* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
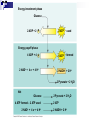
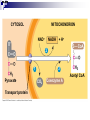
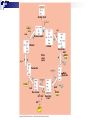
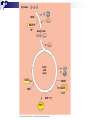
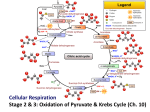
Cellular Respiration Obtain energy from the degradation of sugars Uses Oxygen and produces CO2 Many steps take place in the mitochondria of cells Complementary process to photosynthesis Will recognize many of the same molecules Oxidation-Reduction reactions Type of reaction when an electron is transferred from one atom or molecule to another Electron donor is reducing agent Electron acceptor is oxidizing agent The addition of electron to a molecule or atom is called reduction Energy is released when electrons are transferred to lower energy state molecules Electron transfer chains Cellular Respiration Mechanisms 3 Stages Glycolysis-happens in cytosol of cell Krebs cycle-happens in matrix of mitochondria Electron transport and oxidative phophorylation-cristae Glycolysis Means “sugar splitting”-glucose is split into Pyruvate First step of respiration Broken into two stages Energy investment phase-uses 2ATP Energy Payoff Phase-Yields 4 ATP +2 NADH Net of 2 ATP Energy Investment Phase Begins with Glucose 2 ATPs are used to phosphorylate Carbons 1 and 6 Isomerase converts glucose to fructose structure Activated intermediates Isomerase is enzyme that changes one molecule to an isomer Eventually yields 2 molecules of glyceraldehyde phosphate Enters energy payoff phase Fig. 9-8 Energy investment phase Glucose 2 ADP + 2 P 2 ATP used 4 ATP formed Energy payoff phase 4 ADP + 4 P 2 NAD+ + 4 e– + 4 H+ 2 NADH + 2 H+ 2 Pyruvate + 2 H2O Net Glucose 4 ATP formed – 2 ATP used 2 NAD+ + 4 e– + 4 H+ 2 Pyruvate + 2 H2O 2 ATP 2 NADH + 2 H+ Energy Payoff Phase Starts with Glyceraldehyde phosphate 2 for every glucose Enzyme adds phosphate GP while 2 NADH molecules are produces Phosphates are eventually loss resulting in the production of 4 ATP molecules The final product is Pyruvate Moves into Krebs cycle Transition Once Pyruvate enters Mitochondrion it is converted to Acetyl CoA and CO2 Acetyl CoA is the starting molecule for the Krebs cycle Fig. 9-10 CYTOSOL MITOCHONDRION NAD+ NADH + H+ 2 1 Pyruvate Transport protein 3 CO2 Coenzyme A Acetyl CoA Krebs cycle Completes the oxidation of organic molecules Takes place in matrix of mitochondria Cyclic like Calvin cycle Produces 1 ATP for each acetyl CoA 2 per glucose Many high energy electrons are saved as 3NADH and FADH2 per cycle Also produces 2 CO2 molecules per cycle Fig. 9-12-8 Acetyl CoA CoA—SH NADH +H+ H2O 1 NAD+ 8 Oxaloacetate 2 Malate Citrate Isocitrate NAD+ Citric acid cycle 7 H2O NADH + H+ 3 CO2 Fumarate CoA—SH 6 -Ketoglutarate 4 CoA—SH 5 FADH2 NAD+ FAD Succinate GTP GDP ADP ATP Pi Succinyl CoA NADH + H+ CO2 Fig. 9-11 Pyruvate CO2 NAD+ CoA NADH + H+ Acetyl CoA CoA CoA Citric acid cycle FADH2 2 CO2 3 NAD+ 3 NADH FAD + 3 H+ ADP + P i ATP Transition 2 NADH and FADH2 are used in the electron transport chain Happens in cristae of mitochondrion Uses Oxygen as ultimate electron acceptor