* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is the basis for biological evolution and geolog
Survey
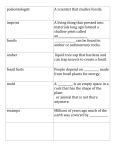
Document related concepts
Transcript
Science Friday to Monday - WOOOOOOOHOOOOOO! December 9 & 12, 2011 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? On your desk: • Paper • Pencil Everything else in the floor! 1 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? 1. In Scenario 1, which beak do you think should be the most adapted to the environment? Why? 2. Based on your observations, which beak was the most adapted to the environment? 3. Did your answer in #1 match your answer in #2? IF it did not, explain. 4. In Scenario 2, which beak do you think should be the most adapted to the environment? Why? 5. Based on your observations, which beak was the most adapted to the environment? 6. Did your answer in #4 match your answer in #5? IF it did not, explain. 7. In Scenario 3, which beak do you think should be the most adapted to the environment? Why? 8. Based on your observations, which beak was the most adapted to the environment? 9. Did your answer in #7 match your answer in #8? IF it did not, explain. 10. What other factors can influence which "Fork Bird" ate the most berry? 11. What Explain what "survival of the fittest" means. 2 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? Answer the following questions from the video. Please copy the question and write complete answers. Be prepared to turn the questions in Monday! 1. Define Geological time theory. 2. Define Plate Tectonics. 3. Define Continental Drift and who developed the theory. 4. Explain how Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics are related to one another. 5. Draw a diagram of plate boundaries that collide and label it. State what type of boundary. 6. Draw a diagram of plate boundaries that expand and label it. State what type of boundary. 7. Draw a diagram of plate boundaries that slide past one another and label it. State what type of boundary. 8. What are some threats to humans, as a result of how the planet behaves? Discuss in detail. 9. Which threat do you think is the greatest threat to us in the United States? 10. What causes the plates to move? 11. Draw a diagram of a convection cell. 12. Draw a diagram of a hot spot, explain how they move. 13. How does the Earth "eat" its crust and recycle it? 14. Draw a diagram of an oceanic ridge. Show where new lava would be located, new rock and older rock. 15. Label the parts of the earth in the diagram below. Include Inner Core, Outer Core, Mantle, Asthenosphere, Lithosphere, Oceanic Crust, and Continental Crust 1 7 2 6 3 4 5 3 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? • Fossils • Most fossils form when living things die and are buried by sediments. The sediments slowly harden into rock and preserve the shapes of the organisms. • Usually found in sedimentary rock - a type or rock that is made of hardened sediment. • Steps to forming a fossil 4 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? Fossils found in rock include: • molds and casts • petrified • carbon films • trace • Other fossils form when the remains of organisms are preserved in substances such as tar, amber, or ice. Molds and Casts • Mold is the hollow area in sediment in the shape of an organism. Forms when the hard part of an animal is buried in sediment. • Water carrying dissolved minerals and sediment fill the empty space and the water will deposit the minerals and form the cast. 5 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? Petrified Fossils • means turned to stone • minerals replace all or part of an organism • formed when sediment covered wood • water rich in dissolved minerals seeped into spaces in the plant's cells • over time the minerals come out of solution and harden, filling in all the spaces • original wood remains, but the minerals have hardened it 6 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? Carbon Films • extremely thin coating of carbon on a rock • when sediment buries an organism, some of the materials that make up the organism evaporate, or become gases • gas escapes leaving only the carbon behind. • eventually only a thin film of carbon is left 7 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? Trace Fossils • only provide evidence that an animal existed • fossilized foot prints • an animal will leave a footprint in mud or sand. that footprint stays and is covered with layers of sediment. • over time the sediment will be come rock preserving the foot print for millions of years • important fossil because they allow us to answer questions about the size and behavior of an animal, how they walked, how they hunted, migration patterns and even if an animal sat down or stood upright all the time • a tail or burrow gives clues about the size and shape of an organism 8 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? Preserved Remains: • Some processes preserve the remains of an organism with little or no change. • Some remains are preserved in tar • Rancho La Brea Tar Pits • Tar soaks into their bones, preserving the bone from decay • Amber is another substance that keeps animals from decaying • Amber is resin or sap from a tree that will encase the animal • Freezing can also preserve remains 9 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? • Scientist that study fossils are called paleontologists. • use their information to determine what past life forms were like • want to know what the organisms ate, what ate the organisms and in what kind of environment they lived. • paleontologist classify organisms, group organisms together, arrange organisms in the order in which they lived from earliest to latest. • all this information together is called the fossil record • the fossil record provides evidence about the history of life and past environments on Earth. The fossil record also shows that different groups of organisms have changed over time. 10 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? • Paleontologist use fossils to build a picture of Earth's past environment • fossils found in an area tell whether or not the area was a shallow bay or an ocean bottom, or a freshwater swamp • fossils provide evidence about past climates - coal found in Antarctica is surprising, because coal only forms from the remains of plants that grow in warm, swampy regions. Shows that the climate of Antarctica is much different today than in the past. • Fossils of ocean or aquatic animals have been found in areas that are now deserts. Scientist have inferred that areas used to be oceans that are now dry today. 11 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? Changes and the Fossil Record The fossil record reveals a surprising fact: • Fossils occur in a particular order • Older rocks contain fossils of simpler organisms • Younger rock contains fossils of more complex organisms. • The fossil record shows that life on Earth has evolved and changed over time. Simple one-celled organisms have given rise to complex plants and animals • Fossil records supports the theory of evolution. • Theory is a well-tested concept that explains a wide range of observations • Evolution is a gradual change in living things over long periods of time • Fossil record shows that millions of types of organisms have evolved, but many have become extinct. 99.9% of all animals that have lived on Earth are no longer here.... • Extinct - an organism that no longer exists and will never again live on Earth 12 EQ: What is the basis for biological evolution and geological evolution? Wrap-Up - Ticket Out The Door! On a clean sheet of paper, copy the question and give a short complete answer. 1. What is a fossil? 2. In general, how do fossils form? 3. Which parts of an organism are most likely to be preserved as a fossil? Why? 4. What are the five different kinds of fossils? 5. How does a carbon film fossil form? 6. How are petrified fossils similar to preserved remains? How are they different? 7. What are two things that scientist can learn from the fossil record? 8. What does the fossil record show about how life has changed over time? 13