* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Guide to Analysis of Music
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
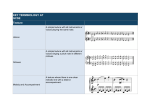
Guide to the Analysis of Music Describe what you hear in this extract in terms of relevant: Musical features: such as (but not limited to) harmony, melody, and rhythm Structural features: such as (but not limited to) form, phrases, motifs and texture Contextual features: such as (but not limited to) style, time, culture, geography and history. STEP 1 – TIMELINE (Musical features) If no score is given, indicate time using minutes and seconds. If a score is given, indicate time using measure numbers from the score. 1. MEDIUM Voices or instruments or both Type of ensemble (quartet, orchestra, etc.) Orchestration – instruments assigned to various materials Division of parts – doubling Special effects – pizzicato, tremolo, harmonics, mutes, percussion, electronics 2. METER, TEMPO, RHYTHM Duple, Triple, Simple, Compound, Complex Multimetric – different time signatures in one line of music Non-metric – no meter Tempo – fast, slow, changes (use appropriate Italian words) Rhythm – prominence of rhythmic element (ex. running 16ths, triplets) 3. HARMONY Major, Minor, Modal, Whole-tone, Pentatonic Kinds of intervals Chords structure/progression Intervals of root movement Figured bass Emphasis on different scale degrees (I, IV, V) Diatonic or Chromatic Cadence structure 4. MELODY Prominence of melodic element General Qualities / Dimension Conjunct/Disjunct Range – narrow, wide, medium Contour – wave, ascending, descending, static Phrases – long continuous lines or short motivic fragments Ornamentation – embellishments, improvisation Dynamics Text and programmatic considerations Guide to Analysis of Music cont. 5. TEXTURE Monophonic – one melody line Homophonic – Melody with chordal accompaniment Chordal Homophony Sustained chord accompaniment Repeated chord accompaniment Arpeggiated accompaniment Polyphonic – Contrapuntal movement with two or more melodic lines Number of parts Degree of melodic independence Spacing of parts Voices of parts Imitation Hybrid – combinations of homophonic and polyphonic parts Special Effects – antiphonal, responsorial, instrumental/vocal effects STEP 2 – ANALYZE (Structural features) 6. FORM Basic Internal Structure Sectional – Binary, Ternary, Rondo, etc. Variation – Theme and Variation Developmental – Sonata Allegro Form Fugal – Fugue, Motet, Madrigal Through Composed Twelve Tone / Dodecaphonic Toccata, Prelude, Fantasy, Rhapsody Number and relationship of movements Time factors – total length / length of movements STEP 3 – ANALYZE (Contextual features) 7. CONTEXT Style/Genre Historical era Historical context Nationality / culture Sacred / Secular Socio / religious / political / economic implications