* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Area of Study 03
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
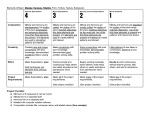
Area of Study 03: Texture and Melody “Melody” AQA GCSE Music Areas of Study • AoS 01: Rhythm and Metre • AoS 02: Harmony and Tonality • A0S 03: Texture and Melody • AoS 04: Dynamics and Timbre • AoS 05: Structure and Form Melody What is meant by Melody? • A melody is a rhythmically organised pattern of single notes arranged in succession, one after the other. In melody the notes are arranged horizontally (whereas in harmony that are arranged vertically) • Or…..THE TUNE Melody • Counter Melody – A second, less important tune to support the main melody • Pitch – how high or low the note is • Scale – a group of notes played in ascending or descending order Melody cont… • Interval – The gap in pitch between two notes Perfect Perfect • Arpeggio – Playing the notes of a chord one by one (bit like a broken chord) Conjunct, Disjunct, Triadic and Scalic • These are all different kinds of melodic note patterns. • Conjunct – notes in the melody move mainly by step (they are mostly next to each other in pitch) • Disjunct – moves mainly by leaps (big intervals between the notes) • Triadic – the melody begins by using notes that belong to the triad (of chord) e.g. C E G (C Chord) • Scalic – melody that is made up of notes that follow the order of a particular scale Different Scales • Pentatonic scale – a five note scale. Often used in Chinese, African and Celtic Folk melodies • Whole Tone Scale – a scale made up of only whole tones. E.g. C, D, E, F#, G#, A# • Chromatic Scale – scale made up of semitones • Passing notes are the notes in between the notes of the accompanying chord. • Blue notes the flattened notes in a Blues Scale. Often slide up or down to these notes. They make a piece sound ‘bluesy’. e.g. - C, Bb, G, Gb, F, Eb, C Melody Cont. • Sequence – when a tune is repeated a step higher (ascending sequence) or a step lower (descending sequence). • Pitch bend – bending the note on a guitar or any string instrument/voice or keyboard/synthesizer. Repetition • 3 Words for same meaning – just use the correct word for the style of music • Ostinato – Classical • Riff – Popular music • Loop – Electronic/technology based music Ornamentation • This is about decorating parts of the melody • Trills – 2 notes that are next to each other played rapidly • 57 seconds and beyond, shows Trills being used. • All instruments perform trills, especially in Baroque Music Video 02 • Double Stopping - Cont. – This is when ‘2 notes are played at the same time (Two strings at the same time). This is term only applies to string instruments. • 1 Min 20 Secs shows an example of Double Stopping • There is extensive use of this throughout the piece • 1 Min 8 Secs – Pizzicato, followed by staccato bowed Video 03 Tremolo • • Another string effect, means, ‘trembling’ or ‘quivering’ Rapid up-and-down movements of the bow on the strings, creating an agitated or shimmering effect • Listen and look at the opening to “Bruckner Symphony 9” • The Strings open the piece, using a Tremolo effect. Very short bowing, but very fast to capture that shimmering effect. Video 5 Glissando • Glissando (instruments)/ Portamento (voice) – ‘sliding’ between 2 notes. Track 05 Rhapsody in Blues • Listen to the Slide at the start by the Clarinet – just after the trill On the next slide, look at video of the guitar playing a melody. It focusses mainly on using Glissando’s (slides) Video 04 Video 04 Articulation • Articulation – how the notes are played: • Staccato – short, detached notes (Spikey) Staccato Non-Staccato (Legato) • Legato – notes are played attached, smoothly Legato Sometimes indicated by a ‘slur’ Played Staccato Articulation cont. • Pizzicato – Short, plucked notes on a stringed instrument • Con Arco – Simply means, use of Bow Video 01 This example shows extensive use of Pizzicato Melody Cont. • Phrase – a musical sentence (where you’d naturally take a breath). Often 2, 4 or 8 bars long. Indicated by a curved line above the stave. • Improvisation – when a player makes the music up on the spot. In jazz/blues/pop players will often improvise a solo – commonly on a guitar/sax/trumpet/keyboard.