* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Systems - Net Start Class
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
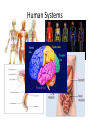
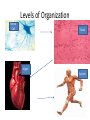
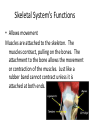
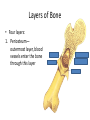
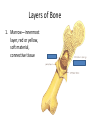
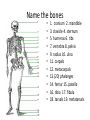
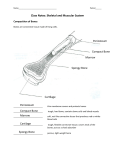
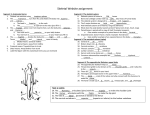
Human Systems Create Flow Chart Graphic Organizer Levels of Organization Nerve Cell Tissue organ System Heading Notes Meanings Questions Main ideas Vocabulary Copy this diagram in your notebooks. This is called Cornell Notes Summary Cell •Are all cells the same? •Unicellular or multicellular • Basic unit of structure and function • Carries on life functions • Organisms are one cell or many cells---Human has over a trillion cells • Smallest unit of organization The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living things that keeps the organism Living. Tissue Examples: Connective---blood, bone, fat, tendons, cartilage Muscle---allows body to move, moves blood and food through body Nerve- - - brain, spinal cord, senses—hear, smell, think Epithelial—skin, line digestive system •Group of similar cells doing the same job •Four types of tissue a. Connective 1. provides support 2. connects all parts of body to each other b. Muscle 1. provides movement 2. contract c. Nerve 1. directs and controls body 2. carries impulses between brain and rest of body d. Epithelial 1. covers surfaces of body—inside and out 2. Protects 3. Releases chemicals You write a summary of this slide Possible Example: Tissue is the second level of organization. There are four basic types of tissues that do different jobs, connective, muscle, nerve and epithelial. Organ •3rd level of organization Composed of different tissues working together to perform a specific function. cell tissue organ Example: Heart—pumps blood, Made up of nerve tissue, muscle tissue, connective tissue and epithelial tissue Stomach-churns and mixes food and digestive juices. Made up of smooth muscle tissue, nerve tissue, epithelial tissue Write a summary Possible summary: The third level of organization is the organ which is composed of different kinds of tissues working together to perform a function. Organ System Group of different organs working together to accomplish a specific task •Fourth level of organization Examples: Circulatory system—heart-artery-vein-capillaries Digestive system-contains organs like esophagusstomach-small intestine-large intestine Skeletal System-206 different organs (bones) like the femur-patella-cranium-ribs-phalanges Muscular System- over 600 different organs (muscles) like the triceps-biceps-pectorals Nervous System-brain-peripheral nerves-spinal cord Write your summary Possible summary: The fourth level of organization is the organ system. The organ system consists of different organs working together to perform a task. For example, the digestive system is made up of organs like the stomach, small intestine, pancreas etc. that break down food for absorption by the body. Organ System Skeletal System Background Bones-made from elements phosphorus and calcium 206 bones in average human. Newborns have more (some have not fused yet!) Smallest bones are in the ear—Hammer, anvil, and stirrup Largest bone is the femur (thigh bone) Skeletal System’s Functions 5 major functions 1. Shape and support unique structure for each organism-skeleton provides the framework while supporting the body and the organs within Skeletal System’s Functions • Allows movement Muscles are attached to the skeleton. The muscles contract, pulling on the bones. The attachment to the bone allows the movement or contraction of the muscles. Just like a rubber band cannot contract unless it is attached at both ends. Skeletal System’s Functions • Protects • Bones have a compact and a spongy layer. • Compact and spongy layers give the bones their strength and allow them to absorb forces • Bones surround the chest cavity (rib cage), cranium surrounds the soft tissues of the brain Skeletal System’s Functions • Produces blood cells • Certain bones, like the femur, have central layer called red marrow • Red marrow produces blood cells for the body Skeletal System’s Functions • Stores materials until body needs them • Certain bones have central layer called yellow marrow • Yellow marrow stores fats for energy reserves • Bones will also release phosphorus and calcium in small amounts when the body needs those minerals Layers of Bone • Four layers: 1. Periosteum— outermost layer, blood vessels enter the bone through this layer Layers of Bone 1. Compact layer— 2nd layer dense material, has canals in it that carry blood vessels and nerve cells Layers of Bone 1. Spongy layer-3rd layer, at ends of bones, has spaces within it. Makes the bones lighter while maintaining the strength Layers of Bone 1. Marrow—innermost layer, red or yellow, soft material, connective tissue Name the bones • • • • • • • • • • • 1. cranium 2. mandible 3. clavicle 4. sternum 5. humerus 6. ribs 7. vertebra 8. pelvis 9. radius 10. ulna 11. carpals 12. metacarpals 13.(20) phalanges 14. femur 15. patella 16. tibia 17. fibula 18. tarsals 19. metatarsals Skeleton Across 2.upper arm 5.Backbone 7.Palm 9.Ribs 11. Collarbone 13. Skull 16. hips 17. shoulder blade Down 1. breastbone 3. Arch 4. Thigh 6. Ankle 8. Lower leg large bone 9. lower arm near thumb 10. Lower arm near little finger 12. Kneecap 13. Wrist 14. lower leg thin bone 15. toes