* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Packet
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
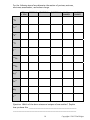
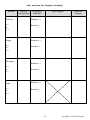
*STUDENT* *STUDENT* Regents Chemistry PRACTICE PACKET Unit 2: Atomic Theory 2 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Name ____________________________ History of Atomic Theory Period _______ Fill in the missing information in the chart below: Name of Researcher Equipment/ Experiment Sketch of Model Major Idea/Discovery N/A All atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties N/A Electrons travel around the nucleus in welldefined paths called orbits (like planets in a solar system) Thomson Rutherford Electrons have distinct amounts of energy and move in areas called orbitals Developed after the famous discovery that energy can behave as both waves & particles N/A 3 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 4 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 5 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Atomic Structure Worksheet **Assume all are neutral atoms! Fill in the blanks in the following worksheet. Please keep in mind that the isotope represented by each space may NOT be the most common isotope or the one closest in atomic mass to the value on the periodic table. Atomic symbol C Atomic number Protons Neutrons Electrons Mass number 8 12 24 31 40 40 30 89 35 42 98 W 183 105 95 71 243 Cr 27 83 209 90 142 Md 259 Se 80 40 51 Notice there are two different atoms of zirconium (Zr) listed. These different versions are called ISOTOPES. What one subatomic particle is different from one isotope to the other? __________________________________ 6 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Atomic Theory- Neutral Atoms and their subatomic parts **IMPORTANT**If the mass number is not given to you, round the atomic mass that you find on the Periodic Table for that element. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are present in the following neutral atoms? vanadium potassium P= N= e= nitrogen platinum argon helium What is the name of the element that has neutral atoms that contain: 5 protons? 16 electrons? _____________________ _____________________ 17 protons? 32 electrons? _____________________ _____________________ 25 protons? 1 electron? _____________________ _____________________ 82 protons? 8 electrons? _____________________ _____________________ 92 protons? 2 electrons? _____________________ _____________________ 7 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Complete the following chart: (assume the overall charge on all atoms = 0….except the last one!) Element Symbol Atomic Number # of Protons Hydrogen # of Neutrons Mass Number (amu) 1 He 4 Na 12 Potassium 39 20 20 26 30 Rb 86 Carbon 6 Xenon 131 16 At 15 126 14 Copper 7 64 Ne 10 23 Lithium Ion # of Electrons Li+ 27 3 8 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos P, n, e of ions **IMPORTANT**If the mass number is not given to you, round the atomic mass that you find on the Periodic Table for that element. Write the full chemical symbol for the ion with: 1) 12 protons and 10 electrons: P= N= e= 2) 74 protons and 68 electrons: 3) 95 protons and 89 electrons: 4) 33 protons and 36 electrons: Determine the number of p, n, e for the following ions: Cu2+ Li+ O2- Al3+ I7+ p= n= e= Cl- # protons Lithium1+ # electrons # neutrons 3 Phosphorus3- 18 31 23 Krypton0 Uranium5- Mass # 4 Vanadium0 Barium4+ Atomic # 48 56 51 36 137 97 146 9 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos For the following atoms/ions determine the number of protons, neutrons, electrons, mass number, and nuclear charge. ATOM or ION? PROTONS NEUTRONS ELECTRONS MASS NUMBER NUCLEAR CHARGE 15 N Cu+2 8 +3 B 17 O F-1 206 Pb 208 Pb Ag+1 Zn+2 Mg S-2 Question: Which of the above atoms are isotopes of one another? Explain how you know this. ___________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ 10 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos ATOM or ION? PROTONS NEUTRONS ELECTRONS MASS NUMBER NUCLEAR CHARGE Al+3 37 Cl 23 Na+1 He 15 O-2 14 C C Au+3 U 222 Rn Cu+1 Cu+2 Question: Which of the above atoms are isotopes of one another? Explain how you know this. ___________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ 11 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Calculate the atomic mass of each of the following isotopes. SHOW ALL WORK. Element Mass Percent Abundance 1) copper-63 copper-65 62.9396 amu 64.9278 amu 69.17% 30.83% 2) uranium-235 uranium-238 235.0439 amu 238.0510 amu 0.72% 99.28% 3) hydrogen-1 hydrogen-2 1.0078 amu 2.0140 amu 99.985% 0.015% 4) element Q-8 element Q-9 element Q-10 8.0 amu 9.0 amu 10.0 amu 10.0% 20.0% 70.0% 12 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Weighted Averages HW (SHOW ALL WORK!) Name _____________________ *You can round the masses given to you or use them as given – just be consistent! 