* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mutations Mutations occur when inserting and deleting one or
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
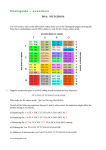
Mutations Mutations occur when inserting and deleting one or multiple nucleotides alter genes. There are many ways that mutations can build up over a lifetime through environmental factors such as smoking. Smoking can change the genes in your DNA. This may affect the way your tissue replicates itself in your lungs. Another way is UV radiation. This can change the DNA sequences in your skin cells so they do not replicate correctly. Radioactivity is another risk factor for mutations. Also changes the genes in your DNA to read for incorrect proteins. If you do not exercise enough, your cells do not divide enough and get lazy and make more mistakes. These mistakes could happen on your extrons. There are many chemicals in foods and other products we use every day that can get into our cells and have an effect on out DNA sequences. You can also get mutations in your DNA due to factors that you cannot control. One is heredity. If your parents or grandparents have had cancer or other mutations, you are at risk also. Another is age. Throughout your lifetime you experience the aging process which presents you many factors that could give mutations. This is what an original DNA sequence: TAC, CGC, TTG, CTA, TCG, CGA, TGT, GGC, CTC, TAA, ACT Complimentary DNA sequence: ATG, GCG, AAC, GAT, AGC, GCT, ACA, CCG, GAG, ATT, TGA mRNA sequence of original: AUG, GCG, AAC, GAU, AGC, GCU, ACA, CCG, GAG, AUU, UGA tRNA sequence: UAC, CGC, UUG, CUA, UCG, CGA, UGU, GGC, CUC, UAA, ACU Protein sequence: Start, Alanine, Asparagine, Asparate, Serine, Alanine, Threonine, Proline, Glutamate, Isoleucine, Stop Point mutation: TAC, CGC, TTG, CTA, TCG, CGA, TGT, GGC, CTC, TAA, ACT TAC, CGC, TTG, CTA, TCG, AGA, TGT, GGC, CTC, TAA, ACT AUG, GCG, AAC, GAU, AGC, UCU, ACA, CCG, GAG, AUU, UGA Protein sequence: Start, Alanine, Asparagine, Asparate, Serine, Serine, Threonine, Arganine, Glutamate, Isoleucine, Stop On the sixth codon, the first nucleotide was changed to a uracil instead of alnine. The codon originally coded for Alanine, but now it codes for Serine. Frame shift deletion: TAC, CGC, TTG, CTA, TCG, CGA, TGT, GGC, CTC, TAA, ACT TAC, CGC, TTG, CTA, TCG, CGA, TGT, GCC, TCT, AAA, CT AUG, GCG, AAC, GAU, AGC, UCU, ACA, CGG, AGA, UUU, GA Protein sequence: Start, Alanine, Asparagine, Asparate, Serine, Serine, Threonine, Arginine, Arginine, phenylalanine, (Glutamate or aspartate) On the 8th codon, the first nucleotide is deleted. All if following nucleotides are shifted over one to the left because of it. It now codes for Arganine, phenylalanine, and glutamate or aspartate instead of glutamate, isoleucine, and stop. Frame Shift insertion: TAC, CGC, TTG, CTA, TCG, CGA, TGT, GGC, CTC, TAA, ACT TAC, CGC, TTG, CTA, TCG, CGA, TGT, GGC, ACT,CTA, AAC, T AUG, GCG, AAC, GAU, AGC, GCU, ACA, CCG, UGA, GAU, UUG, A Protein sequence: Start, Alanine, Asparagine, Asparate, Serine, Alanine, Threonine, Proline, STOP, Aspartate, Leucine, something stating with A In the 8th codon, and alnine is inserted as the first nucletide. This shifts all other nucleotides after over one space to the right. This now codes for stop, aspeartate, leucine, and something starting with A Everyone has mutations, but in most of us, they are not expressed because there are two different types of genes. There are introns and extrons. About 95% of our genes are introns and about 5% are extrons. Extrons are the genes in your DNA that are actually expressed or used. The introns are not used. There are so many more instrons than extrons because your DNA is bound to make mistakes, but if there are a lot more useless genes, there is a better chance the mistakes will be made on them, not he extrons. Also it there is a mutation on your extrons, there is still a chance that it will not affect you. This is because it a nucleotide is changed (most likely a third nucleotide) it still may code for the same protein. Example: GCG They still both code for Alanine even though the guanine isnow a adamine GCA