* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bone Diversity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
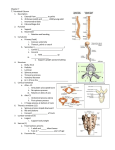
Bone Diversity Dr. Anderson GCIT Bone Diversity • There are normally 206 bones in the adult human body • Each bone is derived from connective tissue and grows to articulate with other bones to form the functional human skeleton The Axial Skeleton • Composed of the skull, vertebrae, ribs (thoracic cage) and coccyx The Skull • Cranium – Made of multiple bones that are immovable (as adult) and connect in sutures, houses the brain Cranium – Frontal Bone (#1) • Shell-shaped frontal bone, anterior to parietal (coronal) sutures • Makes up superior wall of orbits Cranium – Parietal Bone (#2) • Form most of the superior and lateral aspects of the skull and articulate with other skull bones Cranium - Occipital Bone (#4) • Forms most of the skull’s posterior walls and base • Foramen magnum occurs in the inferior surface of this bone, allowing the spinal cord to pass through Cranium - Temporal Bone (#3) • Inferior to parietal bones (3 regions) – Squamous region • Produces the zygomatic process anteriorly to meet the zygomatic bone (makes up the “cheekbone”) and contains the mandibular fossa (meets the mandible to articulate the lower jaw) – Tympanic Region • Contains acoustic meatus and styloid process – Mastoid region • Exhibits mastoid process (anchors some neck musculature) and has the stylomastoid foramen (allows cranial nerve VII to exit the skull) Cranium - Temporal Bone (#3) (con’d) Cranium - Sphenoid Bone (#5) • Very complex, but articulates with almost all other bones – Spans the width of the middle cranial fossa Cranium - Sphenoid Bone (#5) (con’d) Cranium - Sphenoid Bone (#5) - con’d • Openings in sphenoid include – Optic canals – anterior to the sella turcica, allow cranial nerves to pass to the eyes – Superior Orbital Fissure • Allows cranial nerves that control eye movements to exit Facial Bones - Mandible • Lower Jawbone – articulates with mandibular fossa (on temporal bone) • Two main parts – Body (chin) – Ramus (vertical part) Maxillary Bones • Bilateral maxillary bones are fused medially – form the upper jaw and the central part of the face Smaller Facial Bones (pg 213) • • • • • Zygomatic bones – form cheek bones Nasal Bones – forms bridge of nose Lacrimal Bones – medial orbit walls Palatine Bones – posterior part of hard palate Inferior nasal conchae – lateral walls of nasal cavity All of the Aforementioned Bones are Summarized on pp. 214-215 The Vertebral Column • Consists of 33 irregular (in shape) bones • Segmentation = flexibility! • Prone to damage under heavy and/or chronic forces Vertebral Function • Transmits force from upper body to legs • Houses and protects the spinal cord • Attachment points for ribs, and for muscles/ ligaments of the back and neck Spinal Divisions • 7 cervical (neck) vertebrae • 12 Thoracic vertebrae • 5 Lumbar vertebrae • 5 Sacral (fused) vertebrae • 4 Vertebrae in Coccyx Scoliosis • Abnormal curvature of the spine • Leads to gait problems, pain and disability, breathing difficulties • Can be corrected early by bracing, in extreme cases- surgery Spinal Arrangement • Alternating arrangement of vertebrae and discs • Peripheral nerves from spinal cord extend from each vertebral “level” Intervertebral Discs • Serves as a shock absorber between vertebrae- composed of collagen and fibrocartilage • Composed of 2 layers – Inner, gel-like layer (nucleus pulposus) – Annulus fibrosus – tough outer covering that resists compression Herniated Discs • Injury leads to rupture of the anulus fibrosis leading to a “bulge” which may press on the spinal nerves causing intense pain, numbness or loss of motor fuction Vertebra (Dorsal View) • Centrum bears the weight of the body (interspersed by discs) • Spinal cord passes through the vertebral foramen • Spinous process and transverse process are for muscle attachment Vertebral Names • Cervical Vertebrae (C1-C7) • Thoracic Vertebrae (T1-T12) • Lumbar Vertebrae (L1-L5) • Sacral Vertebrae (S1-S5) Superior-Inferior Changes • Centra of each vertebrae tend to thicken inferiorly • Vertebral foramen narrows inferiorly • No rib articulation past T12 The Thoracic (Rib) Cage • Roughly cone-shaped • Protects the heart, lungs • Provides a solid foundation for muscles to pull and push against for inhalation and exhalation Sternum • Articulates with the costal cartilages of the ribs (anteriorly) Ribs • Serve to protect the organs of the thoracic cavity (heart, lungs) • 12 pairs (in both genders) – 7 pairs are “true” ribs that articulate directly with sternum – 5 pairs are “false” ribs that articulate indirectly with the sternum Posterior Rib Articulation Appendicular Skeleton • Peripheral to axial skeleton • Includes limb bones (arms and legs) and pelvic a shoulder girdles Shoulder (Pectoral) Girdle • Attach upper limbs to the axial skeleton • Major bones – Scapula (shoulder blade) • Posterior aspect – Clavicle (collar bone) • Anterior aspect Scapula • Bilateral and posterior • Does NOT articulate directly with the axial skeleton – held in place by muscles – This articulation allows for flexibility at the cost of stability Scapula - Anatomy • Triangular bone • Notable features – Glenoid cavity (fossa) articulates with the humerus on lateral border Upper Limb (Arm) Bones • Humerus – Upper Arm • Radius, Ulna – Forearm • Carpal bones – wrists • Metacarpals – palm • Phalanges - Fingers Ulna • Forms elbow joint with humerus • Longer forearm bone (on pinky side), thicker proximally • Notable features – Olecranon (elbow) – Coronoid Process – Trochlear notch Grips trochlea of humerus, forming articulation proximally – Distal head (forms articulation with wrist) Radius • Thicker distally • Notable features – Proximal head – articulates with capitulum of humerus – Radial tuberosity – provides attachment for bicep – Styloid process – provides attachment for wrist ligament Proximal Distal Ulna – Detailed Structure The Hand • Carpals – (8 bones total) • Metacarpals (5 bones) labeled 1-5 (thumb to pinky) • Phalanges – multiple bones each – Two in thumb – Three in all other fingers • Distal, middle, proximal The Hand The Pelvic (Hip) Girdle • Attaches lower limbs to the axial skeleton • More stable but less flexible than shoulder girdle • “Pelvis” is actually three separate bones Pelvic Function • Attaches lower appendicular skeleton to the axial skeleton • Firmly attached with ligaments • Provides a strong foundation for femur articulation and muscle attachment Pelvic Bones • 3 main parts – Ilium (superior) – Ischium (inferior and posterior) – Pubis (inferior and anterior) • The acetabulum (hip socket) is where all three hip bones fuse and where the femur articulates Medial view Lateral view Ischium and Pubis • Ischium – Ischial tuberosity • Bears all weight when sitting • Pubis – Forms anterior part of hip bone – Pubic symphysis (cartilaginous disc connects pubic bones medially) Gender Differences in Pelvic Anatomy • What are the major differences in hip morphology between men and women? The Lower Limb (Leg) Bones • • • • • • Femur – thigh bone Tibia – shin bone 1 Fibula – shin bone 2 Tarsals – ankle bones Metatarsals – foot bones Phalanges - toes Femur • Largest and strongest bone in the body • Transfers all weight from the pelvis to the legs Tibia • Tibia transmits weight of femur to the foot – Lateral and medial condyle articulate with femur (proximal end) • Medial malleolus (distal end) – “bulge” on inside of ankle Fibula • Primarily for muscle attachment – Does not bear weight • Lateral Malleolus – “Outside” bump of ankle Ankle and Foot Bones • Tarsals – ankle bones • Metatarsals – proximal foot bones – Calcaneus – heel bone • Phalanges - Toes