* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
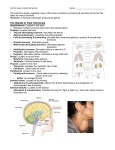
The Endocrine System Endocrine glands: These are ductless, or tubeless, structures that secrete hormones Major glands of the endocrine system include: Pituitary gland Thyroid Parathyroid Pineal gland Thymus Adrenal Pancreas Gonads Pituitary Gland: Regulates and controls the activities of all other endocrine glands Known as the “Master Gland” Pea-sized gland located at the midpoint of the skull Three sections or lobes: o Anterior o Intermediate o Posterior Anterior Lobe: Means “front” Hormones produced by this lobe control a range of body functions. They regulate metabolic activities of cells and stimulate other endocrine glands. Anterior lobe produces 6 hormones: o Somatotropic, or growth, hormone stimulates normal body growth and development by altering chemical activity in body cells. o Thyroid-Stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates hormone productions by the thyroid glands. o Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulates hormone production by the adrenal glands. o Gonadotropic Hormones: Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Triggers the development of egg cells, or ova, in the ovary and stimulates cells in the ovary to produce estrogen, a female sex hormone. Stimulates the testes to produce sperm cells Luteinizing hormone (LH) Responsible for ovulation, or the release of a mature ovum from the ovary Stimulates cells in the ovaries to produce progesterone, female sex hormones. Prolactin stimulates milk production in females Stimulates cells in the testes to produce testosterone, a male sex hormone. Intermediate Lobe: This lobe secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) Controls the darkening of the skin by stimulating pigment cells in the skin Posterior Lobe: Secretes two hormones: o Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): Principal function is to regulate the balance of water in the body. Stimulates the kidneys to return water to the blood o Oxytocin: Stimulates the smooth muscles in the uterus of a pregnant female, causing contractions during the birth of a baby. Thyroid Gland: One of the largest glands of the endocrine system. Located in front of the neck, just below the larynx. Produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth. Principal hormone produced by the thyroid gland is Thyroxine. o Regulates the way cells release energy from nutrients or use energy to create other substances, such as proteins. The Parathyroid Glands: Smallest glands of the endocrine system Regulates the body’s calcium and phosphorus balance. Pineal Gland Secretes Melatonin o Melatonin regulates sleep cycles and is thought to affect the onset of puberty. Thymus Regulates development of the immune system The Adrenal Glands: Two glands located on the top of the kidneys. o Adrenal cortex o Adrenal medulla Adrenal Cortex: Secretes a hormone that inhibits the amount of sodium excreted in urine and serves to maintain blood volume and pressure. Secretes hormones that aid metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. These hormones also play a role in immunity and the body’s response to stress. Adrenal Medulla: Highly dependent on the hypothalamus and the autonomic nervous system Secretes the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) Pancreas: Largest gland in the endocrine system: Lies behind the stomach Attached to the first part of the small intestine Secrete two hormones: o Glucagons Raises blood sugar levels o Insulin Lowers blood sugar levels Gonads: Only gland that is different in the male and female Hormones from these glands are responsible for the development and maintenance of the secondary sex characteristics. Problems in the Endocrine System: Diabetes Mellitus Disorder in which the pancreas produces too little or no insulin, resulting in high blood pressure glucose levels. o Symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, thirst, and frequent urination. Graves Disease Disorder in which an overactive and enlarged thyroid gland produces excessive amounts Thyroxine. o Hyperthyroidism: Symptoms include Nervousness, weight loss, increased thirst, rapid heartbeat, and intolerance for heat o Hypothyroidism: Symptoms fatigue, dry skin, weight gain, constipation, and sensitivity to cold. Cushing’s Disease Results from the overproduction of adrenal hormones. o Symptoms include: Round face, humped upper back, thin and easily bruised skin, and fragile bones. Goiter Caused mainly by a lack of iodine in the diet.