* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Epi-modif, glands
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gap junction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
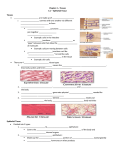
Today: Epithelial Tissue Modifications of epithelium (Classification of epithelial membranes) Epithelial Glands Stratified squamous (nonkeratinized) epithelium -location, function Stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium -keratin in cells -location, function Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Stratified Columnar Epithelium Transitional Epithelium Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium -ciliated What epithelia have in common: -polarity. The luminal and serosal surfaces Apical and basolateral surfaces -cell surface specializations eg. -apical domain/basolateral domain Some epithelial cells have: Microvilli -striated border, brush border, stereocillia -actin filaments cross linked and attached to apex by villin -terminal web has actin, spectrin, and intermediate filaments. Glands: Parenchyma - glands and ducts Stroma - connective tissue (CT) supporting the parenchyma Exocrine glands -secretory portion and duct portion Endocrine glands Multicellular Exocrine Glands -Simple *tubular *branched tubular *coiled tubular *acinar *branched acinar -Compound *tubular *acinar *tubular acinar Know glands by the type of secretion: -mucous -serous -mixed glands -serous demilunes in salivary glands Know glands by the way the secretion is released: -Merocrine, by conventional exocytosis -Apocrine, a portion of the cell breaks off (lactation) -Holocrine, entire cell is released (sebaceous gland) Unicellular exocrine glands -goblet cells - Junctional Complex: Terminal bars -Occluding junctions -Adhering junctions Occluding Junction: -aka zonua occludens, tight junction -transmembrane junctional proteins, like a zipper -leakiness of the junction depends on the number of zipper rows -the branching rows of transmembrane junctional proteins can be seen by freeze fracture TEM -membrane is pentalamellar by thin section TEM Adhering Junctions: zonula adherens - encircle cells macula adherens - desmosome - like spot welds Zonula Adherens: -intercellular space is 15 - 20 nm This space contains cadherins - calcium dependent transmembrane linker proteins. -on the intracellular side, proteins, vinculin and a-actinin bind the mb to actin web Macula adherens (desmosome): -intercellular space is 30 nm -attachment plaque on the intracellular side of the mb made of desmoplakin. -cytokeratin (intermediate filaments, 10 nm) attach to the plaque. -intercellular space has desmoglein and cadherins Hemidesmosomes: Anchor epithelial cells to the basal lamina -attachment plaque with desmoplakin -IF, keratin tonofilaments don’t enter the plaque -trans-membrane linker proteins are integrins -these bind to laminin & type IV collagen of basal lamina Gap Junctions are communicating junctions -intercellular space is 2 - 3 nm -adjoining windows between cells -windows are connexons, made of protein connexin -gap junctions pass ions, small molecules (cAMP) -opening and closing of the gaps can be regulated