* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Citric Acid Cycle
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
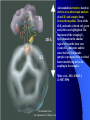
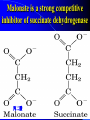
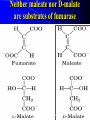
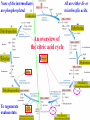
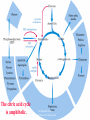
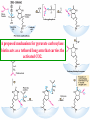
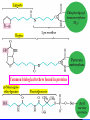
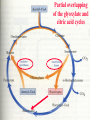
For Biochemistry II lecture of September 25, 2007 Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle A central metabolic hub, with catabolic pathways leading in and anabolic pathways leading out. More than 95% of the energy for the human being is generated through this pathway (in conjunction with the oxidative phosphorylation process). Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Carbon compounds that might be intermediates in the intracellular oxidation of pyruvate to CO2 and H2O were searched in the 1930s Four-carbon dicarboxylic acids (first fumarate, then succinate, malate, oxaloacetate) were found to catalyze the O2 uptake by suspensions of minced pigeon-breast muscle (Szent-Gyogyi, 1935); Then six-carbon tricarboxylic citric acid was also found to exert a similar catalytic effect (Krebs and Johnson, 1937). Malonate was found to inhibit pyruvate oxidation regardless of which active organic acid is added! Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Carbon compounds that might be intermediates in the intracellular oxidation of pyruvate to CO2 and H2O were searched in the 1930s Citrate was found to be synthesized from oxaloacetate and a substance which could be derived from carbohydrate, like pyruvate or acetate (Krebs and Johnson, 1937). A complete scheme of carbohydrate oxidation was thus formulated (Krebs and Johnson, 1937). Coenzyme A (A for acetylation) was found as a cofactor for the acetylation reactions (Lipmann, 1945). Coenzyme A was then found to be needed for pyruvate Downloaded from oxidation and to participate in citric acid synthesis. www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com ? Acetyl-CoA was discovered only in 1951 acetyl phosphate The original citric acid cycle Krebs and Johnson (1937) “The role of citric acid in the intermediate metabolism in animalDownloaded tissues. from Enzymologica 4:148-156. www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com This paper was submitted to Nature but was rejected!!! The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1953 "for his discovery of co-enzyme A and its importance for intermediary metabolism" "for his discovery of the citric acid cycle" Krebs discovered the urea cycle in 1932 before he elucidated the citric acid cycle! Hans Adolf Krebs (1900-1981) United Kingdom For Many years, Lipmann believed that Acetyl-phosphate, instead of acetyl-CoA, is the two-carbon “active” compound condensing with oxaloacetate. (both were born Downloaded from In www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Germany) Fritz Albert Lipmann (1899-1986) USA The cellular respiration (complete oxidation of most fuels) can be divided into three stages Stage I All the fuel molecules are oxidized to generate a common two-carbon unit, acetyl-CoA. Stage II The acetyl-CoA is completely oxidized into CO2, with electrons collected by NAD+ and FAD via a cyclic pathway (the citric acid cycle, Krebs cycle, or tricarboxylic acid cycle). Stage III Electrons of NADH and FADH2 are transferred to O2 via the respiratory chain (a series of electron carriers), producing H2O and a Downloaded from + www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com H gradient, which will promote ATP formation. Mitochondria was found to be the major site Downloaded from for fuel oxidation to www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com generate ATP. Pyruvate is first transported into mitochondria via a specific transporter on the inner membrane and then oxidized to acetyl-CoA by the catalysis of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com The oxidative decarboxylation of irreversible pyruvateReaction in mitochondria. Stoichiometric cofactors Catalytic cofactors Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Coenzyme A was first discovered by Lipmann in 1945. 辅酶A Coenzyme A (CoA-SH) delivers activated acyl groups (with 2-24 carbons) for Downloaded from degradation or biosynthesis. www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com 硫辛酸 “The arm” (~14 A) Lipoate acts as both electron and acyl carriers. It swings between the three different active sites of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Arsenic compounds are poisonous because they sequester lipoamide. Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com The five reactions catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex: Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com E1 E2 An icosahedral structure, based on electron cryo-microscopic analysis of an E1E2 sub-complex from B.stearothermophilus. Three of the 60 E2 molecules (colored red, green and yellow) are highlighted. The movement of the swinging E2 lipoyl domain in the annular region between the inner core (cyan) of E2 molecules and the outer shell of E1 molecules (purple) is proposed to be a critical feature underlying active site coupling in the complex. Milne et al., 2002, EMBO J. 21:5587-5598 Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com The citric acid cycle consists of eight successive reactions Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com The cycle begins with the condensation of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to form citrate Aldol condensation followed by a hydrolysis 柠檬酸合酶 (草酰乙酸) Hydrolysis of the thioester bond Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com releases a large amount of free energy. (柠檬酸) Citrate synthase before binding to oxaloacetate Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Citrate synthase after binding to oxaloacetate Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Acetyl-CoA analog Active site is located at the interface of the two subunits. A prochiral molecule 顺乌头酸酶 异柠檬酸 Aconitase contains an iron-sulfur center Aconitase then catalyzes the interconversion of citrate and isocitrate via dehydration and hydration. Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Isocitrate is then converted to aketoglutarate via oxidative decarboxylation, producing CO2. a-酮戊二酸 Oxalosuccinate is an intermediate; the carbon released as CO2 did Downloaded from not come from the acetyl-CoA entering the cycle. www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com The a-ketoglutarate is then converted to succinyl-CoA via another oxidative decarboxylation, producing the second CO2. TPP lipoate FAD 琥珀酰辅酶A Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Succinyl-CoA is then converted to succinate, accompanied by the formation of a GTP (or ATP) Synthetase(合成酶): ATP-consuming; Synthase(合酶): not ATP-consuming. Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Proposed mechanism for the succinyl-CoA synthetase catalyzed GDP phosphorylation, via a phosphoenzyme intermediate. A phosphohistidine intermediate in the reaction convinced many biochemists in the 1950's that all of oxidative phosphorylation was due to chemical coupling instead of chemiosmotic coupling! An acyl phosphate ATP The only substrate-level phosphorylation in the cycle Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Succinate is then converted to fumarate via dehydrogenation 延胡索酸 (An alkane) A flavoprotein with a covalently bound FAD and three iron-sulfur centers; the only integral membrane protein for the Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com citric acid cycle. (An alkene) Malonate is a strong competitive inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase 丙二酸 Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Fumarate is then converted to L-malate via hydration A stereospecific enzyme only acting on the trans and L isomers 苹果酸 Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Neither maleate nor D-malate are substrates of fumarase Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com The cycle ends by the regeneration of oxaloacetate from L-malate Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com None of the intermediates are phosphorylated. All are either di- or tricarboxylic acids. An overview of the citric acid cycle 3 To regenerate oxaloacetate. Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com “unexpected” results of an early isotope labeling experiment Chemically indistinguishable Citrate: A symmetrical molecule That reacts asymmetrically Cis-aconitate or isocitrate, instead of citrate, was proposed to be the first condensation product Downloaded from between acetate and oxaloacetate! www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com The symmetric molecule can react asymmetrically in the asymmetric active site of enzymes. X Citrate is a prochiral molecule Active site of aconitase Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Overall efficiency of energy conservation: 65% Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Accumulating evidence also suggest the formation of multienzyme complexes (or metabolons) for the citric acid cycle enzymes, facilitating substrate channeling between the active sites. Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com The citric acid intermediates are important sources for biosynthetic precursors. Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com The citric acid cycle is amphibolic. Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com The citric acid cycle intermediates need to be replenished Activated by acetyl-CoA Activated by Fru-1,6P Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com A proposed mechanism for pyruvate carboxylase: biotin acts as a tethered long arm that carries the activated CO2. Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Common biological tethers found in proteins Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com a-ketoglutarate dyhydrogenase is not present in such organisms! Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Some modern anaerobic microorganisms use an incomplete citric acid cycle as a source of biosynthetic precursors, not of energy! Activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is regulated by allosteric and covalent mechanisms. Phosphorylated E1 is inactive. Enzymes are switched off when the energy charge is high and biosynthetic intermediates are abundant. Inhibits PFK-1 Most of the regulation is provided by substrate availability and product inhibition. Three enzymes of the citric acid cycle are regulated to maintain a steady state level Downloaded from of ATP for the cells. www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Net conversion of acetate to carbohydrates is allowed via the glyoxylate cycle occurring in certain organisms There is no net conversion of acetate (also from fatty acids and amino acids) to any of the citric acid cycle intermediate, thus neither to carbohydrates. Net conversion of acetate to four-carbon citric acid cycle intermediates occurs via the glyoxylate cycle, occurring in plants, certain invertebrates, and some microorganisms (including E. coli and yeast). The glyoxylate cycle was first discovered in bacteria by Kornberg & Krebs in 1957 as a means of converting C2 units of acetate (a growth substrate) for synthesis of other cell constituents such as Downloaded hexoses. from H.L. Kornberg and H.A. Krebs, Synthesis of cell constituents from C2-units by a modified tricarboxylic www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com acid cycle. Nature 179 (1957), pp. 988–991 The glyoxylate cycle 苹果酸合酶 异柠檬酸裂解酶 Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com The two decarboxylation steps of the citric acid cycle are bypassed. Partial overlapping of the glyoxylate and citric acid cycles Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Conversion of fatty acids to glucose (in germinating seeds) occurs in three intracellular compartments Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com Partition of isocitrate between the glyoxylate and citric acid cycles are regulated by the opposite effect of common allosteric effectors on the isocitrate lyase and the isocitrate dehydrogenase. Summary Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA by the action of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, a huge enzyme complex. Acetyl-CoA is converted to 2 CO2 via the eightstep citric acid cycle, generating three NADH, one FADH2, and one ATP (by substrate-level phophorylation). Intermediates of citric acid cycle are also used as biosynthetic precursors for many other biomolecules, including fatty acids, steroids, amino acids, heme, pyrimidines, and glucose. Oxaloacetate can get replenished from pyruvate, via a carboxylation reaction catalyzed by the Downloaded from biotin-containingwww.pharmacy123.blogfa.com pyruvate carboxylase. The activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is regulated by allosteric effectors and reversible phosphorylations. Net conversion of fatty acids to glucose can occur in germinating seeds, some invertebrates and some bacteria via the glycoxylate cycle, which shares three steps with the citric acid cycle but bypasses the two decarboxylation steps, converting two molecules of acetyl-CoA to one succinate. Acetyl-CoA (isocitrate) is partitioned into the glyoxylate cycle and citric acid cycle via a coordinately regulation of the isocitrate dehydrogenase and isocitrate lyase. Downloaded from www.pharmacy123.blogfa.com