* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Accounting? - masif-emba-fais-s12
Survey
Document related concepts
Internal control wikipedia , lookup
Auditor's report wikipedia , lookup
Going concern wikipedia , lookup
Mergers and acquisitions wikipedia , lookup
Institute of Cost Accountants of India wikipedia , lookup
Natural capital accounting wikipedia , lookup
J. Lee Nicholson wikipedia , lookup
James Bray Griffith wikipedia , lookup
Debits and credits wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Dynamics GP wikipedia , lookup
Lean accounting wikipedia , lookup
International Financial Reporting Standards wikipedia , lookup
South African Institute of Chartered Accountants wikipedia , lookup
Mark-to-market accounting wikipedia , lookup
Sustainability accounting wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
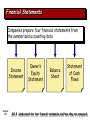
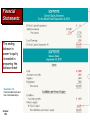
Financial Accounting & Information System Session Objectives: Why Accounting • Introduction • Course Objective & Conduct •Course Outline • What’s Accounting, What it isn’t ? • Accounting Foundations (Chapter_1) • Recording Process (Chapter_2) • Accounting Information System with SAP: By M Asif Jaffer Chapter 1-1 1 Financial Accounting & Information System -Just like there’s positive and negative motivation of a any conduct, so is for study of accounting -Unfortunately, negative motivators are more common for study of Accounting! - Enron, WorldCom - Some Local Cases Accounting Information System with SAP: By M Asif Jaffer Chapter 1-2 2 Financial Accounting & Information System Course Objective To enable students to understand financial accounting concepts and techniques and apply those concepts in financial decision making ….to enable you to study and understand annual reports of…. Accounting Information System with SAP: By M Asif Jaffer Chapter 1-3 3 Financial Accounting & Information System Course Conduct - Must be with the book, calculator and annual report - Case Based Methodology, wherever possible -120 minutes a week at home - Collaborative learning - Attendance norms - Assignments Accounting Information System with SAP: By M Asif Jaffer Chapter 1-4 4 Financial Accounting & Information System Instructor: Muhammad Asif Jaffer - FCMA, ACCA, MA (Economics), B.Com - 10+ years industry experience - 4+ years teaching experience - Credits: Gold Medal at ICMAP - - Participants Introduction Accounting Information System with SAP: By M Asif Jaffer Chapter 1-5 5 Financial Accounting & Information System - Accounting Defined: What Identifying Recording Communicating Of Economic Events of an organization To Interested Users Accounting Information System with SAP: By M Asif Jaffer Chapter 1-6 6 The rest of the slides are taken from the following course website Chapter 1-7 Accounting in Action Chapter 1-8 Accounting Principles, Ninth Edition Chapter Study Objectives Emba_s12_FAIS_iba @yahoogroups.com 1. Explain what accounting is. 2. Identify the users and uses of accounting. 3. Understand why ethics is a fundamental business concept. 4. Explain generally accepted accounting principles and the cost principle. 5. Explain the monetary unit assumption and the economic entity assumption. 6. State the accounting equation, and define its components. 7. Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. 8. Understand the four financial statements and how they are prepared. Chapter 1-9 Accounting in Action What is Accounting? Three activities Who uses accounting data The Building Blocks of Accounting Ethics in financial reporting Generally accepted accounting principles Assumptions Chapter 1-10 Using the Basic Accounting Equation Financial Statements Liabilities Transaction analysis Income statement Owner’s equity Summary of transactions Owner’s equity statement The Basic Accounting Equation Assets Balance sheet Statement of cash flows What is Accounting? The purpose of accounting is to: (1) identify, record, and communicate the economic events of an (2) organization to (3) interested users. Chapter 1-11 SO 1 Explain what accounting is. What is Accounting? Three Activities Illustration 1-1 Accounting process The accounting process includes the bookkeeping function. Chapter 1-12 SO 1 Explain what accounting is. Who Uses Accounting Data? Internal Users Human Resources Finance Management IRS Investors There are two broad groups of users of financial information: internal users and external users. Marketing Customers Chapter 1-13 SEC Labor Unions Creditors External Users SO 2 Identify the users and uses of accounting. Who Uses Accounting Data? Common Questions Asked 1. Can we afford to give our employees a pay raise? User Human Resources 2. Did the company earn a satisfactory income? Investors 3. Do we need to borrow in the near future? 4. Is cash sufficient to pay dividends to the stockholders? Management Finance 5. What price for our product will maximize net income? Marketing 6. Will the company be able to pay its short-term debts? Creditors Chapter 1-14 SO 2 Identify the users and uses of accounting. Who Uses Accounting Data? Discussion Question Q1-1: “Accounting is ingrained in our society and it is vital to our economic system.” Do you agree? Explain. See notes page for discussion Chapter 1-15 SO 3 Understand why ethics is a fundamental business concept. The Building Blocks of Accounting Ethics In Financial Reporting Standards of conduct by which one’s actions are judged as right or wrong, honest or dishonest, fair or not fair, are Ethics. Recent financial scandals include: Enron, WorldCom, HealthSouth, AIG, and others. Congress passed Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. Effective financial reporting depends on sound ethical behavior. Chapter 1-16 SO 3 Understand why ethics is a fundamental business concept. Ethics Review Question Ethics are the standards of conduct by which one's actions are judged as: a. right or wrong. b. honest or dishonest. c. fair or not fair. d. all of these options. Chapter 1-17 SO 3 