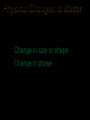* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Chemistry
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
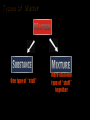
Properties and Changes of Matter Unit One Chapter 2 Properties of Matter • What is Matter? – Anything that has mass and takes up space • What is mass? – Amount of matter an object contains Types of Matter • Substance – Matter that has definite and uniform composition • Mixture – Physical blend of two or more substances that can be separated using physical means. • Filtration • Distillation Types of Matter One type of “stuff” More than one type of “stuff” together Types of Substances • Elements – Simplest form of matter • Compounds – composed of more than one type of atom – Can be separated into simpler substances by chemical means Types of Mixtures • Heterogeneous – Multiple phases • Homogeneous – All in a single phase Homogeneous Mixtures are Solutions • Solvent – The substances that does the dissolving – Present in the greater amount • Solute – The substances that gets dissolved – Present in the smaller amount Heterogenous or Homogeneous • • • • • • Saltwater Spaghetti sauce Muddy water Cough syrup Salad Brass Physical Properties of Matter – Quality of a subtance that can be observed or measured without changing the substance • Melting/boiling point, color, density. Mass Types of Physical Properties • Two types of Physical Properties – Intensive • Are constant regardless of the amount of the substance – Melt. Pt/Boil. Pt – Density – Extensive • Vary depending on amount of substance present – Mass – Volume • Intensive properties are inherent to a substance and can aid in identifying an unknown sample Phases of Matter soli d • 3 common phases –Solid •Definite shape •Definite volume •Highly rigid and organized – particles vibrate around fixed points •Nearly incompressible, does not flow –Liquid •Definite volume •Indefinite shape •Fluid – takes the shape of its container, slightly compressible –Gas •Indefinte shape – •Indefinite volume •Very fluid - takes shape and volume of containter •Particles move randomly with high energy, very compressible Additional Phases of Matter • Bose-Einsten Condensate – Exists as temperatures approach absolute zero (-273 °C) – Extremely dense, but less structured than solid • Plasma – Energy similar to gas – Contains ions rather than atoms • Attraction of ionic charges pull molecules closer together than in gas Definitions related to changes in Matter • Vapor – Gaseous state of a substance that is in the liquid or solid state at normal temperatture • Temperature – Average kinetic energy of the particles (atoms, molecules, etc.) of the substance Physical Changes to Matter • Changes that do not alter the chemical compostion • Change in size or shape • Change in phase Chemical Properties of Matter • Ability of a substance to react and form a new substance –Can only be observed or measured by changing the substance into a different substance Chemical Changes to Matter • Results in the formation of a new substances – A chemical reaction takes place • Evidence that a chemical reaction has taken place – Change in energy • Temperature increase or decrease – Production of a gas • Formation of bubbles or detection of odor – Formation of a precipitate • Presence of a solid – Color change Chemical Reactions • One or more substances change into a new substance –Reactants • The substances that exist before the reaction/chemical change takes place –Products • The substances that form as a result of the reaction/chemical change Evidence of a Chemical Reaction • • • • Formation of a gas Formation of a solid (precipitate) Color change Change in energy (absorbed or given off) Practice: classify the following as physical or chemical properties of water 1. Colorless 2. Changes from a liquid to a gas at 100ºC 3. Decomposed by electricity into hydrogen and oxygen 4. Freezes at 0 ºC 5. Produces acetylene gas when dropped in calcium carbide 6. Produces a gas when reacted with sodium Practice: Classify the following as physical or chemical changes: 1. Bending a piece of wire into a new shape 2. Cooking a steak 3. Cutting the grass 4. Souring of milk 5. Burning coal 6. Dissolving sugar in water 7. Growing grass 8. Stretching a rubber band Law of Conservation of Mass • The amount of matter present before the reaction takes place will equal the amount of matter at the completion of the reaction Food for Thought: If 4.0 g of hydrogen are combined with a mass of oxygen to make 36.0 g of water, how many grams of oxygen were used in the reaction?