Slipping past one another (Transform) •Colliding into each other (Convergent) PARTS OF THE GEOSPHERE • A fault is a fracture or break in the Earth’s crust due to plate movement. • The vibrations that occur during plate movement is felt as an earthquake! RING OF FIRE – IS THERE A SIMILARITY BETWEEN THIS AND MAP OF TECTONIC PLATES? PARTS OF THE GEOSPHERE - EARTHQUAKES • Earthquakes are measured by their magnitude, or how much energy they release. • The Richter scale is used to measure earthquakes’ magnitudes. PARTS OF THE GEOSPHERE • A volcano is a mountain built from magma. • Magma is melted rock that is underground. • Volcanoes are typically found near tectonic plates, either on land or in the ocean, where they eventually turn into islands. • http://www.snopes.com/photos/natural/maiken.asp EFFECTS ON THE PLANET Earthquakes can do millions of dollars in damage to cities and infrastructures (roadways) Volcanic eruptions can damage surrounding areas and can cause human loss Hot ash can hurt buildings, bury crops and damage car engines and people if inhaled Volcanic eruptions can change global climate due to blocking sunlight!