* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is an organism?
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cambrian explosion wikipedia , lookup
Biotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Taxonomy (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
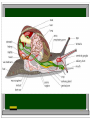
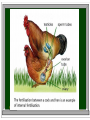
Characteristics of Living Organisms What is an organism? -any living thing -There are 7 characteristics that distinguishes living from nonliving. All living organisms ……. 1. Are made up of one or more cells. Cells are the: basic unit of function and structure of all living organisms. Plus one fungus is unicellular…… yeast Unicellular: -organisms made up of only one cell. Bacteria Protist Multicellular: -organisms made up of two or more cell all working together. Fungi Plants Animals Multicellular organisms must display levels of organization: CELLS: the basic unit of life A group of like cells make up : TISSUES Layers of like tissues make up : ORGANS A group of organs working together for one purpose is a: SYSTEM Examples? Digestive, Reproductive, Nervous, etc….. Organism = a series of organ systems working together to create one individual (frog) Species = group of like organisms that can reproduce and produce a fertile offspring. (spring peepers) Population = group of individuals of the same species living in one place. ( All the spring peepers living in Mrs. O'Neill's pond). Community = groups of many different populations living in one area. ( all the different types of frogs, fish, turtles and cat tails in Mrs. O’Neill’s pond). Ecosystem = all the different organisms and their physical environment both biotic and abiotic Biotic: bio= life -anything alive in the ecosystem like plants, animals, etc… Abiotic a= bio= non life = anything nonliving like air, water, soil, etc.. Biosphere = is the region of our universe where organisms live (land, air and water). What’s the difference between the man and the rock? Man -made up of cells and displays all levels of organization. Rocks -not made up of cells. Made up of only atoms and molecules All living organisms…… 2. Must be able to successfully reproduce. -Reproduce means to make more organisms . -This trait pertains to the species and NOT to an individual. 2 types of reproduction: 1. Asexual Reproduction: A = not Sexual = well you know what that means... -Asexual reproduction is when one organism divides into two new organisms. -It produces new organisms that are genetically identical. -clones Binary Fission Genetically identical to each other and to…. Examples include: Bacteria, protist, some fungi, some plants and some animals. Which are clones? Planarians Budding Hydras Rooting a plant clipping in water Strawberry Plants 2. Sexual Reproduction: -Requires two things -sperm -egg -Produces organisms that are genetically different. 23 23 46 Zygote In most species it requires two different organisms to reproduce Few species are hermaphrodites One organisms has the ability to produce both sperm and egg Most flowering plants Sponges Some organisms can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Can you think of any??? 2 types of Sexual Reproductin Internal Fertilization: verses External Fertilization Internal Fertilization: -sperm and egg meet: inside the females body -offspring remain inside the mother or inside a hard shell and are protected. Internal Fertilization Examples: Reptiles Birds Mammals Plants External Fertilization: Sperm and egg are released into water and randomly come together by chance. Offspring develop on their own, many ending up as a prey or as “fish food” Fish External Fertilization Frogs 3. All living organisms must be able to grow and develop. Grow: to get bigger by the increase in the number of cells. Develop: to change in form. Growth and development may occur at the same time. 4. All living organisms must obtain and use energy -need energy to do everything -grow, develop, reproduce…..even sleep. Why do babies sleep so much???? Ways to get food: Heterotrophs: Hetero = different trophs = to nourish -organisms that get energy by consuming other organisms. Examples of who is heterotrophic: -some bacteria -some protist -all fungi -all animals Autotrophs: -organisms which make their own food through the process of Photosynthesis Auto = self operating trophs = to nourish Examples of who is Autotrophic? -some bacteria -some protist -all plants What do all these organisms have in common that make them successful at photosynthesis? -all green -all contain chlorophyll Metabolism Is the sum total of ALL chemical reactions that occur within a cell/a living organism. It includes the: Breaking down the food Using the food for energy and to make new cells. Heterotrophs can be: Herbivores: -plant eaters Carnivores: -meat eaters Omnivores: -eats both plants and animals Decomposers / Saprophytes: -breaks down once living matter into useable molecules 5. All living organisms must adapt to their environment. (adaptions occur over long pd of time/evolve in a species) Camouflaging WHY? Survival………….. Chameleons Snowshoe rabbit in the winter and summer. Organisms that are best adapted to their environment are the ones who survived and reproduced. (Survival of the fittest) -leading cause of evolution -slow, gradual change over time Survival of the fittest 6. All living organisms must be able to respond to their environment. (immediate response) WHY? Survival……………………. STIMULUS coldness heat no food light RESPONSE Humans shiver Humans sweat Birds fluff up their feathers Dogs Dogs get pant a thick coat of fur Alligators move into the water Birds migrate south Plants grow towards the light 7. All living organisms must be able to display some form of homeostasis. Homo = same Heart beat/pulse Blood pressure stasis = Water balance stationary Body temperature Homeostasis is the ability to maintain stable and constant internal conditions. All living organisms must display homeostasis but it may be by different means and to different degrees… Example: Blood sugar rises body senses change pancreas secretes insulin into blood insulin effectively lowers the blood sugar level by moving sugar into the cells. Once blood sugar levels reach homeostasis the pancreas stops releasing insulin If a person can not perform this negative feedback loop then what is wrong with the person? - Example: Blood vessel is damaged platelets cling to injured site and release chemicals to attract more platelets platelets continue to pile up and release these chemicals until a clot is formed. Homeostasis happens in all organisms, even plants. Plants need to regulate: -water loss -CO2 intake