* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 10 Plants
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
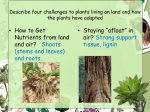
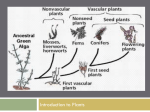
Kingdom Plantae The Big Five Review Pg 139 • How many cells? Multicellular • What type of cell? Eukaryotic • Cell wall or no? If so, what’s it made of? Yes, Cellulose • Nutrition? Autotrophic • Motility? NO! The Big Five for Plantae PG 139 • Multicellular • Eukaryotic • Cell walls – cellulose • Autotrophic • Non-motile • Plus…all have roots, stems, leaves, chlorophyll, chloroplasts Adaptations to Land PG 139 • PROBLEM – Loss of water – Needs water in all tissues – Will get blown away; needs water (its windy! Plus need nutrients) – No water for swimming gametes – Embryos dry out • SOLUTION – Waxy cuticles on leaves – Vascular tissue (tubes) – Roots – Pollen – Seeds Plant Groups PG 139 • Bryophytes – Mosses, liverworts – Have true roots, stems, leaves (RSL) – Like moist/wet environments – Rely on osmosis and diffusion Plant Groups • Pterophytes – Ferns, horsetails – Have vascular tissue – Very diverse most in tropics Plant Groups • Gymnosperms – Conifers, evergreens, pine trees – Have seeds (naked ones!) seeds develop on surface Plant Groups • Angiosperms – Flowering plants – Covered seeds (in fruits) – Largest most diverse group Review: 4 Groups draw on your nb paper • Gymnosperms • Bryophytes – – – – – Have RSL Nonvascular No seeds No flowers Ex: mosses • Pterophytes – – – – – RSL Vascular No seeds No flowers Ex: Ferns – – – – – RSL Vascular Seeds No flowers Ex: Conifers • Angiosperms – – – – – RSL Vascular Seeds Flowers Ex: Rose (all flowers) Early plants faced challenges living on land: 1. Algae floating does not need to conserve H2O it is already immersed in water and nutrients….so if a plant is on land it no longer has the ability to automatically take in water and nutrients it must conserve it somehow. 2. Embryos need a moist and wet environment….water automatically provided that for algae…..plants on land needed someway to keep the embryo from drying out and dying….seeds! 3. Need H2O everywhere…..algae already had water everywhere…..examples of vascular tissue sunflower, fern, maple tree and pine tree example of plants that have vascular tissue 1. Need to be able to work and grow against gravity… also wind can blow them away…..plus they need nutrients! Algae did not have to worry about this…. 2. Used to gametes would swim in the water until it was fertilized with another gamete…….if a plant is on land it no longer has the channel of water to send gametes through there is none…..so it needs another way to reproduce. Adaptations & Phylogeny Bryophytes Pterophytes Gymnosperms Naked Seeds Seeds Vascular Tissue Angiosperms Covered Seeds (in Fruits) Vascular Tissue PG 140 • XYLEM – Carries water (& nutrients) UP (from roots) and IN (to rest of plant) • PHLOEM – Carries food (sugars/glucose) DOWN and AROUND Vegetative Structures • ROOTS – Soak up water and minerals from soil – Anchor in place – Root hairs increase surface area for more water absorption Roots (write on nb paper) • Common Roots: Carrots & Beets (taproot) one big structure with tiny projections off of it • Fibrous: system that have many small branching roots that grow from a central point Vegetative Structures • STEMS – Carry substances up and down plant – Provide support for leaves & other parts *may be woody (trees) or herbaceous (green) Stems (on nb paper) • Usually above ground & they support the leaves and flowers • Contain the vascular tissue. What are the names? ______&_______ • If the stem is a soft, green, herbaceous stem, it has the ability to carry out Protein Synthesis Vegetative Structures PG 140 • MODIFIED STEMS • Modifications are usually for food storage, • Stolon: grow horizontally instead of vertically • Tuber is a swollen, underground stem that has