* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Noun and Pronoun Cases
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Nominative determinism wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latvian declension wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Archaic Dutch declension wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish pronouns wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
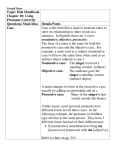
Student Name Ms. Haywood English 8 February 2016 Noun and Pronoun Cases NOUN and PRONOUN CASES The CASE of a noun tells us about the position of that noun in a sentence. It also shows the form that a pronoun takes to show its relationship to other words in a sentence. In English there are THREE CASES. They are: • Nominative case • Objective case • Possessive case 1. Nominative case: SUBJECT of the verb A noun is said to be in the nominative case if it is the subject of a verb. (SUBJECT is the person or the thing who or which carries out the action of the verb in the sentence) Examples: • Mr. Green is an intelligent man. Mr. Green is a proper noun in nominative case. • The painter paints the portraits. The painter is a common noun in nominative case. • I am buying vegetables for my family. “I" is a pronoun in nominative case. • My favorite artists are Frida Kahlo and she. “she" is a pronoun in nominative case because it is the predicate nominative. For example: I, We, You, He, She, it and they are subject pronouns that are in the NOMINATIVE CASE Student Name Ms. Haywood English 8 February 2016 2. Objective case: Direct Object that receives the action of the verb or Object of the preposition (Accusative) Nouns or pronouns are said to be in objective case if they are the direct objects of verbs or if they are the objects of preposition (Direct object is the person or the thing upon whom or upon which the action of the verb is carried out). Examples: • The guide showed us the way out. “us" is a pronoun in objective case. • The vendors sell mangoes. “mangoes" is in objective case. • The book is on the table. “table" is in objective case. It is object of the preposition ‘on’. • This is one of my policies. “policies" is in objective case. It is object of the preposition ‘of’. 3. Possessive case: Possession or ownership (Genitive) A noun is said to be in possessive case, if it denotes possession or ownership. A noun or pronoun in the possessive case is governed by the noun that follows it. Examples: • This is your pencil. “your" is in possessive case. • It is our idea. “our" is in possessive case. • John’s sister has been hospitalized. “John’s" is in possessive case. Student Name Ms. Haywood English 8 February 2016 Most personal pronouns have different forms in all three cases because of their different uses. PERSONAL PRONOUNS NOMINATIVE OBJECTIVE POSSESSIVE SINGULAR I, you he , she, it me you him, her, it my, mine, your, yours his, her, hers, its PLURAL we you they us you them our, ours your, yours their, theirs