* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio 20-Cellular Respiration Assignment Part A
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
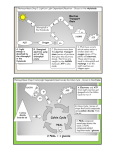
Bio 20-Cellular Respiration Assignment Part A-Multiple Choice 1. /34 The greatest amount of energy is released by the a. Oxidation of glucose to lactic acid b. Conversion of carbon dioxide and water to glucose c. Oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide and water d. Conversion of glucose to pyruvate 2. In aerobic respiration, the final hydrogen (electron) acceptor is a. Coenzyme A b. Water c. Molecular oxygen d. Carbon dioxide 3. Pyruvic acid must be converted to __________ before it can enter the Kreb’s cycle a. Lactic acid b. Acetyl coenzyme A c. Ketoglutaric acid d. NADH 4. The total amount of ATP formed by aerobic respiration is a. 2 ATP b. 32 ATP c. 4 ATP d. 36 ATP 5. Aerobic respiration involves the process(es) of a. Glycolysis b. Electron transport chain c. Kreb’s cycle d. All of the above 6. Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration a. Use carbon dioxide as a raw material (reactant) b. Liberate energy from glucose c. Liberate carbon dioxide and oxygen d. Form ATP through the ETC 7. Glycolysis takes place in the ____________ of the cells a. Mitochondrial matrix b. Mitochondrial cristae c. Nucleus d. Cytoplasm 8. The carbon containing compounds formed at the end of glycolysis are two molecules of: a. Citric acid b. Carbon dioxide c. Pyruvate d. Lactic acid 9. Muscle fatigue and cramps are caused by an acculumation of a. ADP b. Lactic acid c. Citric acid d. Pyruvate 10. Which of the following parts of the cell is the site of most respiratory enzymes? a. Cell membrane b. Nucleus c. Endoplasmic reticulum d. Mitochondria 11. During energy transfer, hydrogen and its electrons move from a. ATP to FADH2 in the electron transport chain b. NADH to ATP in the electron transport chain c. Strong to progressively weaker electron acceptors in the electron transport chain d. Weak to progressively stronger electron acceptors in the electron transport chain 12. ATP is formed during energy transfer whne a. FADH2 and coenzyme A are formed b. Energy is released as electrons are transferred to various electron acceptors c. NADH is formed d. Hydrogen is added to oxygen to produce water Part B-Written Response 1. Identify the stage of cellular respiration which is made up of a series of electron acceptors. State two main functions of this stage. (3) 2. Explain the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. (4) 3. Which culture would produce the greatest amount of ATP? Explain why. Give reasons why the culture you selected would produce more ATP than each of the other three cultures. (4) 4. Identify the stage of cellular respiration where carbon dioxide is given off. State one main function of this stage and where it is located within the cell. (3) 5. Compare respiration and photosynthesis by stating yes or no to the following statements. (4) Characteristic ATP produced during reaction Oxidation Reaction Oxygen is a product Occurs in plant cells Photosynthesis Respiration