1) Element X exists in three isotopic forms. The isotopic mixture consists of 10.0% 10X, 20.0% 11X, and 70.0% 12X. What is the average atomic mass of this element? 2) Element Y exists in three isotopic forms. The Isotopic mixture consists of 15.0% 21X, 65.0% 22X, and 20.0% 23X. That is the average atomic mass of this element? 3) A mystery element occurs in nature as two isotopes. Isotope A has a mass of 10.0130 amu and its abundance is 19.9%; Isotope B has a mass of 11.0093 amu and its abundance is 80.1%. From this data, calculate the atomic mass of the element and show all work. Lastly, identify the element. 4) A mystery element occurs in nature as two isotopes. Isotope A has a mass of 62.939598 amu and its abundance is 69.17%; Isotope B has a mass of 64.927793 amu and its abundance is 30.83%. From this data, calculate the atomic mass of the element and show all work. Lastly, identify the element. 13 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 5) A mystery element occurs in nature as three isotopes. Isotope A has a mass of 15.994915 amu and its abundance is 99.762%; Isotope B has a mass of 16.999132 amu and its abundance is 0.0380%; Isotope C has a mass of 17.999160 amu and its abundance is 0.2000%. From this data, calculate the atomic mass of the element and show all work. Lastly, identify the element. Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass Example: A sample of cesium is 75% 133Cs, 20% the average atomic mass? 132 Cs, and 5% 134 Cs. What is Determine the average atomic mass of the following mixtures of isotopes. 1. 80% 127 I, 17% 126I, 3% 128I 2. 50% 197 Au, 50% 198Au 14 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 3. 15% 55 56 Fe, 85% Fe 4. 99% 1H, 0.8% 2H, 0.2% 3H 5. 95% 14 N, 3% 15 N, 2% 16 N 6. 98% 12C, 2% 14C 15 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Regents Chemistry Name _________________________ Principal Energy Level Worksheet Element Carbon e-configuration 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ Helium 1s __ Neon 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ Oxygen 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ Sulfur 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ 3s __ 3p __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ Aluminum 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ 3s __ 3p __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ Sodium 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ 3s __ 3p __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ Lithium 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ 16 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Calcium 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ 3s __ 3p __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ 4s __ 4p __ __ __ 4d __ __ __ __ __ 4f __ __ __ __ __ __ __ Fluorine 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ Chlorine 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ 3s __ 3p __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ Hydrogen 1s __ Magnesium 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ 3s __ 3p __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ Tin 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ 3s __ 3p __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ 4s __ 4p __ __ __ 4d __ __ __ __ __ 4f __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 5s __ 5p __ __ __ 5d __ __ __ __ __ 5f __ __ __ __ __ __ __ Potassium 1s __ 2s __ 2p __ __ __ 3s __ 3p __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ 4s __ 4p __ __ __ 4d __ __ __ __ __ 4f __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 17 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Construct Bohr diagrams for the following: Na electron configuration ___________ F O electron configuration ___________ Li + electron configuration ___________ Cl- electron configuration ___________ Ne electron configuration ___________ 18 electron configuration ___________ Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 19 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 20 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 21 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Draw Lewis Dot Diagrams for the following: Charge ____ # Valence e- ____ N Charge ____ # Valence e- ____ C # unpaired valence e- ____ # of bonds _____ # unpaired valence e- ____ # of bonds _____ Charge ____ # Valence e- ____ Charge ____ # Valence e- ____ Li+ He # unpaired valence e- ____ # of bonds _____ # unpaired valence e- ____ # of bonds _____ Charge ____ # Valence e- ____ Charge ____ # Valence e- ____ O B # unpaired valence e- ____ # of bonds _____ # unpaired valence e- ____ # of bonds _____ Charge ____ # Valence e- ____ Charge ____ # Valence e- ____ S Kr # unpaired valence e- ____ # of bonds _____ # unpaired valence e- ____ # of bonds _____ Charge ____ # Valence e- ____ Charge ____ # Valence e- ____ Se2- # unpaired valence e- ____ # of bonds _____ Ca+2 # unpaired valence e- ____ # of bonds _____ 22 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Bohr and Lewis Dot Diagrams Element Carbon p= n= e= Oxygen p= n= e= Sodium Electron Configuration # Valence e# Kernel e- Lewis Dot Diagram Valence e- = Kernel e- = Valence e- = Kernel e- = Valence e- = p= n= e= Kernel e- = Neon Valence e- = p= n= e= Bohr Diagram Kernel e- = 23 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Bohr and Lewis Dot Diagrams (continued) Element Fluorine p= n= e= Argon p= n= e= Nitrogen Electron Configuration # Valence e# Kernel e- Lewis Dot Diagram Valence e- = Kernel e- = Valence e- = Kernel e- = Valence e- = p= n= e= Kernel e- = Lead Valence e- = p= n= e= Bohr Diagram Kernel e- = 24 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 25 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 26 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 27 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 28 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 29 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos Regents Chemistry Electron Configuration Worksheet Name _________________________ Period ____ For the questions 1-10, assume all atoms are neutral. Use the electron configurations to determine the identity of the element and whether it is in the ground or excited state. Electron Configuration 1. 2-8-1 2. 2-8-16-3 3. 2-8-2 4. 2-7-8 5. 1-3 6. 2-8-6 7. -18-32-18-4 8. -18-32-17-3 9. 2-7 10. 1-8 Identity Ground/Excited Give an electron configuration for the following: 11. Sulfur in its ground state. 12. Helium in an excited state. 13. Give the ground state electron configuration for calcium. _____________________ 14. Give the correct electron configuration for the Ca+2 ion. ______________________ 15. How many valence electrons are there in atom of bromine? ________ 16. How many valence electrons are there in a Cl- ion? ________ 17. How many kernel electrons are there in a phosphorus atom? ________ 18. How many valence electrons are there in a neon atom? ________ 19. How many principal energy levels are there in a iron atom? ________ 30 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 20. When atoms of an element are emitting a certain wavelength (or color) of light, it means that a) the atoms have gained energy and electrons have jumped to an excited state. b) the atoms have gained energy and electrons have fallen back to the ground state. c) the atoms have lost energy and electrons have fallen back to the ground state. d) the atoms have lost energy and electrons have jumped to an excited state. Use the emissions spectra results below to answer questions 14 and 15: Gas A Gas B Gas C Gas D Unknown Gas 21. According to these experimental spectra results, the unknown gas is a mixture of which gases? ___________ 22. The lines on the visible light spectrum for the gases above represent a) electrons jumping to the same excited state or energy level. b) electrons falling back down to their ground state from the same energy level. c) electrons jumping to multiple excited states or energy levels. d) electrons falling back down to their ground state from multiple energy levels. 23. How do the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? a) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. b) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is farther from the nucleus. c) In the third shell, an electron has less energy and is closer to the nucleus. d) In the third shell, an electron has less energy and is farther from the nucleus. 24. An atom of oxygen is in an excited state. When an electron in this atom moves from the third shell to the second shell, energy is Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos 31 a) b) c) d) emitted by the nucleus absorbed by the nucleus emitted by the electron absorbed by the electron 25. Which electron configuration could represent a strontium atom in an excited state? a) 2–8–18–7–1 b) 2–8–18–8–1 c) 2–8–18–7–3 d) 2–8–18–8–2 26. Imagine an emission spectrum produced by a container of hydrogen gas. Changing the amount of hydrogen in the container will change the colors of the lines in the spectrum. a) True b) False 27. In the previous question, changing the gas in the container from hydrogen to helium will change the colors of the lines occurring in the spectrum. a) True b) False 28. An absorption spectrum appears as a continuous spectrum interrupted by a series of dark lines. a) True b) False 29. Emission spectra are characterized by narrow bright lines of different colors. a) True b) False 32 Copyright © 2015 Tim Dolgos