Understand why ethics is a fundamental business concept. The Building Blocks of Accounting Various users need financial information The accounting profession has attempted to develop a set of standards that are generally accepted and universally practiced. Chapter 1-18 Financial Statements Balance Sheet Income Statement Statement of Owner’s Equity Statement of Cash Flows Note Disclosure Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) US GAAP, UK GAAP PK GAAP! SO 4 Explain generally accepted accounting principles and the cost principle. The Building Blocks of Accounting Organizations Involved in Standard Setting: Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan (SECP) International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) Institute of Chartered Accountants of Pakistan (ICAP) Chapter 1-19 SO 4 Explain generally accepted accounting principles and the cost principle. The Building Blocks of Accounting Cost Principle (Historical) – dictates that companies record assets at their cost. Issues: Reported at cost when purchased and also over the time the asset is held. Cost easily verified, whereas market value is often subjective. Fair value information may be more useful. Chapter 1-20 SO 4 Explain generally accepted accounting principles and the cost principle. Assumptions Monetary Unit Assumption – include in the accounting records only transaction data that can be expressed in terms of money. Economic Entity Assumption – requires that activities of the entity be kept separate and distinct from the activities of its owner and all other economic entities. Proprietorship. Partnership. Forms of Business Ownership Corporation. Chapter 1-21 SO 5 Explain the monetary unit assumption and the economic entity assumption. Forms of Business Ownership Proprietorship Chapter 1-22 Partnership Corporation Generally owned by one person. Owned by two or more persons. Often small service-type businesses Often retail and service-type businesses Ownership divided into shares of stock Owner receives any profits, suffers any losses, and is personally liable for all debts. Generally unlimited personal liability Separate legal entity organized under state corporation law Limited liability Partnership agreement SO 5 Explain the monetary unit assumption and the economic entity assumption. Assumptions Review Question Combining the activities of Kellogg and General Mills would violate the a. cost principle. b. economic entity assumption. c. monetary unit assumption. d. ethics principle. Chapter 1-23 SO 5 Explain the monetary unit assumption and the economic entity assumption. Forms of Business Ownership Review Question A business organized as a separate legal entity under state law having ownership divided into shares of stock is a a. proprietorship. b. partnership. c. corporation. d. sole proprietorship. Chapter 1-24 SO 5 Explain the monetary unit assumption and the economic entity assumption. Double Entry Accounting Basics Every economic event for a business has two perspectives Resources = Sources This is exactly what Islam preaches that nothing is yours own ‘ Sinkandar jab gaya dunya se dono haath khali the’ Chapter 1-25 SO 5 Explain the monetary unit assumption and the economic entity assumption. The Basic Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity Provides the underlying framework for recording and summarizing economic events. Assets are claimed by either creditors or owners. Claims of creditors must be paid before ownership claims. Chapter 1-26 SO 6 State the accounting equation, and define its components. The Basic Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity Provides the underlying framework for recording and summarizing economic events. Assets Resources a business owns. Provide future services or benefits. Cash, Supplies, Equipment, etc. Chapter 1-27 SO 6 State the accounting equation, and define its components. The Basic Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity Provides the underlying framework for recording and summarizing economic events. Liabilities Claims against assets (debts and obligations). Creditors - party to whom money is owed. Accounts payable, Notes payable, etc. Chapter 1-28 SO 6 State the accounting equation, and define its components. The Basic Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity Provides the underlying framework for recording and summarizing economic events. Owner’s Equity Ownership claim on total assets. Referred to as residual equity. Chapter 1-29 Capital, Drawings, etc. (Proprietorship or Partnership). SO 6 State the accounting equation, and define its components. Chapter 1-30 Owners’ Equity Illustration 1-6 Revenues result from business activities entered into for the purpose of earning income. Common sources of revenue are: sales, fees, services, commissions, interest, dividends, royalties, and rent. Chapter 1-31 SO 6 State the accounting equation, and define its components. Owners’ Equity Illustration 1-6 Expenses are the cost of assets consumed or services used in the process of earning revenue. Common expenses are: salaries expense, rent expense, utilities expense, tax expense, etc. Chapter 1-32 SO 6 State the accounting equation, and define its components. Using The Basic Accounting Equation Transactions are a business’s economic events recorded by accountants. May be external or internal. Not all activities represent transactions. Each transaction has a dual effect on the accounting equation. Chapter 1-33 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions (Question?) Q1-15: Are the following events recorded in the accounting records? Owner An employee is hired. withdraws cash for personal use. Event Supplies are purchased on account. Criterion Is the financial position (assets, liabilities, or owner’s equity) of the company changed? Record/ Don’t Record Chapter 1-34 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Discussion Question Q1-18: In February 2010, Paula King invested an additional $10,000 in her business, King’s Pharmacy, which