* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IIASA International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
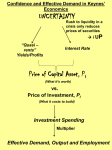
What is IIASA? An introduction to the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis CONTENTS 1. Major Global Challenges 2. IIASA’s History 3. IIASA’s Approach 4. Research Strategy, Output and Impact MAJOR GLOBAL CHALLENGES MAJOR GLOBAL CHALLENGES FOOD FOOD • 870 million people were undernourished in 2012 (FAO) • By 2030, the world’s population will have increased by one billion (IIASA) • Agriculture accounts for 70% of freshwater withdrawals (UN Water) MAJOR GLOBAL CHALLENGES WATER WATER • 783 million people have inadequate access to safe freshwater (WHO & UNICEF) • Water use has been growing at more than twice the rate of population increase in the last century (FAO & UN-Water) • Hydropower supplies about 20% of the world’s electricity (ICOLD) MAJOR GLOBAL CHALLENGES ENERGY ENERGY • 2.5 billion people are without access to modern energy (IIASA/GEA) • World primary energy demand expected to increase by 33% between 2011 & 2035 (IEA) • Energy production and consumption contributes over 80% of global GHG emissions (IIASA) MAJOR GLOBAL CHALLENGES CLIMATE CHANGE CLIMATE CHANGE • Each of the last three decades has been successively warmer at the Earth’s surface than any preceding decade since 1850 (IPCC) • Global surface temperature change for the end of the 21st century is likely to exceed 1.5°C relative to 1850 for all scenarios (IPCC) • 70 million Africans could suffer from devastating floods as a result of climate change (IPCC) MAJOR GLOBAL CHALLENGES POVERTY & EQUITY POVERTY & EQUITY • 1.2 billion people are still living in extreme poverty (UN MDG) • 60.9 % of workers in the developing world still live on less than US$4 a day (UN MDG) • “Hunger is a cause of poverty, not just a consequence of it.” (FAO) INEXTRICABLY LINKED Energy & Climate Change Food & Water Poverty & Equity RESEARCHING GLOBAL CHALLENGES • • • • • • • Integrated Interdisciplinary International Independent Solution-oriented Long term Trade offs = Systems Analysis IIASA helps to put the puzzle together IIASA’S HISTORY THE 1960s Sources: nuclearweaponarchive.org, The Guardian, US Department of Interior, 1972 Sources: IIASA IIASA’S APPROACH ATTRACT THE BEST SCIENTISTS Scientific Staff Research visitors to IIASA Other worldwide collaborators (including ~25% of 300 1,400 ~800 IIASA alumni network) TOTAL (for 2013) ~2500 In addition, IIASA collaborates with almost 300 institutions from 65 countries NOBEL PRIZE WINNERS Professor Tjalling Koopmans and Professor Leonid Kantorovich Nobel Prize in Economics (1975) NOBEL PRIZE WINNERS Professor Paul Crutzen Nobel Prize for Chemistry (1995) NOBEL PRIZE WINNERS Professor Thomas C. Schelling Nobel Prize for Economics (2005) NOBEL PRIZE WINNERS Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Nobel Peace Prize (2007) YOUNG SCIENTISTS SUMMER PROGRAM INTERDISCIPLINARY SCIENTISTS 29% 30% 41% Natural Scientists & Engineers Social Scientists Mathematicians and others INTERNATIONAL COLLABORATIONS HOME OF IIASA SINCE 1972 IIASA’S MEMBERS: Represent scientific community of a country and are often the National Academy or principal research funding agency FUNDING • Annual income in 2013 was €17.9 million of which 53% was from IIASA’s National Member Organizations • Additional funding comes from contracts and grants. Between 2006 and 2013, IIASA’s research was awarded grants that amounted to €62.5 million. This was part of a total funding portfolio of €308.5 million of the external projects in which IIASA was and is involved. RESEARCH STRATEGY, OUTPUT AND IMPACT IIASA’S STRATEGY 2011-2020 MISSION To provide insight and guidance to policymakers worldwide by finding solutions to global and universal problems through applied systems analysis in order to improve human and social wellbeing and to protect the environment. OUTPUT: JOURNAL ARTICLES 2010 2011 2012 2013 Peer-reviewed journal articles according to SCOPUS 129 150 175 254 JOURNAL ARTICLES & CITATONS 8000 300 7000 250 6000 200 4000 150 3000 100 2000 50 1000 0 0 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Citations 2008 2009 Journal Articles 2010 2011 2012 2013 Journal Articles Citations 5000 EXAMPLE OF IIASA’S IMPACT EFFECTS OF AIR POLLUTION CAUSES OF AIR POLLUTION Cut sulfur dioxide by 30% Moderate costs Ecosystem highly resilient to acid rain Cut sulfur dioxide by 30% Very high costs Ecosystem highly vulnerable to acid rain THE RAINS MODEL For 43 European countries: • Pollution generation & control options, including costs • Atmospheric transport and deposition • Impacts on the environment ASK THE RAINS MODEL Any number of “What if…?” questions: • How much would it cost to reduce sulfur dioxide levels to a given standard for all of Europe? • For the worst-affected areas only? • What is the cheapest way to stop acidification of forest soils in Bohemia? • What would be the impact of a new emissions standard for, say, power plants on eutrophication? On acidification? On ozone formation? RAINS gives answers to such questions, usually within minutes. INTERNATIONAL TREATY Convention on Long-range Transboundary Air Pollution • Signed by 33 European governments • One of the most successful multilateral treaties protecting the environment • Helped Europe to cut sulfur dioxide emissions by 60% over the past 20 years • With support of RAINS, treaty and EU now tackles multiple air pollutants (SO2, NOX, NH3, VOCs, PMs) RAINS extended to include greenhouse gases (GAINS) and used by numerous parties and organizations involved in climate change negotiations CLEAN AIR IN EUROPE Thank you For further information about IIASA: www.iiasa.ac.at or [email protected] Subscribe to IIASA’s publications: www.iiasa.ac.at/keepintouch