buds from which new plants can grow (Potato) • Rhizomes are underground stems that store food so they are root-like stems • Bulb: short stem with fleshy “leaves” or “scales” that act as a food storage organs. EX: onions & garlic Vegetative Structures PG 140 • LEAVES – Make food for the plant (photosynthesis) – Often covered with waxy cuticle (waterproof!) – Main pigment is green (chlorophyll), but may have others Leaves • The color that we see depends on the amount and type of pigment in the leaf • Others: carotene & lycopene cause orange, yellow, & red • Xanthophyll, flavone, & flavonol causes yellow • anthocyanin cause red, blue, purple, magenta appearance Vegetative Structures pg 140 • LEAVES DICOT LEAF (branching veins) MONOCOT LEAF (parallel veins) Vegetative Structures PG 140 •LEAF PARTS…what is each part for? Cuticle Guard cells Stomata Xylem/phloe m P. Mesophyll S. Mesophyll Epidermis (upper & lower) Leaf Parts 10-2 • Stomata: openings in leaf tissue that control the exchange of gasses, usually found on the bottom surface • Guard cells controls the opening and closing of the stomata which regulates the flow of water vapor from leaf tissues Bell Ringer • Quick Write: bottom of 10-2 – Explain how roots, stems, and leaves along with vascular tissue function to ensure the survival of a land plant. (4-5 sentences) Bell Ringer- write & answer! pg138 • All of the following organelles would be found in a root cell of a plant except: • • • • Cell wall Chloroplast Nucleus Vacuole • Complex transport tubes which H2O, nutrients, & sugar throughout some plants belong to what level of organization? • • • • Organelle Cell Tissue organ Vegetative Structures • MODIFIED LEAVES tendrils, spines, succulents, colored bracts Transpiration PG 140 • The loss of water through the stomata is called transpiration • Leaves must balance gas exchange with water loss Transpiration…Adaptation PG 140 • In hot, dry areas too much water is lost (transpiration), so alternate methods must be used • Stomata opens leaves • Stomata only open at night Reproductive Structures PG 140 • FLOWERS – Reproductive structures of angiosperms – Are “showy” if meant to attract animals – Are tiny and plain if “nature” helps out (wind, etc) Reproductive Structures PG 141 draw it & label • FLOWER ANATOMY Must know all of these… Petals Sepals – usually green; cover young bud Pistil (Carpel) – female parts ~ stigma – sticky to catch pollen ~ style – tube to carry pollen down ~ ovary – holds eggs (ova) Stamen – male parts ~ anther – holds mature pollen ~ filament – tube sends pollen up Name the parts… petal stamen pistil sepal Reproductive Structures 10-3 POLLEN have tough, protective walls around the sperm cells (preserved in fossil record) Adapted for various types of transmission: ~ insects…sticky ~ animals…hooks/sticky ~ wind …numerous & light ~ digestion …tough coverings Reproductive Structures • FRUITS – a mature ovary; contains seeds (embryos) Fruits Reproductive Structures • SEED STRUCTURE Seed – the embryo Seed coat – protective covering Radicle – becomes root Endosperm – food for embryo Plant Responses • Phototropism – Move toward light + – Move away from - • Gravitropism (geotropism) – To ground (roots) – Away from ground (stems) • Thigmotropism – Curls around solids (vines) Plant Hormones • Auxins – Stimulate growth • Gibberellins – Stimulate growth, especially in flowers & fruits • Abscissic Acid – Stimulates cell death; leaves falling off • Ethylene – Stimulate ripening Two Groups of Angiosperms MONOCOTS: DICOTS: Vegetative Structures pg 141 • ROOTS DICOT ROOT MONOCOT ROOT Vegetative Structures • STEMS DICOT STEM MONOCOT STEM Reproductive Structures pg 141 FERTILIZATION Pollen lands on stigma Pollen tube grows down to ovary Two sperm discharged ~ one fertilizes egg to make the zygote ~ other joins with 2 polar bodies to form endosperm (nutritive tissue for embryo)