is organized as a proprietorship. King’s accountant, Lance Jones, recorded this receipt as an increase in cash and revenues. Is this treatment appropriate? Why or why not? See notes page for discussion Chapter 1-35 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Analysis Transaction (1). Investment By Owner. Ray Neal decides to open a computer programming service which he names Softbyte. On September 1, 2010, he invests $15,000 cash in the. The effect of this transaction on the basic equation is: Chapter 1-36 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Analysis Transaction (2). Purchase of Equipment for Cash. Softbyte purchases computer equipment for $7,000 cash. Chapter 1-37 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Analysis Transaction (3). Purchase of Supplies on Credit. Softbyte purchases for $1,600 from Acme Supply Company computer paper and other supplies expected to last several months. Chapter 1-38 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Analysis Transaction (4). Services Provided for Cash. Softbyte receives $1,200 cash from customers for programming services it has provided. Chapter 1-39 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Analysis Transaction (5). Purchase of Advertising on Credit. Softbyte receives a bill for $250 from the Daily News for advertising but postpones payment until a later date. Chapter 1-40 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Analysis Transaction (6). Services Provided for Cash and Credit. Softbyte provides $3,500 of programming services for customers. The company receives cash of $1,500 from customers, and it bills the balance of $2,000 on account. Chapter 1-41 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Analysis Transaction (7). Payment of Expenses. Softbyte pays the following Expenses in cash for September: store rent $600, salaries of employees $900, and utilities $200. Chapter 1-42 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Analysis Transaction (8). Payment of Accounts Payable. Softbyte pays its $250 Daily News bill in cash. Chapter 1-43 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Analysis Transaction (9). Receipt of Cash on Account. Softbyte receives $600 in cash from customers who had been billed for services [in Transaction (6)]. Chapter 1-44 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Analysis Transaction (10). Withdrawal of Cash by Owner. Ray Neal withdraws $1,300 in cash from the business for his personal use. Chapter 1-45 SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Transactions Analysis Summary of Transactions Chapter 1-46 Illustration 1-8 Tabular summary of Softbyte transactions SO 7 Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. Financial Statements Companies prepare four financial statements from the summarized accounting data: Income Statement Chapter 1-47 Owner’s Equity Statement Balance Sheet Statement of Cash Flows SO 8 Understand the four financial statements and how they are prepared. Financial Statements Review Question Net income will result during a time period when: a. assets exceed liabilities. b. assets exceed revenues. c. expenses exceed revenues. d. revenues exceed expenses. Chapter 1-48 SO 8 Understand the four financial statements and how they are prepared. Financial Statements Income Statement Reports the revenues and expenses for a specific period of time. Net income – revenues exceed expenses. Illustration 1-9 Financial statements and Net loss – expenses exceed revenues. their interrelationships Chapter 1-49 SO 8 Understand the four financial statements and how they are prepared. Financial Statements Net income is needed to determine the ending balance in owner’s equity. Illustration 1-9 Financial statements and their interrelationships Chapter 1-50 Financial Statements Owner’s Equity Statement Statement indicates the reasons why owner’s equity has increased or decreased during the period. Chapter 1-51 Illustration 1-9 Financial statements and their interrelationships SO 8 Understand the four financial statements and how they are prepared. Financial Statements The ending balance in owner’s equity is needed in preparing the balance sheet Illustration 1-9 Financial statements and their interrelationships Chapter 1-52 Financial Statements Balance Sheet Illustration 1-9 Financial statements and their interrelationships Chapter 1-53 SO 8 Understand the four financial statements and how they are prepared. Financial Statements Illustration 1-9 Financial statements and their interrelationships Chapter 1-54 Financial Statements Statement of Cash Flows Illustration 1-9 Financial statements and their interrelationships Chapter 1-55 SO 8 Understand the four financial statements and how they are prepared. Financial Statements Discussion Question Q1-19: “A company’s net income appears directly on the income statement and the owner’s equity statement, and it is included indirectly in the company’s balance sheet.” Do you agree? Explain. See notes page for discussion Chapter 1-56 SO 8 Understand the four financial statements and how they are prepared. Accounting Career Opportunities Public Accounting Careers in auditing and taxation serving the general public. Private Accounting Careers in industry working in cost accounting, budgeting, accounting information systems, and taxation. Opportunities in Government Careers with the IRS, the FBI, the SEC, and in public colleges and universities. Forensic Accounting Careers with insurance companies and law offices to conduct investigations into theft and fraud. Chapter 1-57 SO 9 Explain the career opportunities in accounting. Copyright Copyright © 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in Section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the express written permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The Publisher assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages, caused by the use of these programs or from the use of the information contained herein. Chapter 1-58