* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Measles, Mumps and Rubella
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
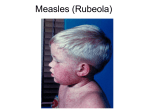
Measles, Mumps and Rubella Ruth Carrico PhD RN FSHEA CIC Associate Professor Division of Infectious Diseases University of Louisville [email protected] Reported Cases of Measles, Mumps, Rubella in the US during 2011 Rubella: 4 Measles: 220 Mumps: 404 Summary of Notifiable Diseases. MMWR 2013;60(53):1-120 Rubella Rubella • • • • • • • Name derived from a Latin term meaning “little red” Also known as German Measles or 3-day Measles Acute viral illness causing fever and rash Rash [maculopapular] and fever last 2-3 days Transmission via respiratory droplets Incubation period of 17 days [range 12-23 days] Most infectious when rash erupting; can shed virus 7 days before to 7 days after rash onset • Most concerning impact is when infection occurs during pregnancy Measles • • • • RNA virus; Paramyxovirus Highly contagious viral illness Systemic infection Airborne transmission with the viral particles being rapidly inactivated by heat and light. Survival time <2 hrs on objects and surfaces • Preferential toward winter season Measles, United States, January – June 17, 2011 Source of Importations WHO Region Total number of cases Countries Genotype Identified African 2 Kenya (1), Nigeria (1) B3 (2) Eastern Mediterranean 2 Pakistan (1), Jordan (1) D4 (1) European 25 France (12), Italy (4), Poland (1), Romania (1), Spain (1), United Kingdom (4), France/United Kingdom*(1), France/Italy/Spain/Germany *(1) D4 (11), G3 (1) Americas 1 Dominican Republic†(1) D4 (1) South-East Asia 16 India (15), Indonesia (1) D8 (5), D4 (1) Western Pacific 7 China (2), Philippines (4), Philippines/Vietnam/Singapore /Malaysia*(1) H1 (1), D9 (2) 70% of importations among U.S. residents traveling abroad *Patient visited more than 1 country during the incubation period † Likely acquired disease from French tourist Measles – Outbreak 2011 MMWR May 24, 2011 Measles – Outbreak 2011 MMWR May 24, 2011 Measles • Incubation period 10-12 days [range 7-18 days] • Prodrome includes fever of 103 or higher • Cough, chorya, conjunctivitis • Rash is maculopapular lasting 5-4 days • 30% or more who have the disease will have complications Mumps Mumps • Viral illness caused by a paramyxovirus • Classic symptoms include parotitis in about 50% (unilater or bilateral) developing 16-18 day after exposure • Nonspecific symptoms (myalgia, malaise, anorexia, fever may precede parotitis. • 15-20% of infections are asymptomatic • Incubation period 16-18 days [range 12-25 days]. • Most infectious 1-2 days before until 5 days after parotitis Mumps • Virus replicates in upper respiratory tract • Droplet transmission as well as contact with respiratory secretions, saliva or items contaminated with those fluids • Severe complications are rare, but adults have higher risk of meningoencephalitis than do children • Males may experience orchitis in up to 30-40% of those infected Measles-Mumps-Rubella Vaccine (MMR) • Contains live attenuated viruses • 1-dose efficacy varies from 80% (mumps) to 95% (measles and rubella) • Duration of immunity probably lifelong • Schedule is 2 doses, 28 days apart • All adults born in 1957 or later should have documentation of 2 doses (or other evidence of immunity) Vaccine uses a diluent Given subcutaneously in the upper arm Adults at High Risk for Measles • • • • College students Those living in crowded or congregate settings International travelers Healthcare personnel MMR Vaccine Contraindications • Severe allergic reaction to vaccine component or following prior dose • Pregnancy • Those indicating that pregnancy within the next 4 weeks is likely • Immunosuppression (severe) MMR Adverse Reactions Fever Rash Joint Symptoms Thrombocytopenia Parotitis Deafness Encephalopathy 5-15% 5% 25% 1/30,000 doses Rare Rare 1/1,000,000 doses Addressing a Low Incidence Disease • Remember why it is low incidence • Identify high risk populations for acquisition and transmission • Determine populations with opportunity to aid in transmission or be impacted by the disease