* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roman Empire Part II - Northwest ISD Moodle
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Slovakia in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
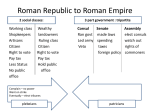
Welcome to World History Rome IT WASN’T BUILT IN A DAY The People Latins Settled around the Tiber River Etruscans north of Rome Borrowed alphabet and religion from them Ruled over the Romans until they kicked them out Republic Kicked out Etruscans and set up a government “by the people” Senate was governing body (patricians) Consuls: supervised business of government Plebeians begin to rise…..plebeians who? Laws of the Twelve Tables – laws written down so that plebeians could appeal a patrician judgment Plebeians would take higher positions in government (tribunes) and even the senate Rome expanded into Macedonia, Greece, and Asia minor The Empire With expansion came wealthy class Gracchus Brothers (Who were these guys?) Rome was in series of civil wars ? Who should hold power? – Senate or Political leaders Chaos, war, greed, ambition…what is Rome to do? Julius Caesar Ruled with Pompey Brought Gaul under Roman control Fought against Pompey for Rome Crossed the Rubicon River Put down rebellions across the empire “veni, vidi, vici” Julius Caesar Reforms Death Public works “Ides of March” programs for employment Granted Roman Citizenship Julian Calendar Mark Antony (chief general) and Octavian (grandnephew) hunted down murders Octavian (Augustus Caesar) Defeated Antony and Queen Cleopatra Was called Augustus (Exalted One) Ruled from 31 B.C.E. to 14 A.D. Pax Romana 200 year span of Roman peace Starts with Augustus and ends with Marcus Aurelius Empire was from Euphrates River (East) to Britain (West) Roman Empire Part II Greco-Roman Civilization The blending of Greek, Hellenistic, and Roman traditions. Occurred due to trade during the Pax Romana (remember?) Art Borrowed many ideas from the Greeks, but modified statues and paintings to give their subjects facial expressions. bobax.tripod.com Architecture Romans elaborated on Greek columns Improved the arch and the dome (Pantheon) crystalinks.com Engineering Built roads, bridges, and harbors throughout the empire. Aqueducts: bridgelike stone structures that brought water from the hills into Roman cities. These water systems were important to Romans’ fresh water supply and baths. richmond.ashraechapte rs.org Science Though the Romans did not create scientific ideas like Galen and Ptolemy, Romans were known to compile works of geography, zoology, ect. Pliny the Elder mlahanas.de Roman Law Most similar to law in the United States Two systems: Civil Law: law applying only to the citizens Law of Nations: applied to all people under roman rule The two systems would merge when Rome began extending citizenship across the empire. Principles of Law People of the same status are equal before the law 2. An accused person is presumed innocent until proven guilty 3. The accused should be allowed to face his or her accuser and defend against the charge 4. Guilt must be established clearly through evidence 5. Decisions should be based on fairness allowing judges to interpret the law Recognize any? 1. Rise of Christianity Romans were typically tolerant of other religions as long as they still recognized the Roman gods (most people were polytheistic at the time) Jews were the exception once Rome conquered Palestine (called it Judea) Split in Jewish Faith Jews began to absorb Greek customs Jewish priests not happy Zealots wanted to split from Rome and have independent Israel – they believed a messiah was coming Revolts 66 AD, Jews tried to rebel – Rome ended up leveling the city of Jerusalem… 135 AD, Rome kicks the Jews out completely (diaspora) Who is this guy Jesus? Born in Bethlehem around 4 BC. (originally from Nazareth) Angel appeared to mother that her son would be the son of the “most high God” Worked as a carpenter, then at age 30 he began his preaching near the sea of Galilee. The Message There is only one true God He called himself the Son of God He was the messiah that the Jews had been looking for. Love your enemies Non-violence The Crucifixion Jewish priests believed that Jesus challenged their authority Romans believed that he would lead the Jews into another rebellion and must be stopped. Was tried and condemned to be crucified (death by the cross) It is said that he had not died after all, his disciples (followers) had seen and talked with him just before he ascended into heaven Christianity Originally a sect within Judaism Paul is given credit for the widespread teachings of Christianity. Blamed by the Romans for everything that went bad because of their “evil doings” – would not sacrifice to the emperor Many became martyrs The Church Each community had a Priest Priests answered to the Bishop Bigger cities had Archbishops (presided over other Bishops) Therefore, the Bishop of Rome (big city) became the Pope Simon Peter is said to have been the first Pope (“upon this rock I will build my church”) Councils convened to decide official Christian teachings (put together the New Testament) Battled Heresies Persecution ended 313 AD when Constantine issued the Edict of Milan. The Declining Empire After the death of Marcus Aurelius in 180, the Pax Romana ended. Constant change in emporor, high taxes – people started to work for wealthy landowners Infrastructure failing Diocletian (284) – split the empire into two halves (eastern and western) Constantine (312) – moved capital to Constantinople Theodosius Roman emperor from 379-395 Made Christianity the official religion of the Roman Empire. Recognized as St. Theodosius Foreign Invasions Germanic tribes to the north Huns in East Asia Visigoths (Germanic tribe) seeking safety from the Huns In 410, Alaric (Visigoth general) overran Italy and plundered Rome. 434, Attila the Hun – called the “scourge of God” 476, Odoacer (Germanic leader) ousted the emperor of Rome (Rome has fallen).