* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stimulus transduction and encoding
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
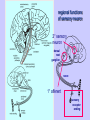
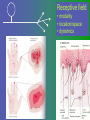
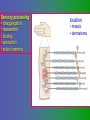
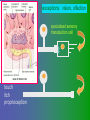
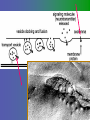
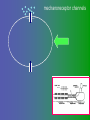
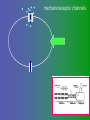
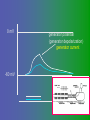
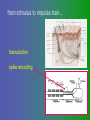
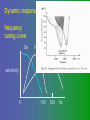
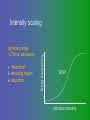
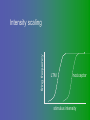
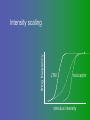
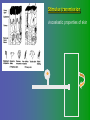
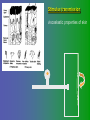
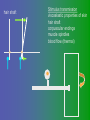
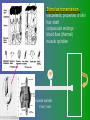
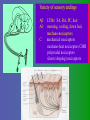
פיסיולוגיה מורחב 08-9 Somatosensory System and Pain lecture 2: Stimulus transduction and encoding Prof. Marshall Devor, Ph.D. Dept. of Cell & Animal Biology and Center for Research on Pain Institute of Life Sciences Hebrew University of Jerusalem "psychophysics" stimulus (physical units) neural representation (1,2,3,4) 4 perception 3 early processing 2 nerve transmission 1 transduction & encoding evolution planerian סנדלית • • • bacteria, protozoa (tropism) separation of sensation and effect sensation response (effector organ) perception (information, emotional/affective vector) regional functions of sensory neuron 2° sensory neuron dorsal root ganglion nerve 1° afferent sensory receptor ending Receptive field • modality • location/space • dynamics Sensory processing • disaggregation • reassembly • binding • perception • action/ memory location • mosaic • dermatome Transduction and encoding occur in the region of the sensory ending קידוד,התמרה exceptions: vision, olfaction audition vestibular sense taste pain vibration touch itch proprioception specialized sensory transduction cell transduction molecules anterograde axoplasmic transport How does transduction occur ? התמרה mechanoreceptor channels mechanoreceptor channels 0 mV -60 mV generator potential (generator depolarization) generator current mechano-gated channels thermal-gated channels ligand-gated receptors (some are channels) receptor types/ sensory transduction: mechanical, thermal (<, >), chemical mechanical: receptor cells vs. C.elegans – DEG/ENaC, receptor drosophila – TRPn, painless molecules vertebrates ? thermal: heat - TRPV1, TRPV2, TRPV3 (vanilloid, capsaicin) cold - menthol-R TRPM8 chemical: capsaicin – TRPV1 garlic, mustard – TRPA1 histamine H1,H2 ASICs (acid sensing ion channels) BK-Rs (bradykinin) PG-Rs (prostaglandins) etc. capsaicin receptor cloned (by D.Julius & M.Caterina et al. Nature ‘97) (cDNA from rodent DRG injected into HEK cells, screen for >Ca 2+ fluorescence on capsaicin application) vanilloid-R1 V1 by sequence homology very similar to drosophila “transient receptor potential” channel TRP TRPV1 TRP receptor family…TRPVs, TRPAs, TRPMs, TRPCs TRPV1: sensitive to capsaicin, protons (pH), heat, some endocannabinoid lipids from stimulus to impulse train… transduction spike encoding Pacinian corpuscle stimulus encoding vibration, texture adaptation vs. habituation Dynamic response of sensory receptors frequency tuning curve SA RA Pacinian corpuscle sensitivity 0 100 300 Hz dynamic range • LTM vs. nociceptor "threshold" encoding region saturation firing frequency Intensity scaling WDR stimulus intensity firing frequency Intensity scaling LTM nociceptor stimulus intensity firing frequency Intensity scaling LTM nociceptor stimulus intensity from stimulus to impulse train… 1. force transmission to sensory ending 2. transduction 3. spike encoding Stimulus transmission viscoelastic properties of skin Stimulus transmission viscoelastic properties of skin hair shaft Stimulus transmission viscoelastic properties of skin hair shaft corpuscular endings muscle spindles blood flow (thermal) Stimulus transmission viscoelastic properties of skin hair shaft corpuscular endings blood flow (thermal) muscle spindles muscle spindle כישור השריר Variety of sensory endings (to code stimulus intensity, quality, dynamics) 1. force transmission to sensory ending 2. transduction 3. spike encoding RA SA RA Variety of sensory endings A: LTMs: SA, RA, PC, hair A: warming, cooling, down hair, mechano-nociceptors C: mechanical nociceptors mechano-heat nociceptors CMH polymodal nociceptors silent (sleeping) nociceptors פיסיולוגיה מורחב Somatosensory System and Pain lecture 2: Sensory transduction and encoding Prof. Marshall Devor, Ph.D. Dept. of Cell & Animal Biology and Center for Research on Pain Institute of Life Sciences Hebrew University of Jerusalem Somato-visceral sensation Receptive Field tissue skin deep (musculoskeletal, visceral, brain) modality/ quality touch (static-dynamic (vibration, movement)) thermal chemical sensory processing disaggregation signal processing reassembly quality binding intensity perception location action/ memory dynamics
















![[SENSORY LANGUAGE WRITING TOOL]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014348242_1-6458abd974b03da267bcaa1c7b2177cc-150x150.png)