* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 15 - MSU Billings
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
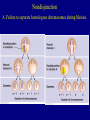
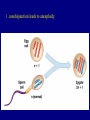
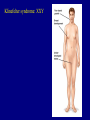
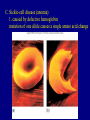
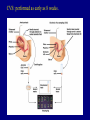
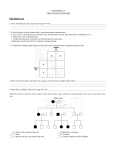
Nondisjunction A. Failure to separate homologous chromosomes during Meiosis 1. nondisjunction leads to aneuploidy 2. nondisjunction of autosomal chromosomes: a. monosomics 2. nondisjunction of autosomal chromosomes: b. trisomics if one of the 5 smaller ones, somewhat viable 13, 15, 18, 21, 22 trisomy 21 and 22 may be survivable into adulthood 3. nondisjunction of sex chromosomes: Klinefelter syndrome: XXY Turner syndrome: XO YY gametes (sperm) XYY XX gametes XXX OY not viable Mutations A. Random changes in genes 1. rare 2. usually recessive B. Hemophilia - loss of any of 12 clotting proteins (genes) 1. recessive 2. 2 important clotting genes are sex-linked C. Sickle-cell disease (anemia) 1. caused by defective hemoglobin mutation of one allele causes a single amino acid change C. Sickle-cell disease (anemia) 2. those homozygous for the sickle-cell allele will have the disease C. Sickle-cell disease (anemia) 3. those heterozygous are basically normal pleiotropy: when a gene produces multiple effects advantage in resisting malaria D. Tay-Sachs 1. caused by a recessive allele 2. leads to deterioration of the nervous system (8 months) 3. increased incidence in certain populations certain Jewish populations in U.S. : 1 in 27 people of Jewish descent carriers 1 in 250 in general population Cystic fibrosis PKU Inbreeding increases the likelihood of recessive disorders. Dominant disorders: Huntington’s disease Achondroplasia Pedigrees: Amniocentesis: performed between weeks 14 and 20. CVS: performed as early as 8 weeks. Blood tests: 1. alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) high in neural tube defect low in Down syndrome 2. triple screen (now quad screen) - can even indicate trisomy 18 risk 3. these tests are not diagnostic, only reflective of risk