* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2. Exanthema
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
2015–16 Zika virus epidemic wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
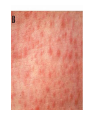
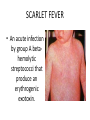
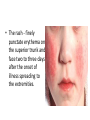
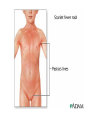
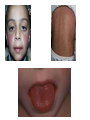
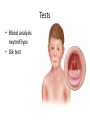
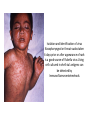
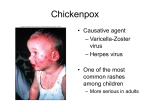
TASHKENT MEDICAL ACADEMY Infectious and children infectious diseases department Theme: Early and Comparative diagnosis of diseases with the syndrome of exanthema Lecturer: •Exanthema –rashes on the skin •Identification of Primary Skin Lesions MACULE • Circumscribed area of change in normal skin color, with no skin elevation or depression; may be any size PAPULE • Solid, raised lesion up to 0.5 cm in greatest diameter NODULE • Similar to papule but located deeper in the dermis or subcutaneous tissue; differentiated from papule by palpability and depth, rather than size PLAQUE • Elevation of skin occupying a relatively large area in relation to height; often formed by confluence of papules VESICLE • Circumscribed, elevated, fluidcontaining lesion less than 0.5 cm in greatest diameter; may be intraepidermal or subepidermal in origin BULLA • Same as vesicle, except lesion is more than 0.5 cm in greatest diameter Measles Measles an infectious viral disease causing fever and a red rash on the skin, typically occurring in childhood. • Symptoms • • • • • Bloodshot eyes Cougf &fever Light sensitivity (photophobiya) Muscle pain & rash Usually appears 3-5 days after the first signs of being sick • May last 4-7 days • Usually starts on the head and spreads to the other areas , moving down the body • Rash may appear as flat,discolored areas(macules)and solid,red,raised areas(papules)that later join together • Itchy • Redness and irritation of the eyes(conjunctivitis) • Runny nose • Sore throat • Tiny white spots inside the mouth (Koplik’s spots) Tests&diagnosis • Measles serology • Viral culture (rarely done) Treatment • • • • Acetaminophen(tylenol) Bed rest Humidified air There is no specific treatment for the measles. SCARLET FEVER • An acute infection by group A betahemolytic streptococci that produce an erythrogenic exotoxin. • The rash - finely punctate erythema on the superior trunk and face two to three days after the onset of illness spreading to the extremities. • White, with red, swollen papillae (white strawberry tongue). By the fourth or fifth day, it becomes bright red (red strawberry tongue). Tests • Blood analysis neytrofilyos • Dik test Treatment • Penicillin • Tetracycline • Bed rest Rubella • Rubella Rubella (German measles) is a disease caused by the rubella virus. Rubella is usually a mild illness. Most people who have had rubella or the vaccine are protected against the virus for the rest of their lives. • Rubella is also called as 3 day Measles or German Measles. Family – Togaviridae Genus Rubivirus In general belong to Togavirus group– RNA virus Diameter 50 – 70 nm Enveloped Spherical Virus carry hemagglutinin Virus multiply in the cytoplasam of infected cell. • begins around the fourth febrile day, with discrete lesions spreading from the hairline downward, sparing the palms and soles. • : Koplik's spots in the oral mucosa. • The exanthema: lasting four to six days, fading gradually in order of appearance, leaving a residual faint desquamation. Isolation and Identification of virus Nasopharyngeal or throat swabs taken 6 days prior or after appearance of rash is a good source of Rubella virus Using cell cultured in shell vial antigens can be detected by Immunofluresecentetmehods Tests • Serology In Rubella Hemagglutination inhibition test for Rubella is of Diagnostic significance ELISA tests are greater importance A raise in Antibody titers must be demonostrated between two serum samples taken at least 10 days apart. Or Detection of Rubella specific IgM must be detected in a single specimen. Treatment • No specific treatment or Antiviral treatment is indicated. • However Laboratory proved and clinically missed Rubella in the Ist 3-4 months of pregnancy is associated with fetal infections. Meningococcemia • NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS (MENINGOCOCCUS) • Gram Stain - Negative • Anaerobic - CO2 enhances growth • Extracellular • Features - diplococci - “coffee bean” or “kidney bean” appearance • Colonies - small, transparent on chocolate agar Thank You…