* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Active Immunity
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
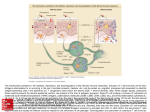
Figure 43.1 An overview of the body's defenses Figure 43.3x Macrophage Phagocytes • Are large cells that attack antigens in your body • They engulf antigens and destroy them • Use lysosomes to destroy the antigens Figure 43.5 A simplified view of the inflammatory response Do I know you? • Your immunity cells, like the phagocyte, don’t attack your own body cells • This is because your body cells have markers on them • Your immunity cells attack antigens because they don’t have the right markers on them. Antigens Figure 43.6 Clonal selection Figure 43.16 Effector mechanisms of humoral immunity Active Immunity • Active immunity occurs when your OWN body makes memory cells. • These cells stay in the body and attack the antigen if it enters the body again • This prevents you from getting the same illness • Ex. Chicken pox • Active immunity can be obtained by vaccinations Figure 43.x2 Vaccination Passive Immunity • Passive immunity is when you DON’T make your own memory cells • An example of passive immunity is when you receive medicine like antibiotics • You only have temporary immunity • Once the medicine leaves your body you can get sick again Question During pregnancy, a mother’s immune system protects the growing baby by creating antibodies and giving them to the baby. Is this active or passive immunity? Figure 43.6 Clonal selection AIDS • Caused by a virus called HIV • HIV attacks and kills helper T cells • Helper T cells cause the B cells to copy themselves to fight off antigens